Question: For this vulnerable code below (stack.c), The above program reads 300 bytes of data from a file called badfile, and then copies the data to
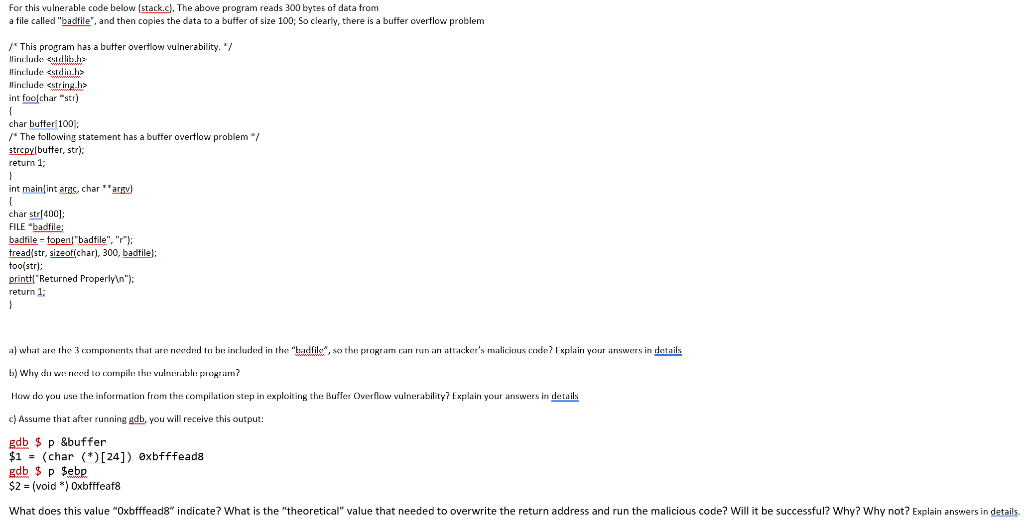
For this vulnerable code below (stack.c), The above program reads 300 bytes of data from a file called "badfile", and then copies the data to a buffer of size 100; So clearly, there is a buffer overflow problem /* This program has a butter overflow vulnerability, llinclude #include #include int foolchar "str) { char buffer 1001: /* The following statement has a buffer overflow problem */ strcpylbutter, stry: retum 1; } int mainint args, char *arg) char str400); FILE "badfile badfile - topen/"badfile", "r"); tread/str, sizeofichar), 300, badfile): too(str); printt/"Returned Properly "); return 1; a) what are the 3 components that are needed to be included in the "hadila, so the program can run an attacker's malicious code? Explain your answers in details b) Why do we need to compile the vulnerable program? How do you use the information from the compilation step in exploiting the Buffer Overflow vulnerability? Explain your answers in details c) Assume that after running gdb, you will receive this output: gdb $ p&buffer $1 = (char (*)[24]) oxbfffeads gdb $ p $ebp $2 = (void *) Oxbfffeafs What does this value "Oxbfffead8" indicate? What is the "theoretical" value that needed to overwrite the return address and run the malicious code? Will it be successful? Why? Why not? Explain answers in details For this vulnerable code below (stack.c), The above program reads 300 bytes of data from a file called "badfile", and then copies the data to a buffer of size 100; So clearly, there is a buffer overflow problem /* This program has a butter overflow vulnerability, llinclude #include #include int foolchar "str) { char buffer 1001: /* The following statement has a buffer overflow problem */ strcpylbutter, stry: retum 1; } int mainint args, char *arg) char str400); FILE "badfile badfile - topen/"badfile", "r"); tread/str, sizeofichar), 300, badfile): too(str); printt/"Returned Properly "); return 1; a) what are the 3 components that are needed to be included in the "hadila, so the program can run an attacker's malicious code? Explain your answers in details b) Why do we need to compile the vulnerable program? How do you use the information from the compilation step in exploiting the Buffer Overflow vulnerability? Explain your answers in details c) Assume that after running gdb, you will receive this output: gdb $ p&buffer $1 = (char (*)[24]) oxbfffeads gdb $ p $ebp $2 = (void *) Oxbfffeafs What does this value "Oxbfffead8" indicate? What is the "theoretical" value that needed to overwrite the return address and run the malicious code? Will it be successful? Why? Why not? Explain answers in details




