Question: For the reaction 2 NO(9) + 2 H2 (9) + N2(g) + 2 H2O(9) at 1100C, the following data have been obtained. [NO] H2) rate
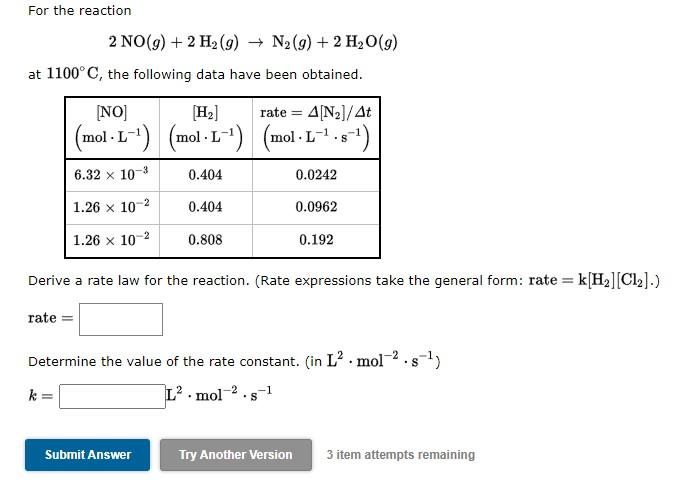
![+ 2 H2O(9) at 1100C, the following data have been obtained. [NO]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f85608b5252_98466f856084d91b.jpg)
For the reaction 2 NO(9) + 2 H2 (9) + N2(g) + 2 H2O(9) at 1100C, the following data have been obtained. [NO] H2) rate = 4(N2]/At = |(mol L-1) (mol L-1) (mol-1-7.5-1) . . 6.32 x 10-3 0.404 0.0242 1.26 x 10-2 0.404 0.0962 1.26 x 10-2 0.808 0.192 Derive a rate law for the reaction. (Rate expressions take the general form: rate = k[Hz] (C12).) rate = Determine the value of the rate constant. (in L. mol-2.5-1) k= La.mol-2.5-1 Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item attempts remaining The reaction NO(g) + O2(g) + NO2(g) + (9) plays a role in the formation of nitrogen dioxide in automobile engines. Suppose a series of experiments measured the rate of this reaction at 500. K and produced the following data. NO [02] |(mol.L-1) (mol L-1) (mol.1-4.51) rate = -A[NO]/At L 0.00195 0.00488 7.61 x 10-17 0.00195 0.00975 1.52 x 10-16 0.00585 0.00488 2.28 x 10-16 Derive a rate law for the reaction. (Rate expressions take the general form: rate = k[H2][Cl2].) rate= Determine the value of the rate constant. k= L/mol/s
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


