Question: I am stuck on these and am having some problems getting the right answer. Can someone help me? Thank you! Some of them I have
I am stuck on these and am having some problems getting the right answer. Can someone help me? Thank you! Some of them I have answered correct, but some portions within the question were wrong.
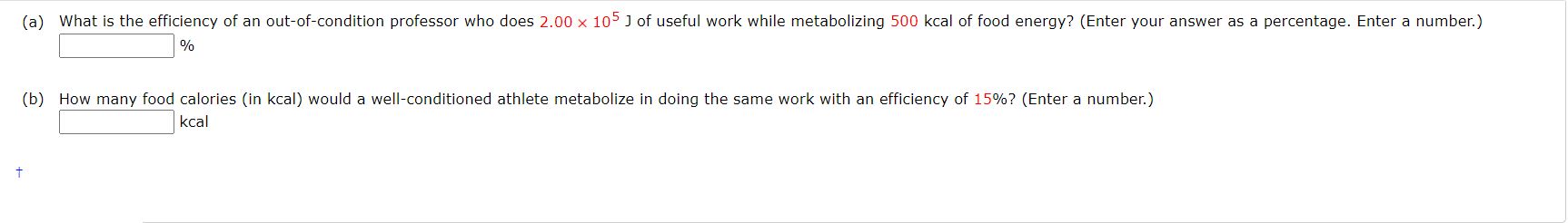

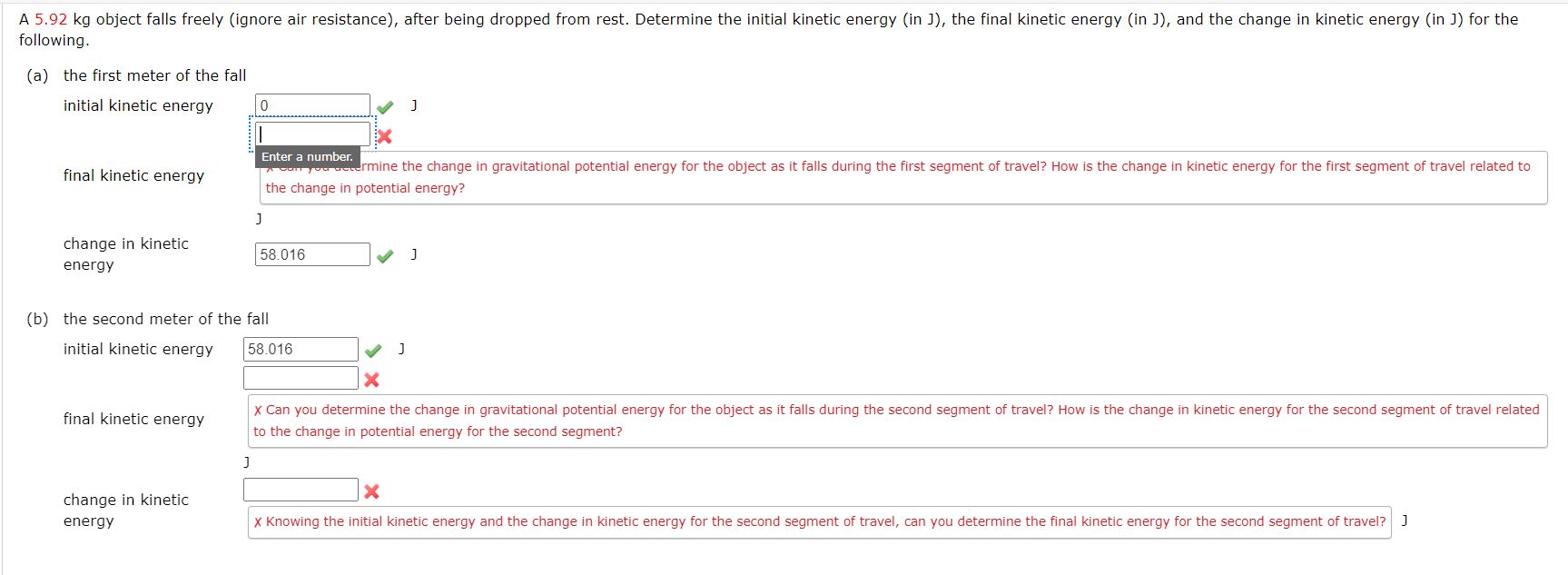

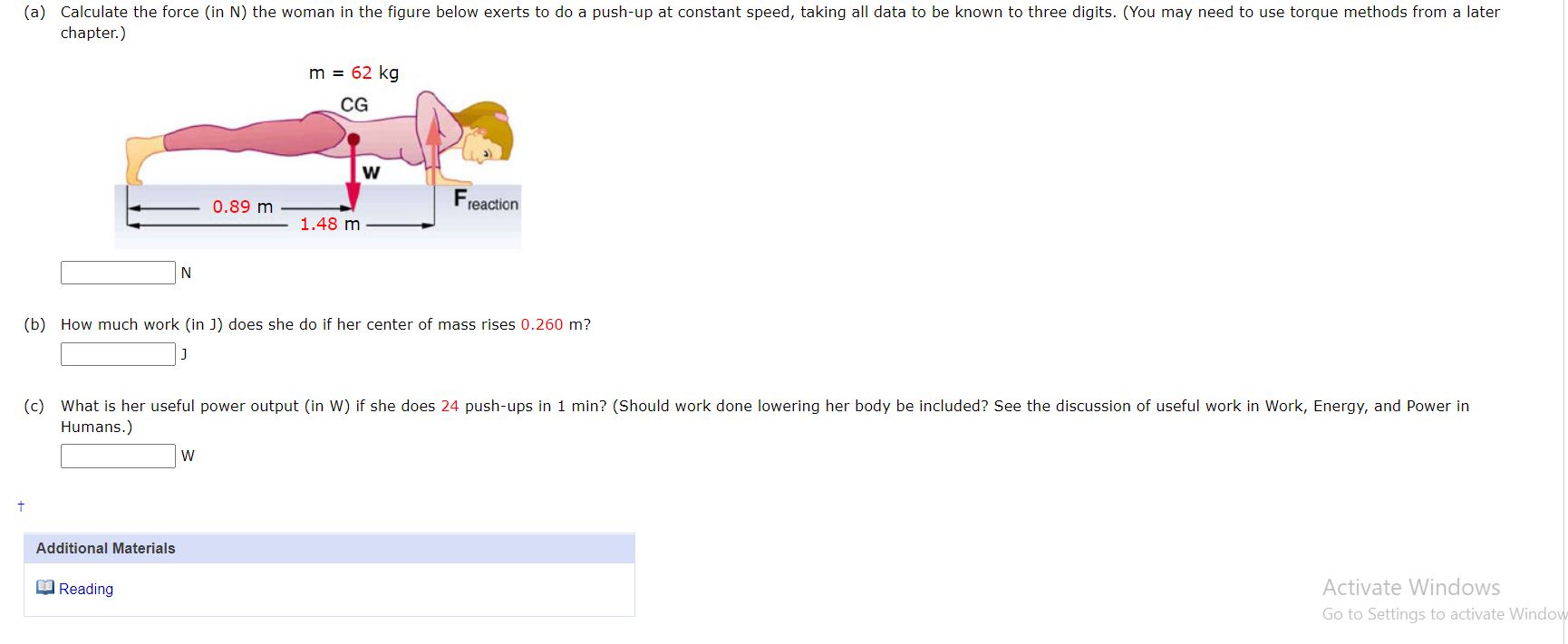
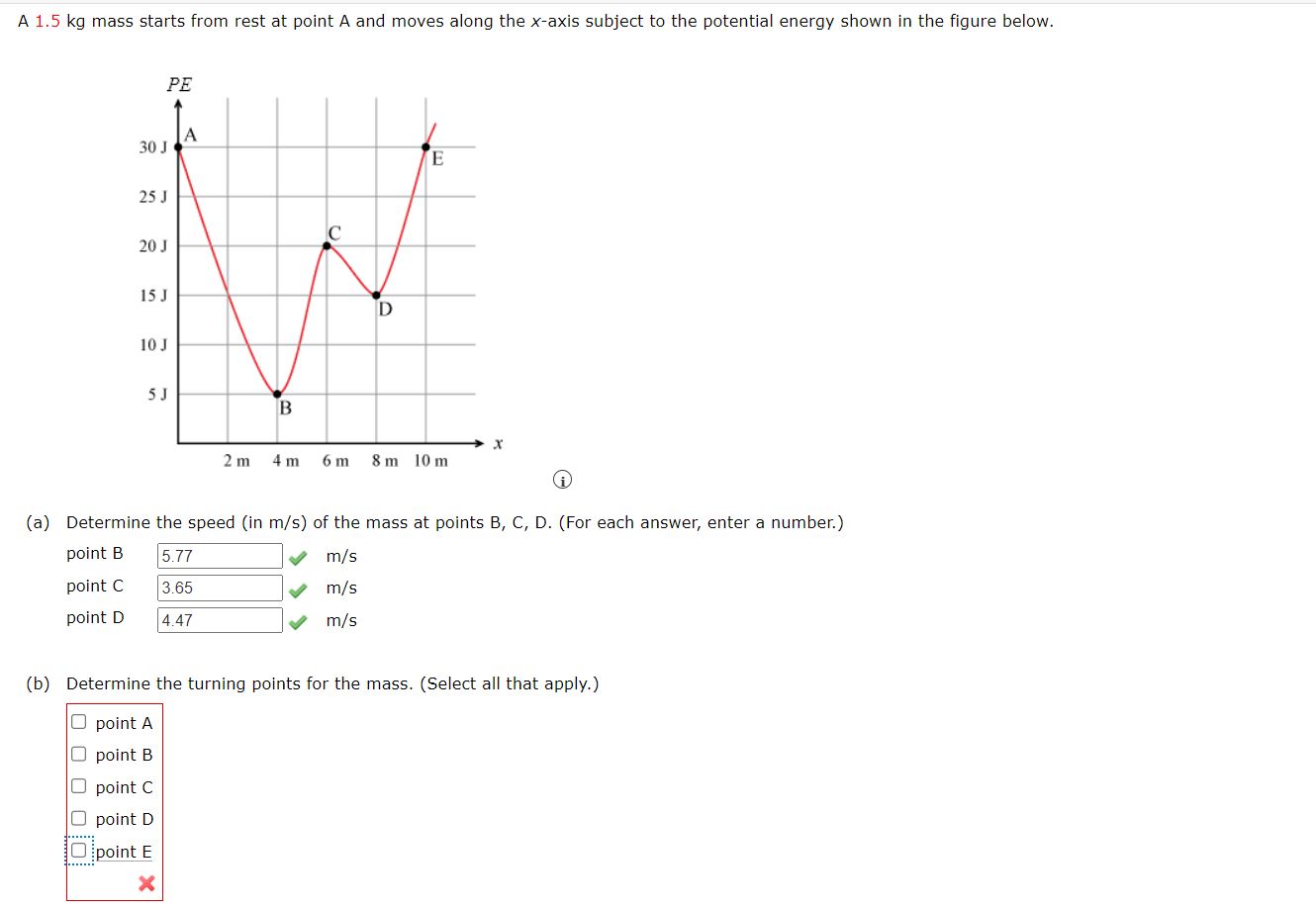
\f(a) How high (in m) a hill can a car coast up (engine disengaged) if friction is negligible and its initial speed is 110 km/h? (Enter a number.) /m (b) If, in actuality, a 750 kg car with an initial speed of 110 km/h is observed to coast up a hill to a height 25.0 m above its starting point, how much thermal energy (in J] was generated by friction? (Enter a number.) 166365 740 ~/ 1 (C) What is the average force of friction (down the slope) it the hill has a slope 2.5\" above the horizontal? (Enter your answer in N. Enter a number.) :xN A 5.92 kg object falls freely (ignore air resistance), after being dropped from rest. Determine the initial kinetic energy (in J), the final kinetic energy (in J), and the change in kinetic energy (in J) for the following (a) the first meter of the fall initial kinetic energy final kinetic energy _. , . . rmine the change in gravitational potential energy for the object as it falls during the first segment of travel? How is the change in kinetic energy for the first segment of travel related to ' the change in potential energy? J change In kinetic 58 016 J ] energy (D) the second meter of the fa ll initial kinetic energy 58,016 J J S x final kinetic energy X Can you determine the change in gravitational potential energy for the object as it falls during the second segment of travel? How is the change in kinetic energy for the second segment of travel related to the change in potential energy for the second segment? J change in kinetic E X energy ' X KnDWing the initial kinetic energy and the change in kinetic energy for the second segment of travel, can you determine the final kinetlc energy for the second segment of travel? J (a) Find the useful power eutput (in W) of an elevator motor that lifts a 2800 kg load a height of 35.0 m in 12.0 5, if it also increases the speed from rest to 4.00 m/s. Note that the total mass cf the counterbalanced system is 10,000 kgiso that only 2800 kg is raised in height, but the full 10,000 kg is accelerated. (Enter a number.) SW (D) What does it cost (in cents), if electricity is $00900 per kW - h? (Enter a number.) (a) Calculate the force (in N) the woman in the figure below exerts to do a push-up at constant speed, taking all data to be known to three digits. (You may need to use torque methods from a later chapter.) m = 62 kg CG W 0.89 m Freaction 1.48 m N (b) How much work (in ]) does she do if her center of mass rises 0.260 m? (c) What is her useful power output (in W) if she does 24 push-ups in 1 min? (Should work done lowering her body be included? See the discussion of useful work in Work, Energy, and Power in Humans.) W Additional Materials Activate Windows Reading Go to Settings to activate WindowA 1.5 kg mass starts from rest at point A and moves along the X-axis subject to the potentiai energy shown in the figure below. 2m 4m 0m 3m lilm (D [3) Determine the speed (in m/s) of the mass at points 8, C, D. (For each answer, enter a number.) -.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


