Question: For heat transfer in a semi-infinite solid with its flat surface and distance x into the solid normal to the surface (see Figure 1) is
For heat transfer in a semi-infinite solid with its flat surface and distance x into the solid normal to the surface (see Figure 1) is subject to a constant heat flux qB, the temperature T(x,t) is a function of distance (x) and time (t), given by
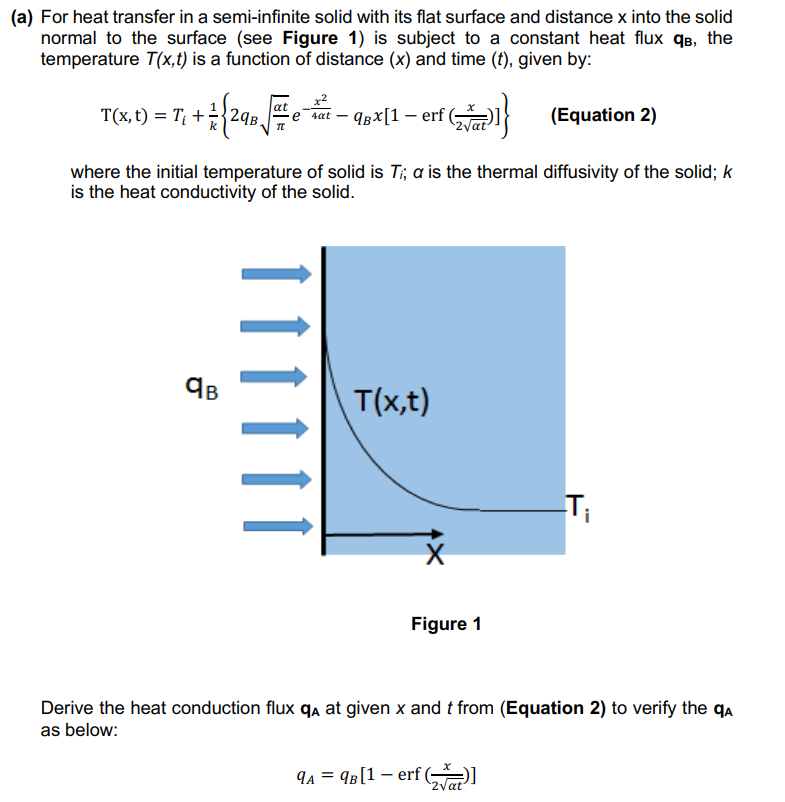
a) For heat transfer in a semi-infinite solid with its flat surface and distance x into the solid normal to the surface (see Figure 1) is subject to a constant heat flux qB, the temperature T(x,t) is a function of distance (x) and time (t), given by: T(x,t)=Ti+k1{2qBte4tx2qBx[1erf(2tx)]} (Equation 2) where the initial temperature of solid is Ti; is the thermal diffusivity of the solid; k is the heat conductivity of the solid. Figure 1 Derive the heat conduction flux qA at given x and t from (Equation 2) to verify the qA as below: qA=qB[1erf(2tx)]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


