Question: Given the tree structure and the tree_fold function, can someone create 2 functions trim and compose using only tree_fold and without using any recursive helpers?

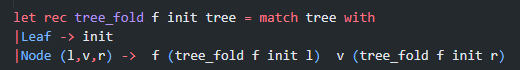
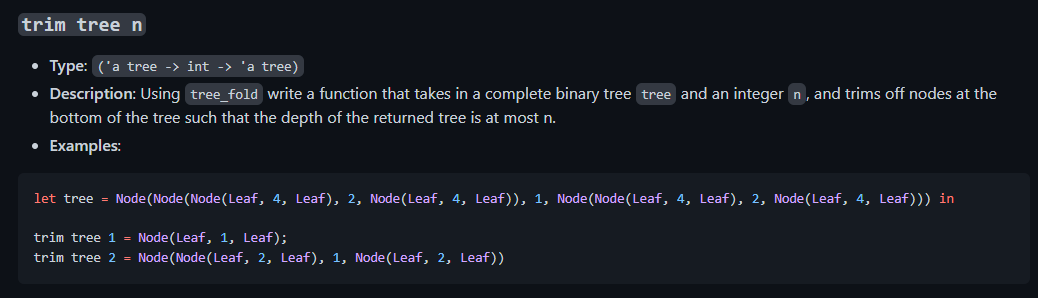
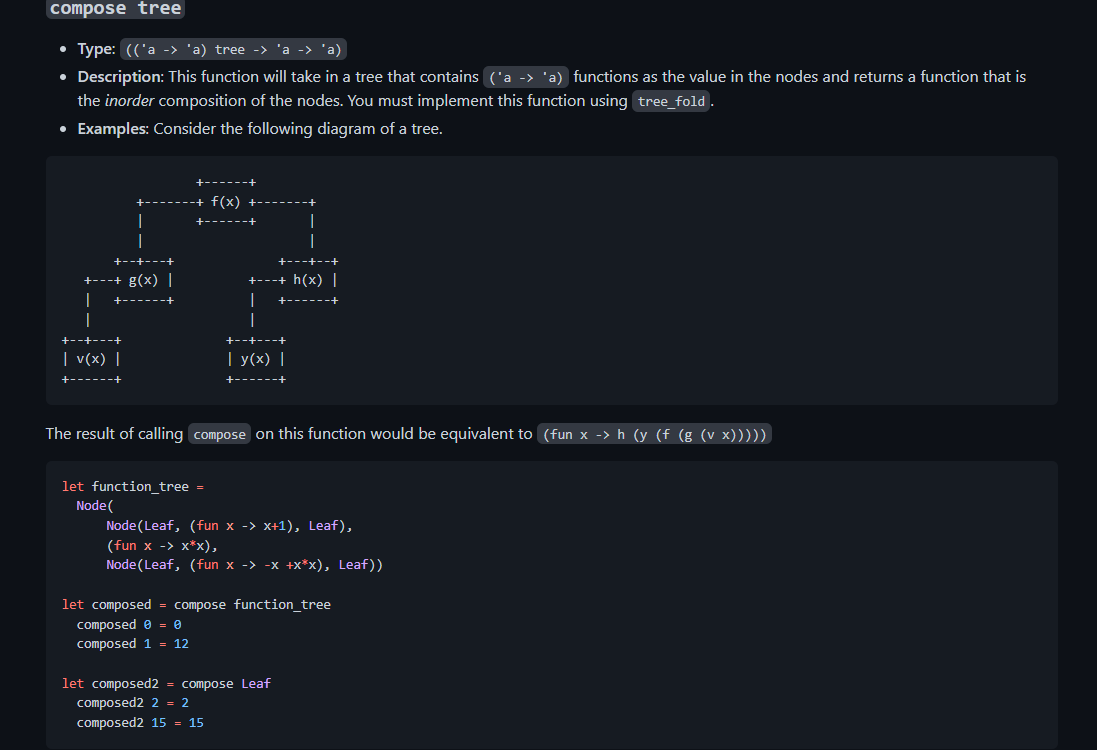
Given the tree structure and the tree_fold function, can someone create 2 functions trim and compose using only tree_fold and without using any recursive helpers?
type 'a tree = | Node of 'a tree *'a * 'a tree | Leaf let rec tree_fold f init tree = match tree with Leaf init Node (1,v,r)f( tree_fold f init 1)v (tree_fold f init r ) trim tree n - Type: ('a tree int ' a tree) - Description: Using tree_fold write a function that takes in a complete binary tree tree and an integer n, and trims off nodes at the bottom of the tree such that the depth of the returned tree is at n. - Examples: let tree =Node(Node(Node( Leaf, 4, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf)), 1, Node(Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf))) in trim tree 1=Node( Leaf, 1, Leaf); trim tree 2=Node(Node( Leaf, 2, Leaf), 1, Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf)) compose tree - Type: (('a ' 'a) tree ' a> ' a ) - Description: This function will take in a tree that contains ( a> ' a ) functions as the value in the nodes and returns a function that is the inorder composition of the nodes. You must implement this function using tree_fold. - Examples: Consider the following diagram of a tree. The result of calling compose on this function would be equivalent to ( fun xh(y(f(g(vx))))) let function_tree = Node( Node(Leaf, ( fun x>x+1), Leaf), ( fun x>xx), Node(Leaf, ( fun x>x+xx), Leaf)) let composed = compose function_tree composed = composed 1=12 let composed2 = compose Leaf composed2 2=2 composed2 15=15 type 'a tree = | Node of 'a tree *'a * 'a tree | Leaf let rec tree_fold f init tree = match tree with Leaf init Node (1,v,r)f( tree_fold f init 1)v (tree_fold f init r ) trim tree n - Type: ('a tree int ' a tree) - Description: Using tree_fold write a function that takes in a complete binary tree tree and an integer n, and trims off nodes at the bottom of the tree such that the depth of the returned tree is at n. - Examples: let tree =Node(Node(Node( Leaf, 4, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf)), 1, Node(Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf))) in trim tree 1=Node( Leaf, 1, Leaf); trim tree 2=Node(Node( Leaf, 2, Leaf), 1, Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf)) compose tree - Type: (('a ' 'a) tree ' a> ' a ) - Description: This function will take in a tree that contains ( a> ' a ) functions as the value in the nodes and returns a function that is the inorder composition of the nodes. You must implement this function using tree_fold. - Examples: Consider the following diagram of a tree. The result of calling compose on this function would be equivalent to ( fun xh(y(f(g(vx))))) let function_tree = Node( Node(Leaf, ( fun x>x+1), Leaf), ( fun x>xx), Node(Leaf, ( fun x>x+xx), Leaf)) let composed = compose function_tree composed = composed 1=12 let composed2 = compose Leaf composed2 2=2 composed2 15=15
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


