Question: Galvanic Cells Using tabulated standard reduction potentials from your text, calculate the standard cell potential, cell always positive for a galvanic cell), based on the
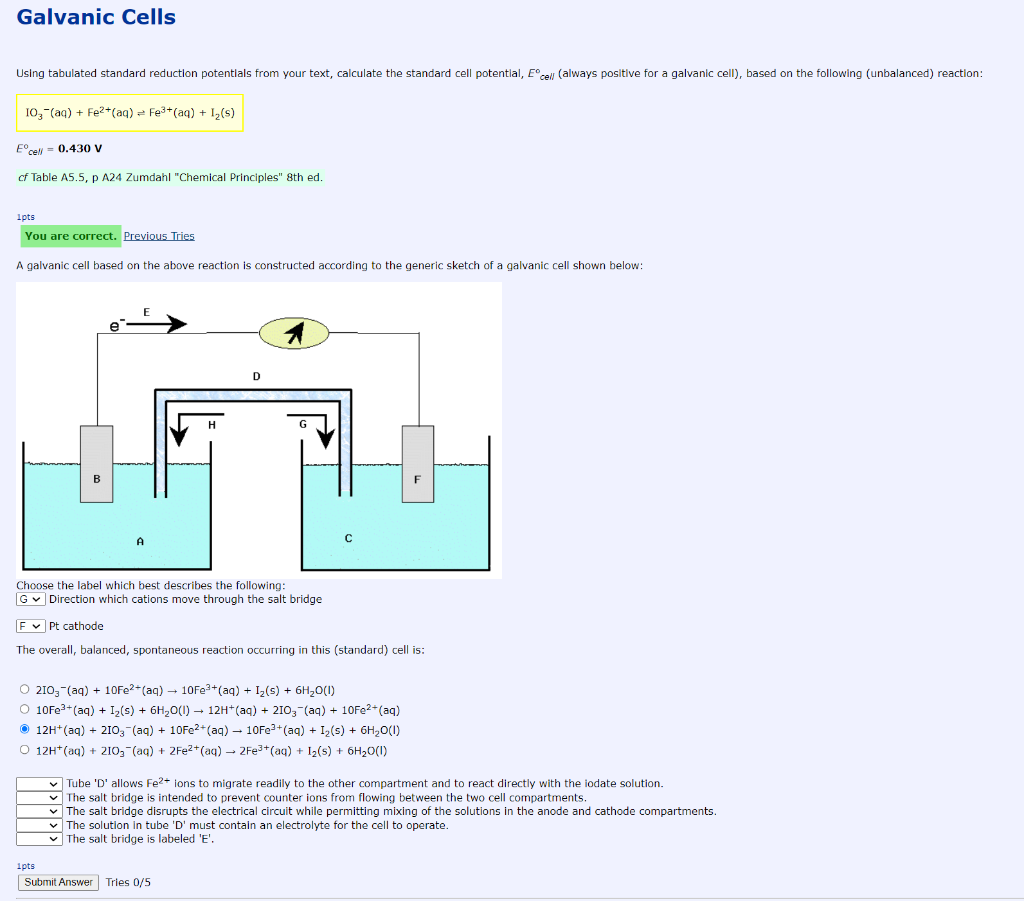
Galvanic Cells Using tabulated standard reduction potentials from your text, calculate the standard cell potential, cell always positive for a galvanic cell), based on the following (unbalanced) reaction: 10,-(aq) + Fe2+(aq) = Fe3+ (aq) + 1 (5) E cell = 0.430 V cf Table A5.5, p A24 Zumdahl "Chemical Principles" 8th ed. 1pts You are correct. Previous Tries A galvanic cell based on the above reaction is constructed according to the generic sketch of a galvanic cell shown below: B Choose the label which best describes the following: G Direction which cations move through the salt bridge F Pt cathode The overall, balanced, spontaneous reaction occurring in this (standard) cell is: O 210,- (aq) + 10Fe2+ (aq) 10Fe3+ (aq) + 12(5) + 6H20(1) 10Fe3+ (aq) + Iz(s) + 6H20(1) - 12H+ (aq) + 2103 - (aq) + 10Fe2+ (aq) 12H+ (aq) + 210,- (aq) + 10Fe2+ (aq) 10Fe3+ (aq) + 1,(s) + 6H2O(1) O 12H+ (aq) + 210, (aq) + 2Fe2+ (aq) 2Fe3+ (aq) + 12(5) + 6H2O(1) Tube 'D' allows Fe2+ ions to migrate readily to the other compartment and to react directly with the iodate solution. The salt bridge is intended to prevent counter ions from flowing between the two cell compartments, The salt bridge disrupts the electrical circuit while permitting mixing of the solutions in the anode and cathode compartments. The solution in tube 'D' must contain an electrolyte for the cell to operate. The salt bridge is labeled 'E'. 1 pts Submit Answer Tries 0/5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


