Question: Given the velocity components for a certain incompressible, steady-flow field as where , , and are the position components in a 3D Cartesian coordinate system,
Given the velocity components for a certain incompressible, steady-flow field as 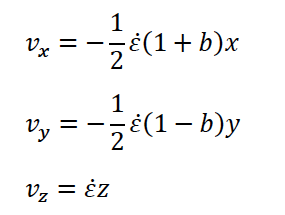
where , , and are the position components in a 3D Cartesian coordinate system, 01, and the parameter (dimension T1) is known as the elongation rate, this type of flow is known as simple shearfree flow.
Complete the following tasks:
- (a) [5 Points] Show that the given velocity field satisfies the continuity equation.
- (b) [10 Points] Applying Newtons law of viscosity for an incopressible fluid of viscosity ,
- =[+()^T]
- Show that the stress tensor becomes
- =[+()^T]
- (c) [5 Points] For steady simple shearfree flows we define two viscosity function 1(,) and 2(,) to describe the two normal stress differences:
=1(,) =2(,)
Show that for the special steady-state shear flow known as the uniaxial elongational flow, where =0 and >0, we have 2=0, and 1=3.
Here, 1 is known as the elongational viscosity, and the ratio of elongational viscosity to shear viscosity is known as the Trouton ratio.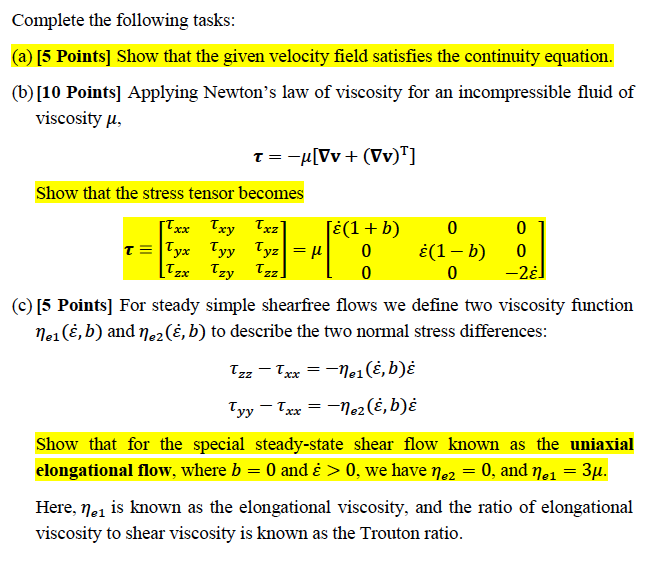
1 Vx = ) (1+b)x v, = -34(1 by E 1 b V2 = z Z Complete the following tasks: (a) [5 Points] Show that the given velocity field satisfies the continuity equation. (b) [10 Points] Applying Newton's law of viscosity for an incompressible fluid of viscosity u, t=-u[Vv + (Vv)T] Show that the stress tensor becomes [Tax Txy Txz [(1 + b) 0 0 T = Tyx Tyy Tyz| = u 0 (1-b) 0 Tzy Tzz 0 0 -2 () [5 Points] For steady simple shearfree flows we define two viscosity function nel, b) and nez(, b) to describe the two normal stress differences: Tzz Txx = -nel, b Tzx = Tyy - Txx = -nez, b) Show that for the special steady-state shear flow known as the uniaxial elongational flow, where b = 0 and > 0, we have nez = 0, and nei = 3u. Here, Nei is known as the elongational viscosity, and the ratio of elongational viscosity to shear viscosity is known as the Trouton ratio
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


