Question: Figure 3: A regression tree predicting the fuel efficiency (in kilometers per litre, km/l ) of cars manufactured in 2019. Drive denotes whether the vehicle
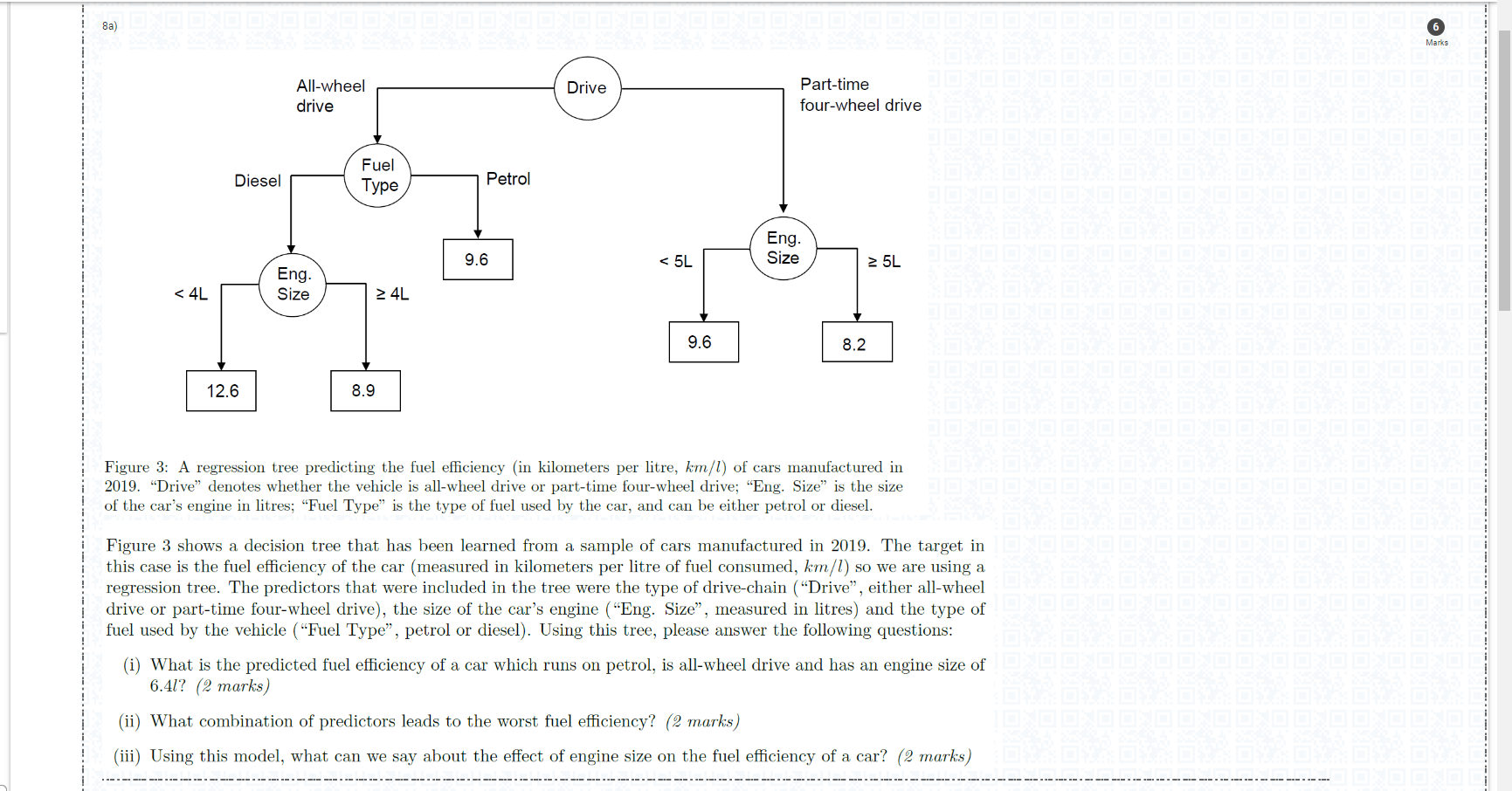
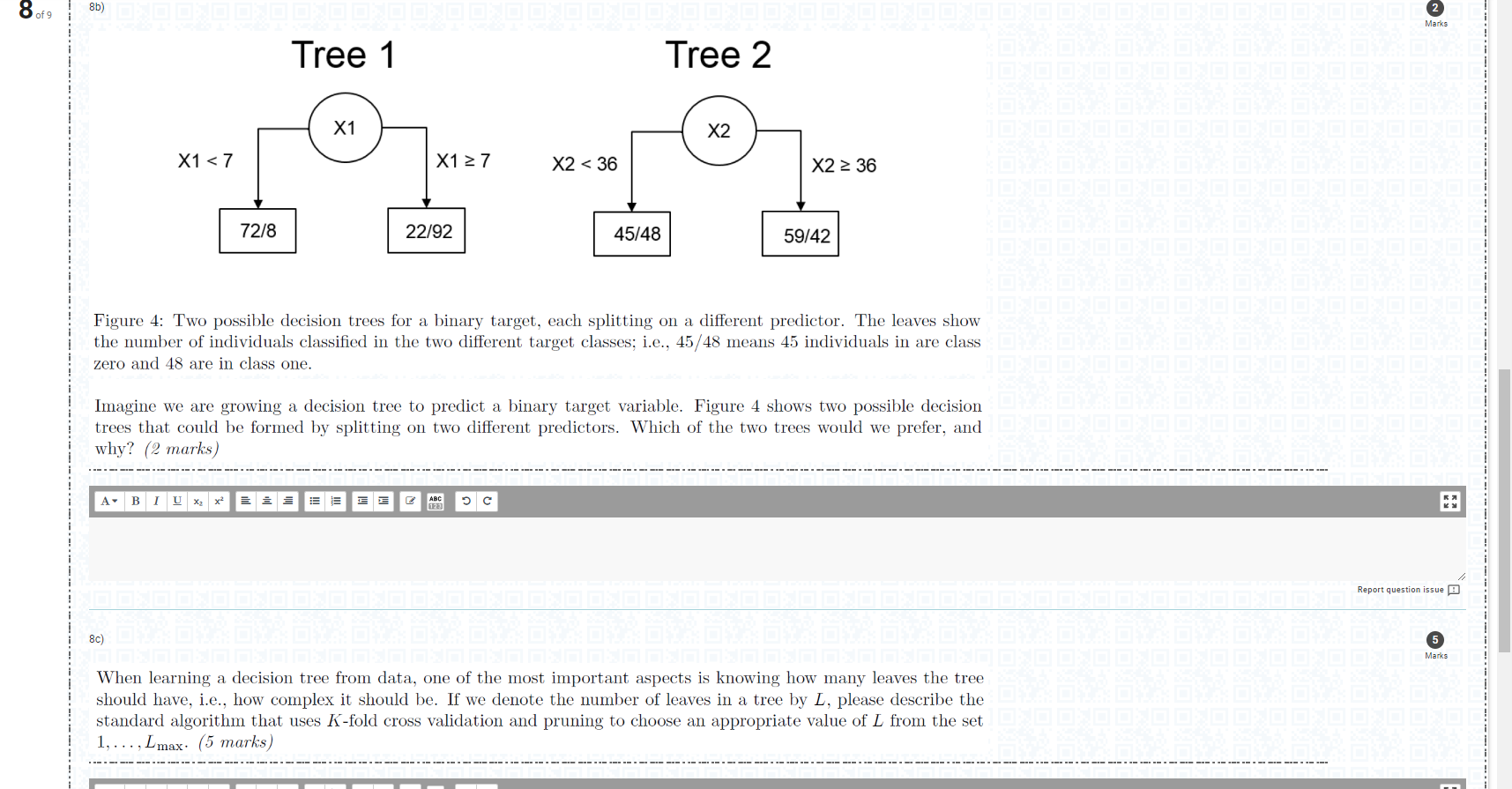
Figure 3: A regression tree predicting the fuel efficiency (in kilometers per litre, km/l ) of cars manufactured in 2019. "Drive" denotes whether the vehicle is all-wheel drive or part-time four-wheel drive; "Eng. Size" is the size of the car's engine in litres; "Fuel Type" is the type of fuel used by the car, and can be either petrol or diesel. Figure 3 shows a decision tree that has been learned from a sample of cars manufactured in 2019 . The target in this case is the fuel efficiency of the car (measured in kilometers per litre of fuel consumed, km/l ) so we are using a regression tree. The predictors that were included in the tree were the type of drive-chain ("Drive", either all-wheel drive or part-time four-wheel drive), the size of the car's engine ("Eng. Size", measured in litres) and the type of fuel used by the vehicle ("Fuel Type", petrol or diesel). Using this tree, please answer the following questions: (i) What is the predicted fuel efficiency of a car which runs on petrol, is all-wheel drive and has an engine size of 6.4l? (2 marks) (ii) What combination of predictors leads to the worst fuel efficiency? (2 marks) (iii) Using this model, what can we say about the effect of engine size on the fuel efficiency of a car? (2 marks) Figure 4: Two possible decision trees for a binary target, each splitting on a different predictor. The leaves show the number of individuals classified in the two different target classes; i.e., 45/48 means 45 individuals in are class zero and 48 are in class one. Imagine we are growing a decision tree to predict a binary target variable. Figure 4 shows two possible decision trees that could be formed by splitting on two different predictors. Which of the two trees would we prefer, and why? (2 marks) When learning a decision tree from data, one of the most important aspects is knowing how many leaves the tree should have, i.e., how complex it should be. If we denote the number of leaves in a tree by L, please describe the standard algorithm that uses K-fold cross validation and pruning to choose an appropriate value of L from the set 1,,Lmax(5 marks ) Figure 3: A regression tree predicting the fuel efficiency (in kilometers per litre, km/l ) of cars manufactured in 2019. "Drive" denotes whether the vehicle is all-wheel drive or part-time four-wheel drive; "Eng. Size" is the size of the car's engine in litres; "Fuel Type" is the type of fuel used by the car, and can be either petrol or diesel. Figure 3 shows a decision tree that has been learned from a sample of cars manufactured in 2019 . The target in this case is the fuel efficiency of the car (measured in kilometers per litre of fuel consumed, km/l ) so we are using a regression tree. The predictors that were included in the tree were the type of drive-chain ("Drive", either all-wheel drive or part-time four-wheel drive), the size of the car's engine ("Eng. Size", measured in litres) and the type of fuel used by the vehicle ("Fuel Type", petrol or diesel). Using this tree, please answer the following questions: (i) What is the predicted fuel efficiency of a car which runs on petrol, is all-wheel drive and has an engine size of 6.4l? (2 marks) (ii) What combination of predictors leads to the worst fuel efficiency? (2 marks) (iii) Using this model, what can we say about the effect of engine size on the fuel efficiency of a car? (2 marks) Figure 4: Two possible decision trees for a binary target, each splitting on a different predictor. The leaves show the number of individuals classified in the two different target classes; i.e., 45/48 means 45 individuals in are class zero and 48 are in class one. Imagine we are growing a decision tree to predict a binary target variable. Figure 4 shows two possible decision trees that could be formed by splitting on two different predictors. Which of the two trees would we prefer, and why? (2 marks) When learning a decision tree from data, one of the most important aspects is knowing how many leaves the tree should have, i.e., how complex it should be. If we denote the number of leaves in a tree by L, please describe the standard algorithm that uses K-fold cross validation and pruning to choose an appropriate value of L from the set 1,,Lmax(5 marks )
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


