Question: Hi, could you explain how to solve this question? How many cost units are spent in the entire process of performing 40 consecutive append operations
Hi, could you explain how to solve this question?
-
How many cost units are spent in the entire process of performing 40 consecutive append operations on an empty array which starts out at capacity 3, assuming that the array will grow by a constant 2 spaces each time a new item is added to an already full dynamic array? As N (i.e., the number of appends) grows large, under this strategy for resizing, what is the amortized big-O complexity for an append?
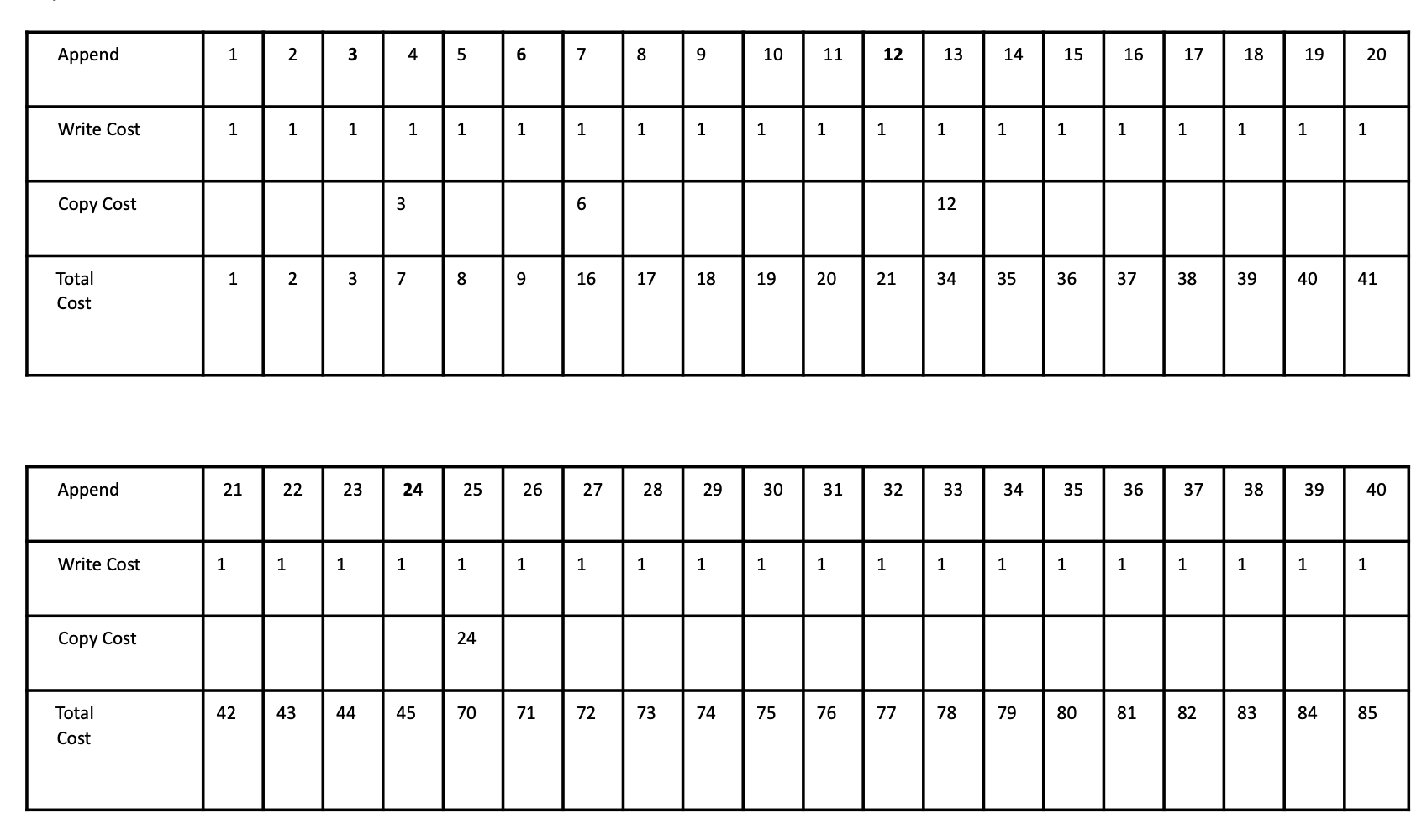



Append 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Write Cost 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Copy Cost 3 6 12 1 2 3 7 8 9 16 17 18 19 20 21 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 Total Cost Append 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Write Cost 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Copy Cost 24 42 43 44 45 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 Total Cost b) As N (i.e., the number of appends) grows large, under this strategy for resizing, the average big-o complexity for an append can be derived using the following calculation: Mathematically, total cost = total write cost (Sw) + total copy cost (Sn). The total write cost, Sw = N. Recall (from the table you prepared in part (a)) the copy cost is a sequence as follows: 3,5, 7, 9, 11, ... (an arithmetic sequence) Now, what is the cost of the last resize (kth term of the sequence)? The kth term is derived from the following equation, and you will assume the sequence contains k terms: ak = a1 + d(k 1) where ay is the first term and d is the difference. In this instance: ak =(you have to calculate it) What is the sum of k terms of the sequence? You can derive that from the following equation: Sk=ktak). 2 In this instance: Sk = (you have to calculate it) The above equation should work for all integers, k, such that k > 1. In this instance, k represents the resize term number. However, we are concerned with appends, so you must express the sum of the sequence in terms of N appends, or in other words, you must derive k resize operations givenN appends. th You already have determined the kth resize cost (ak) before. Now you determine the k resize cost (ak) in terms of N (For example, in part (a) when you had N= 6, the last resize cost was 5 (holds for all N, N> 3)). You can consider either of the cases ( i.e., Nis odd or Nis even). You will find out the value of k in terms of N. Now, use the k and sum equation above (Sk) to derive the total copy cost of the given N appends: Sn= (you have to calculate it) Recall that total cost = total write cost (Sw) + total copy cost (Sn). As we have conducted N appends, the average complexity can be derived from: (Sw + Sn) (you have to calculate it) N This gives us an amortized complexity of O(you have to determine it). Append 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Write Cost 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Copy Cost 3 6 12 1 2 3 7 8 9 16 17 18 19 20 21 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 Total Cost Append 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Write Cost 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Copy Cost 24 42 43 44 45 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 Total Cost b) As N (i.e., the number of appends) grows large, under this strategy for resizing, the average big-o complexity for an append can be derived using the following calculation: Mathematically, total cost = total write cost (Sw) + total copy cost (Sn). The total write cost, Sw = N. Recall (from the table you prepared in part (a)) the copy cost is a sequence as follows: 3,5, 7, 9, 11, ... (an arithmetic sequence) Now, what is the cost of the last resize (kth term of the sequence)? The kth term is derived from the following equation, and you will assume the sequence contains k terms: ak = a1 + d(k 1) where ay is the first term and d is the difference. In this instance: ak =(you have to calculate it) What is the sum of k terms of the sequence? You can derive that from the following equation: Sk=ktak). 2 In this instance: Sk = (you have to calculate it) The above equation should work for all integers, k, such that k > 1. In this instance, k represents the resize term number. However, we are concerned with appends, so you must express the sum of the sequence in terms of N appends, or in other words, you must derive k resize operations givenN appends. th You already have determined the kth resize cost (ak) before. Now you determine the k resize cost (ak) in terms of N (For example, in part (a) when you had N= 6, the last resize cost was 5 (holds for all N, N> 3)). You can consider either of the cases ( i.e., Nis odd or Nis even). You will find out the value of k in terms of N. Now, use the k and sum equation above (Sk) to derive the total copy cost of the given N appends: Sn= (you have to calculate it) Recall that total cost = total write cost (Sw) + total copy cost (Sn). As we have conducted N appends, the average complexity can be derived from: (Sw + Sn) (you have to calculate it) N This gives us an amortized complexity of O(you have to determine it)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


