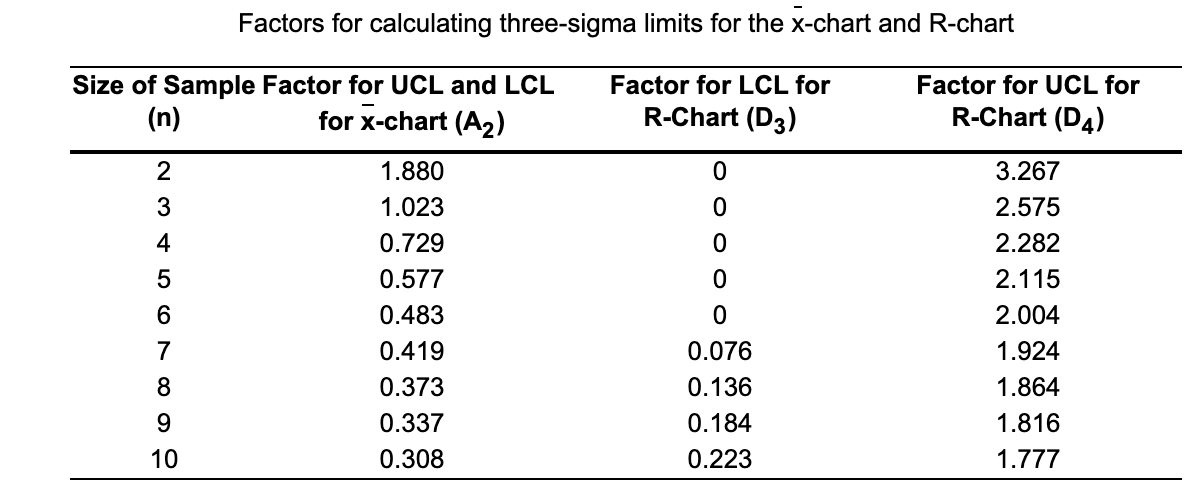
Question: Factors for calculating three-sigma limits for the X-chart and R-chart Size of Sample Factor for UCL and LCL (n) for X-chart (A2) Factor for LCL



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


