Question: Diffusion with fast second-order reaction. In a steady-state, isothermal flow system, a solid A is dissolving in a flowing liquid stream S. Assume in accordance
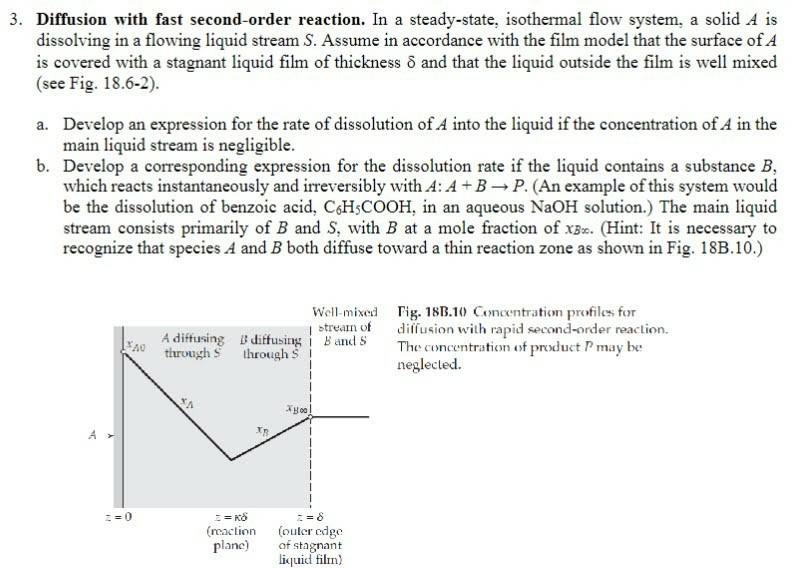
Diffusion with fast second-order reaction. In a steady-state, isothermal flow system, a solid A is dissolving in a flowing liquid stream S. Assume in accordance with the film model that the surface of A is covered with a stagnant liquid film of thickness and that the liquid outside the film is well mixed (see Fig. 18.6-2). a. Develop an expression for the rate of dissolution of A into the liquid if the concentration of A in the main liquid stream is negligible. b. Develop a corresponding expression for the dissolution rate if the liquid contains a substance B, which reacts instantaneously and irreversibly with A:A+BP. (An example of this system would be the dissolution of benzoic acid, C6H5COOH, in an aqueous NaOH solution.) The main liquid stream consists primarily of B and S, with B at a mole fraction of xB. (Hint: It is necessary to recognize that species A and B both diffuse toward a thin reaction zone as shown in Fig. 18B.10.) Fig. 18B.10 Concentration profiles for diffusion with rapid second-order reaction. The concentration of product P may be: neglected. Diffusion with fast second-order reaction. In a steady-state, isothermal flow system, a solid A is dissolving in a flowing liquid stream S. Assume in accordance with the film model that the surface of A is covered with a stagnant liquid film of thickness and that the liquid outside the film is well mixed (see Fig. 18.6-2). a. Develop an expression for the rate of dissolution of A into the liquid if the concentration of A in the main liquid stream is negligible. b. Develop a corresponding expression for the dissolution rate if the liquid contains a substance B, which reacts instantaneously and irreversibly with A:A+BP. (An example of this system would be the dissolution of benzoic acid, C6H5COOH, in an aqueous NaOH solution.) The main liquid stream consists primarily of B and S, with B at a mole fraction of xB. (Hint: It is necessary to recognize that species A and B both diffuse toward a thin reaction zone as shown in Fig. 18B.10.) Fig. 18B.10 Concentration profiles for diffusion with rapid second-order reaction. The concentration of product P may be: neglected
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


