Question: Exercise 1 A program scheduling manager for a TV station needs to select exactly 5 shows for a partic- ular evening, from among the 9


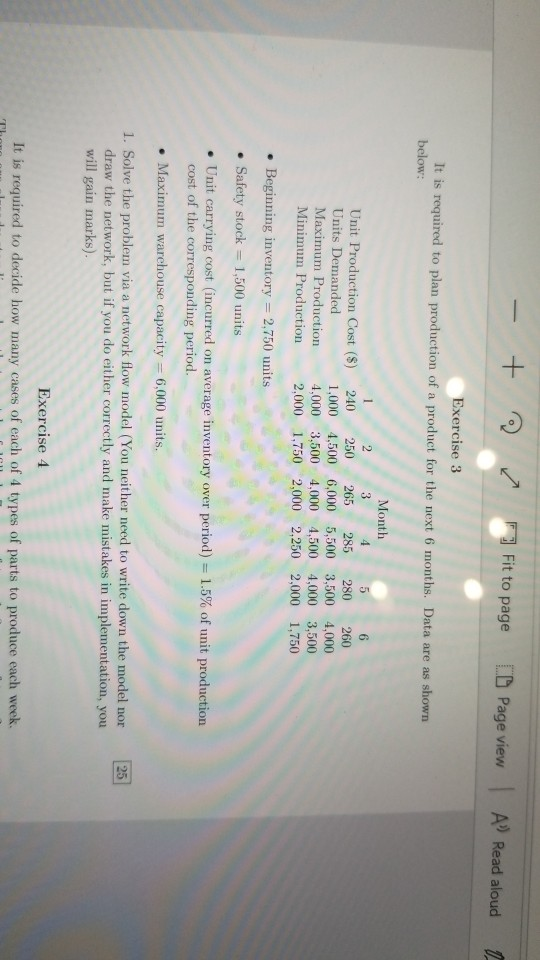
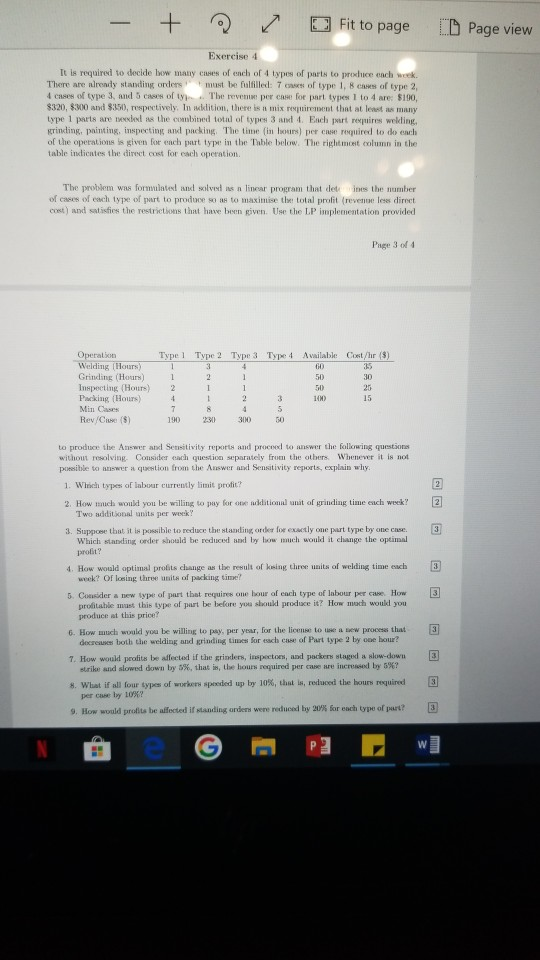
Exercise 1 A program scheduling manager for a TV station needs to select exactly 5 shows for a partic- ular evening, from among the 9 possible listed in the Table, which shows estimated advertising revenue (in $ million) of each show and the categories to which it belongs. The following conditions apply: There must be at least as many shows selected that are categorized as public interest as there are shows selected that are categorized as containing violence. If P7 is selected, then P3 or P4 or both must be selected. P7 and P9 must not be both selectexi. If two or more shows in the comedy category are selected, then at least one show in the drama category must be selected. If more than three shows in the contains violence category are selected, then an estimated S4 million in advertising revenues will be lost. Show Revenue (s million) Public Interest Contains Violence Comedy Drama P1 P3 P4 P6 P7 P8 P9 15 1. Formulate a linear optimisation model to maximise revenue. In writing down the model make sure to define clealry the various components of the model 2. Solve the model and indicate the optimal selection. e to search Exercise 2 Cal/Packages/Microsoft Microsoft Edge_8wekyb3d8bhwe/TempState/Downloads/DCS - + Fit to page Page view sure to one cii vn mn . 2. Solve the model and indicate the optimal selection Exercise 2 At the beginning of year 1. a sum of $100.000 is to be invested for the next 4 years. There are five possible investments, labelled AE. The timing of cash outflows and cash inflows for these investments is somewhat irregular; viz., for every $1 invested: Investment A: Invest at the beginning of year 1, receive returns of $0.50 and $1.00 at the beginnings of years 2 and 3 Investment B: Invest at the beginning of year 2, receive returns of $0.50 and $1.00 at the beginnings of years 3 and 4. Investment C: Invest at beginning of year I receive $1.20 at beginning of year 2. Investment D: Invest at beginning of year 4, receive $1.90 at beginning of year 5. Investment E: Invest at beginning of year 3 receive $1.50 at beginning of year 4. Page 2 of 4 To create a diversified portfolio, no more than $75,000 can be put into any of the five investments. At the beginning of any year, only cash on hand, which includes returns from previous in vestments, can be invested. Any cash not invested in any year can be put in a short-term money market account that earns 3% annually. The investment strategy is to maximise the amount of cash on hand at the beginning of year 5. 1. Develop and solve a LP spreadsheet model to find the investment plan. State the plan in words. 25 BINe G P WT - + Fit to page 1 Page view A Read aloud o Exercise 3 It is required to plan production of a product for the next 6 months. Data are as shown below: 2 Month 3 4 5 6 Unit Production Cost ($) 240 250 265 285 280 260 Units Demanded 1,000 4,500 6,000 5,500 3,500 4,000 Maximum Production 4,000 3,500 4,000 4,500 4,000 3,500 Minimum Production 2,000 1,750 2,000 2.250 2,000 1,750 Beginning inventory = 2.750 units Safety stock = 1,500 units Unit carrying cost (incurred on average inventory over period) = 1.5% of unit production cost of the corresponding period. Maximum warehouse capacity = 6,000 units. 25 1. Solve the problem via a network flow model (You neither need to write down the model nor draw the network, but if you do either correctly and make mistakes in implementation, you will gain marks). Exercise 4 It is required to decide how many cases of each of 4 types of parts to produce each week. - + ~ Fit to page D Page view Exercise 4 It is required to decide wow many cases of ench of 4 types of parts to produce each week. There are already standing orders must be fulfilled: 7 of type I, BC of type 2 4 cases of type 3, and 5 ofty The event per come for part type 1 to 4 are: $190, $320, $300 and $350), respectively. In wdition, there is a mix optiment that at least as many type 1 parts are well in the combined total of types 3 and Each part i es wekling, krinding, painting, inspecting and packing The time in hours) per competired to do each of the operations is given for each part type in the Table below. The right met column in the table indicates the direct cost for each operation The problem wie fornwinted and solved its n linear program that defines the number of cases of each type of purt to produce so as to maximise the total profit (revenue les direct cuest) and satisfies the restrictions that have been given. Use the LP implementation provided Page 34 Operation Welding Hours Grinding (Hour Inspecting Hours) Packing Hours 4 Min Cases Rev/Case (5) Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 Type 4 Available Cost/hr ($) 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 3 100 190 230 300) to produce the Auswer and Sensitivity reports and proc to answer the following questions without resolving Conder each question separately from the others. Whenever it is not possible to uswer a quention from the Answer and Sensitivity reports, explain why. 1. Which types of Inbour currently limit profit? 2. How much would you be willing to pay for onektion unit of grinding time each week? Two additional units per week? 3. Suppose that it is possible to reduce the standing order for exactly one put type by one case. Which standing order should be reduced and by how much would it change the optimal profit? 4. How would optimal probits change as the result of using three units of welding time each week? Or losing three units of packing time? 5. Consider a new type of part that requires one hour of each type of labour How profitable must this type of purt be before you shoukl produce it? How much would you produce at this price? 6. How much would you be willing to pay per year, for the license to w process that decres both the welding and grinding time for each case of Part type 2 by one hour? 1. How would pratite le atlected if the grindern, inspectors, and packer dag low-down strike and slowed down by 5%, that in the hours required percase are increased by 5%? 3 8. What if all four types of workers spended up by 10%, that is reduced the hours required per case by 10%? 9. How would profits be affected if standing ordeni were reduced by 2018 for each type of part 3 WT Exercise 1 A program scheduling manager for a TV station needs to select exactly 5 shows for a partic- ular evening, from among the 9 possible listed in the Table, which shows estimated advertising revenue (in $ million) of each show and the categories to which it belongs. The following conditions apply: There must be at least as many shows selected that are categorized as public interest as there are shows selected that are categorized as containing violence. If P7 is selected, then P3 or P4 or both must be selected. P7 and P9 must not be both selectexi. If two or more shows in the comedy category are selected, then at least one show in the drama category must be selected. If more than three shows in the contains violence category are selected, then an estimated S4 million in advertising revenues will be lost. Show Revenue (s million) Public Interest Contains Violence Comedy Drama P1 P3 P4 P6 P7 P8 P9 15 1. Formulate a linear optimisation model to maximise revenue. In writing down the model make sure to define clealry the various components of the model 2. Solve the model and indicate the optimal selection. e to search Exercise 2 Cal/Packages/Microsoft Microsoft Edge_8wekyb3d8bhwe/TempState/Downloads/DCS - + Fit to page Page view sure to one cii vn mn . 2. Solve the model and indicate the optimal selection Exercise 2 At the beginning of year 1. a sum of $100.000 is to be invested for the next 4 years. There are five possible investments, labelled AE. The timing of cash outflows and cash inflows for these investments is somewhat irregular; viz., for every $1 invested: Investment A: Invest at the beginning of year 1, receive returns of $0.50 and $1.00 at the beginnings of years 2 and 3 Investment B: Invest at the beginning of year 2, receive returns of $0.50 and $1.00 at the beginnings of years 3 and 4. Investment C: Invest at beginning of year I receive $1.20 at beginning of year 2. Investment D: Invest at beginning of year 4, receive $1.90 at beginning of year 5. Investment E: Invest at beginning of year 3 receive $1.50 at beginning of year 4. Page 2 of 4 To create a diversified portfolio, no more than $75,000 can be put into any of the five investments. At the beginning of any year, only cash on hand, which includes returns from previous in vestments, can be invested. Any cash not invested in any year can be put in a short-term money market account that earns 3% annually. The investment strategy is to maximise the amount of cash on hand at the beginning of year 5. 1. Develop and solve a LP spreadsheet model to find the investment plan. State the plan in words. 25 BINe G P WT - + Fit to page 1 Page view A Read aloud o Exercise 3 It is required to plan production of a product for the next 6 months. Data are as shown below: 2 Month 3 4 5 6 Unit Production Cost ($) 240 250 265 285 280 260 Units Demanded 1,000 4,500 6,000 5,500 3,500 4,000 Maximum Production 4,000 3,500 4,000 4,500 4,000 3,500 Minimum Production 2,000 1,750 2,000 2.250 2,000 1,750 Beginning inventory = 2.750 units Safety stock = 1,500 units Unit carrying cost (incurred on average inventory over period) = 1.5% of unit production cost of the corresponding period. Maximum warehouse capacity = 6,000 units. 25 1. Solve the problem via a network flow model (You neither need to write down the model nor draw the network, but if you do either correctly and make mistakes in implementation, you will gain marks). Exercise 4 It is required to decide how many cases of each of 4 types of parts to produce each week. - + ~ Fit to page D Page view Exercise 4 It is required to decide wow many cases of ench of 4 types of parts to produce each week. There are already standing orders must be fulfilled: 7 of type I, BC of type 2 4 cases of type 3, and 5 ofty The event per come for part type 1 to 4 are: $190, $320, $300 and $350), respectively. In wdition, there is a mix optiment that at least as many type 1 parts are well in the combined total of types 3 and Each part i es wekling, krinding, painting, inspecting and packing The time in hours) per competired to do each of the operations is given for each part type in the Table below. The right met column in the table indicates the direct cost for each operation The problem wie fornwinted and solved its n linear program that defines the number of cases of each type of purt to produce so as to maximise the total profit (revenue les direct cuest) and satisfies the restrictions that have been given. Use the LP implementation provided Page 34 Operation Welding Hours Grinding (Hour Inspecting Hours) Packing Hours 4 Min Cases Rev/Case (5) Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 Type 4 Available Cost/hr ($) 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 3 100 190 230 300) to produce the Auswer and Sensitivity reports and proc to answer the following questions without resolving Conder each question separately from the others. Whenever it is not possible to uswer a quention from the Answer and Sensitivity reports, explain why. 1. Which types of Inbour currently limit profit? 2. How much would you be willing to pay for onektion unit of grinding time each week? Two additional units per week? 3. Suppose that it is possible to reduce the standing order for exactly one put type by one case. Which standing order should be reduced and by how much would it change the optimal profit? 4. How would optimal probits change as the result of using three units of welding time each week? Or losing three units of packing time? 5. Consider a new type of part that requires one hour of each type of labour How profitable must this type of purt be before you shoukl produce it? How much would you produce at this price? 6. How much would you be willing to pay per year, for the license to w process that decres both the welding and grinding time for each case of Part type 2 by one hour? 1. How would pratite le atlected if the grindern, inspectors, and packer dag low-down strike and slowed down by 5%, that in the hours required percase are increased by 5%? 3 8. What if all four types of workers spended up by 10%, that is reduced the hours required per case by 10%? 9. How would profits be affected if standing ordeni were reduced by 2018 for each type of part 3 WT
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


