Question: eBook A university is applying classification methods in order to identify alumni who may be interested in donating money. The university has a database of
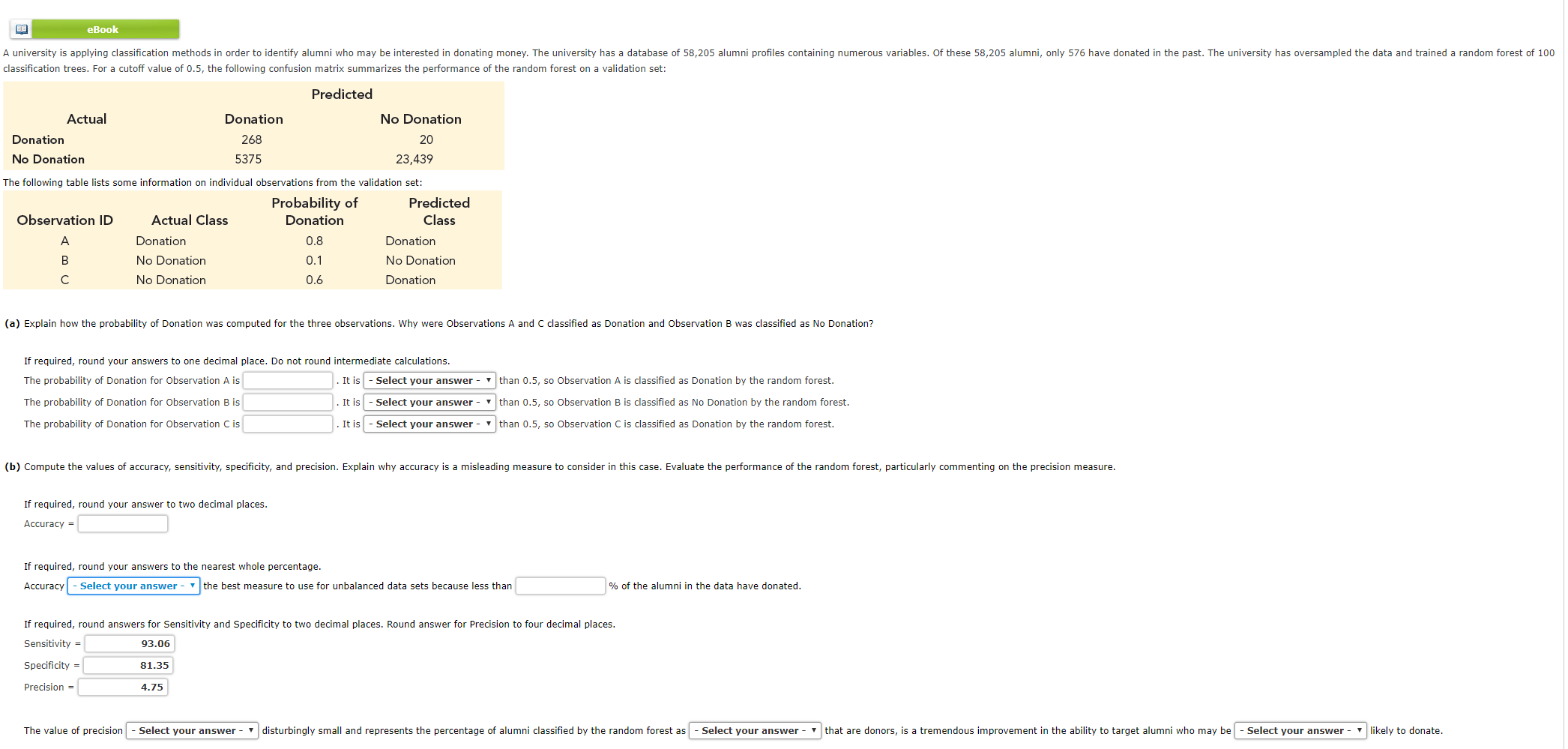
eBook A university is applying classification methods in order to identify alumni who may be interested in donating money. The university has a database of 58,205 alumni profiles containing numerous variables. Of these 58,205 alumni, only 576 have donated in the past. The university has oversampled the data and trained a random forest of 100 classification trees. For a cutoff value of 0.5, the following confusion matrix summarizes the performance of the random forest on a validation set: Actual Donation No Donation Donation 268 Predicted No Donation 20 23,439 5375 The following table lists some information on individual observations from the validation set: Probability of Predicted Observation ID Actual Class Donation Class Donation 0.8 Donation No Donation No Donation No Donation Donation 0.6 (a) Explain how the probability of Donation was computed for the three observations. Why were Observations A and C classified as Donation and Observation B was classified as No Donation? If required, round your answers to one decimal place. Do not round intermediate calculations. The probability of Donation for Observation A is . It is - Select your answer The probability of Donation for Observation B is . It is - Select your answer - The probability of Donation for Observation C is . It is - Select your answer than 0.5, so Observation A is classified as Donation by the random forest. than 0.5, so Observation B is classified as No Donation by the random forest. than 0.5, so Observation C is classified as Donation by the random forest. (b) Compute the values of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and precision. Explain why accuracy is a misleading measure to consider in this case. Evaluate the performance of the random forest, particularly commenting on the precision measure. If required, round your answer to two decimal places. Accuracy = If required, round your answers to the nearest whole percentage. Accuracy - Select your answer the best measure to use for unbalanced data sets because less than % of the alumni in the data have donated. If required, round answers for Sensitivity and Specificity to two decimal places. Round answer for Precision to four decimal places. Sensitivity = 93.06 Specificity = 81.35 Precision = 4.75 The value of precision - Select your answer - disturbingly small and represents the percentage of alumni classified by the random forest as - Select your answer that are donors, is a tremendous improvement in the ability to target alumni who may be - Select your answer - likely to donate. eBook A university is applying classification methods in order to identify alumni who may be interested in donating money. The university has a database of 58,205 alumni profiles containing numerous variables. Of these 58,205 alumni, only 576 have donated in the past. The university has oversampled the data and trained a random forest of 100 classification trees. For a cutoff value of 0.5, the following confusion matrix summarizes the performance of the random forest on a validation set: Actual Donation No Donation Donation 268 Predicted No Donation 20 23,439 5375 The following table lists some information on individual observations from the validation set: Probability of Predicted Observation ID Actual Class Donation Class Donation 0.8 Donation No Donation No Donation No Donation Donation 0.6 (a) Explain how the probability of Donation was computed for the three observations. Why were Observations A and C classified as Donation and Observation B was classified as No Donation? If required, round your answers to one decimal place. Do not round intermediate calculations. The probability of Donation for Observation A is . It is - Select your answer The probability of Donation for Observation B is . It is - Select your answer - The probability of Donation for Observation C is . It is - Select your answer than 0.5, so Observation A is classified as Donation by the random forest. than 0.5, so Observation B is classified as No Donation by the random forest. than 0.5, so Observation C is classified as Donation by the random forest. (b) Compute the values of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and precision. Explain why accuracy is a misleading measure to consider in this case. Evaluate the performance of the random forest, particularly commenting on the precision measure. If required, round your answer to two decimal places. Accuracy = If required, round your answers to the nearest whole percentage. Accuracy - Select your answer the best measure to use for unbalanced data sets because less than % of the alumni in the data have donated. If required, round answers for Sensitivity and Specificity to two decimal places. Round answer for Precision to four decimal places. Sensitivity = 93.06 Specificity = 81.35 Precision = 4.75 The value of precision - Select your answer - disturbingly small and represents the percentage of alumni classified by the random forest as - Select your answer that are donors, is a tremendous improvement in the ability to target alumni who may be - Select your answer - likely to donate





