Question: everything that i have flow we need it its part of answer II. Problem #1 (35 points) Show the complete goal, scope definition and life

everything that i have
flow we need it its part of answer
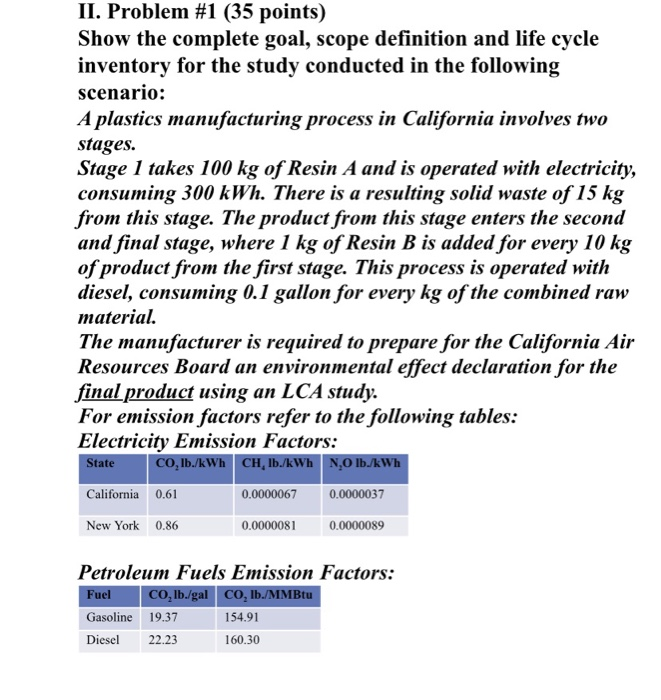
II. Problem #1 (35 points) Show the complete goal, scope definition and life cycle inventory for the study conducted in the following scenario: A plastics manufacturing process in California involves two stages. Stage 1 takes 100 kg of Resin A and is operated with electricity, consuming 300 kWh. There is a resulting solid waste of 15 kg from this stage. The product from this stage enters the second and final stage, where 1 kg of Resin B is added for every 10 kg of product from the first stage. This process is operated with diesel, consuming 0.1 gallon for every kg of the combined raw material. The manufacturer is required to prepare for the California Air Resources Board an environmental effect declaration for the final product using an LCA study. For emission factors refer to the following tables: Electricity Emission Factors: State c o, lb./kWh CH, Ib./kWh NO lb./kWh California 0.61 0.0000067 0.0000037 New York 0.86 0.0000081 0.0000089 Petroleum Fuels Emission Factors: Fuel Co, lb./gal CO, lb./MMBtu Gasoline 19.37 154.91 Diesel 22.23 160.30 IV. Problem #3 Part 2 (15 points) The process also results in a by-product of 200 kg of molasses and 500 kg of bagasse per day. Bagasse, which can be used as a biofuel in many manufacturing processes, has energy content of 2.5 kWh/kg and emission of 1.6 lb. of CO2 per kg. Draw the full expanded flow model and compute the environmental loads per kg of sugar produced when the electricity generated from Bagasse is used by the sugar manufacturing plant. Show calculations and Units of Measure. Expanded Flow Model Environmental Loads per kg of sugar considering by- products Inflows Outflows II. Problem #1 (35 points) Show the complete goal, scope definition and life cycle inventory for the study conducted in the following scenario: A plastics manufacturing process in California involves two stages. Stage 1 takes 100 kg of Resin A and is operated with electricity, consuming 300 kWh. There is a resulting solid waste of 15 kg from this stage. The product from this stage enters the second and final stage, where 1 kg of Resin B is added for every 10 kg of product from the first stage. This process is operated with diesel, consuming 0.1 gallon for every kg of the combined raw material. The manufacturer is required to prepare for the California Air Resources Board an environmental effect declaration for the final product using an LCA study. For emission factors refer to the following tables: Electricity Emission Factors: State c o, lb./kWh CH, Ib./kWh NO lb./kWh California 0.61 0.0000067 0.0000037 New York 0.86 0.0000081 0.0000089 Petroleum Fuels Emission Factors: Fuel Co, lb./gal CO, lb./MMBtu Gasoline 19.37 154.91 Diesel 22.23 160.30 IV. Problem #3 Part 2 (15 points) The process also results in a by-product of 200 kg of molasses and 500 kg of bagasse per day. Bagasse, which can be used as a biofuel in many manufacturing processes, has energy content of 2.5 kWh/kg and emission of 1.6 lb. of CO2 per kg. Draw the full expanded flow model and compute the environmental loads per kg of sugar produced when the electricity generated from Bagasse is used by the sugar manufacturing plant. Show calculations and Units of Measure. Expanded Flow Model Environmental Loads per kg of sugar considering by- products Inflows Outflows
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


