Question: For each shock identified below, shift the AD curve, the SRAS curve, or both to show its effects on aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply. Then

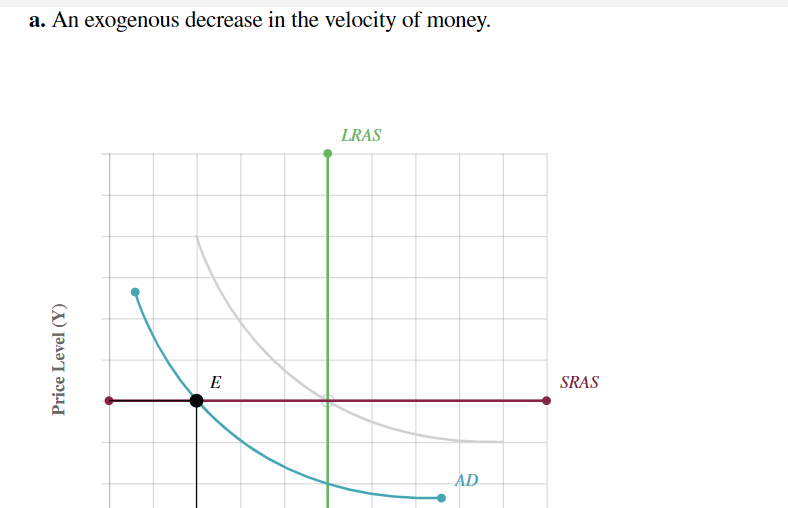
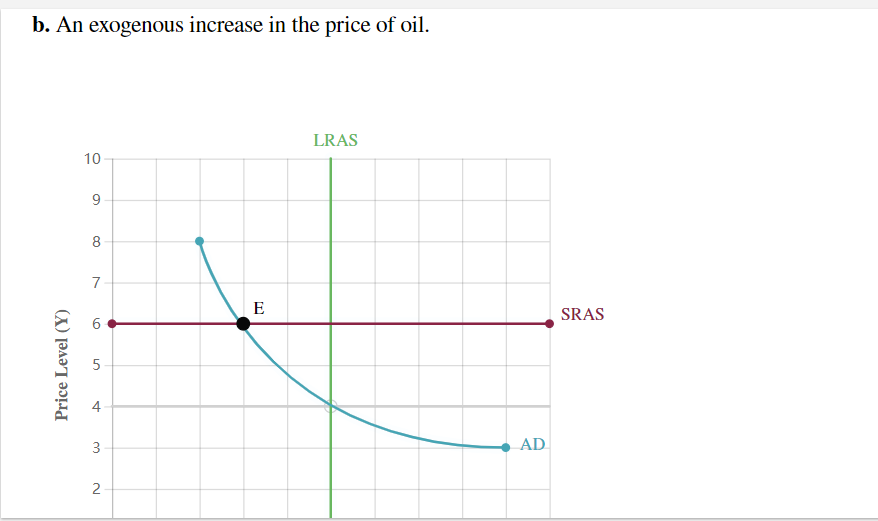


For each shock identified below, shift the AD curve, the SRAS curve, or both to show its effects on aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply. Then move point E to the new short-run equilibrium to indicate the new price level P and output Y. Assume the economy starts out in long-run equilibrium.
A,B part were correct,
Please solve C and D.

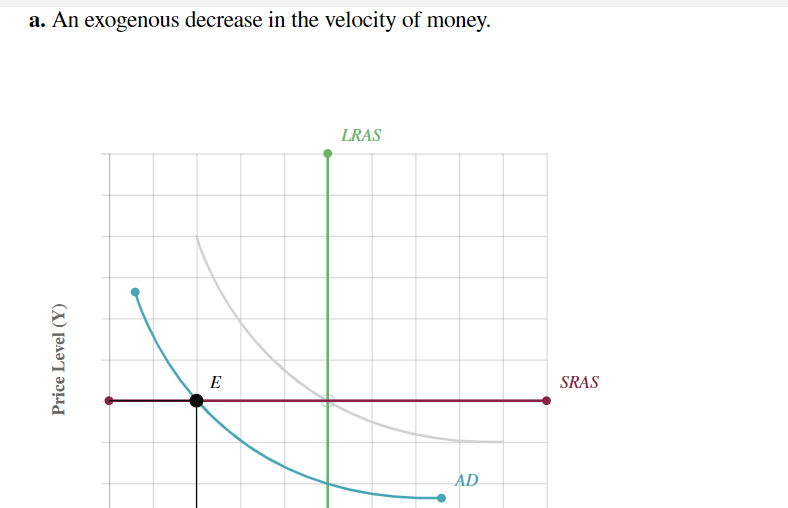
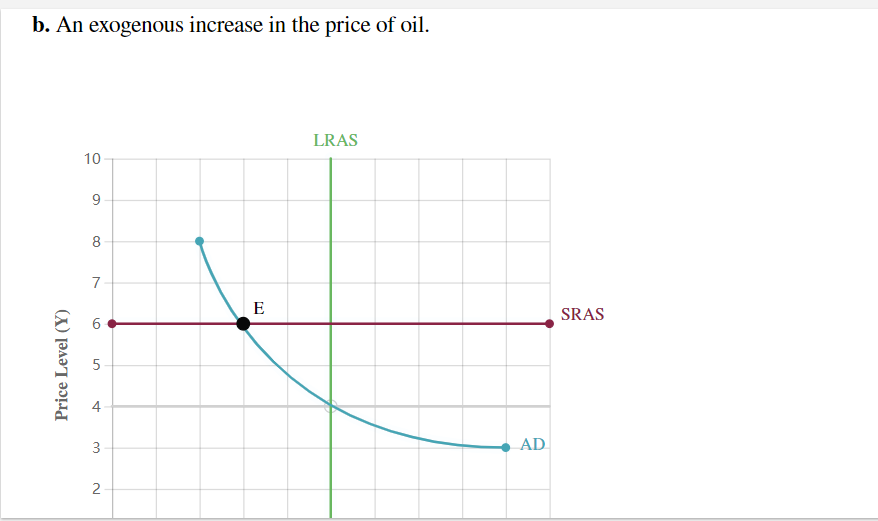

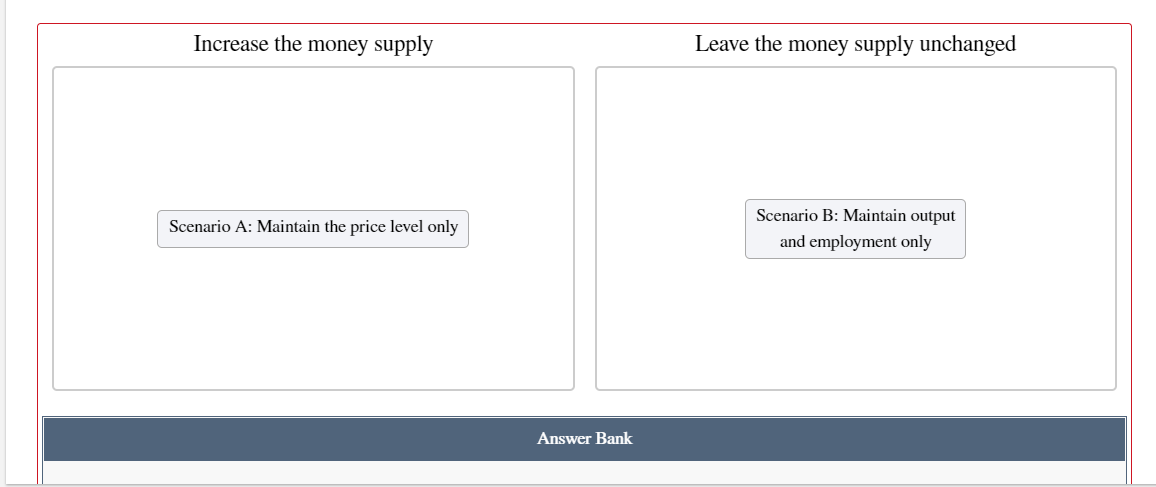

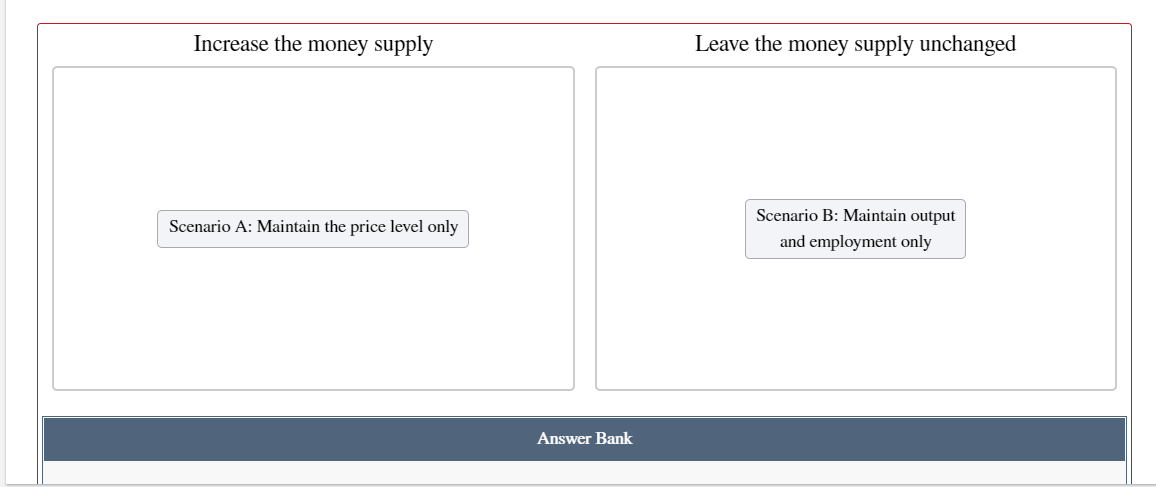
Introduction to Economic Fluctuations End of Chapter Problem For each shock identied below, shift the AD curve, the SRAS curve, or both to Show its effects on aggregate demand andfor aggregate supply. Then move point E to the new short-run equilibrium to indicate the new price level P and output Y. Assume the economy starts out in long-run equilibrium. a. An exogenous decrease in the velocity of money. a. An exogenous decrease in the velocity of money. SRAS Price Level (Y) b. An exogenous increase in the price of oil. LR AS 1!] Price Level (Y) c. Now consider how the goals of the Fed inuence its response to these shocks. Suppose that in scenario A, the Fed cares only about keeping the price level stable, whereas in scenario B, it cares only about keeping output and employment at their natural levels. Place scenario A and scenario B in the appropriate category describing the Fed's proper response to a decrease in the velocity of money. \fd. Now place scenario A and scenario B in the appropriate category describing the Fed's proper response to an increase in the price of oil. Increase the money supply Leave the money supply unchanged Scenario A: Maintain the price level only scem'w'o 3:1Ma'\"m\" imp\" emp oyment o y
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


