Question: I have linearized dynamic bicycle model state space representation from Snider, Jarrod. ( 2 0 1 1 ) . Automatic Steering Methods for Autonomous Automobile
I have linearized dynamic bicycle model state space representation from Snider, Jarrod. Automatic Steering Methods for Autonomous Automobile Path Tracking. I am using Eq attachedwith error states. Path Tracking Control Using a Dynamic Model.
I want to modify this model. I will use states as lateral position error, lateral velocity error, longitunal position error, longitunal velocity error, yaw angle error and yaw rate error. My inputs are steering angle and longitunal velocity change dv
Could you calculate new state space model?
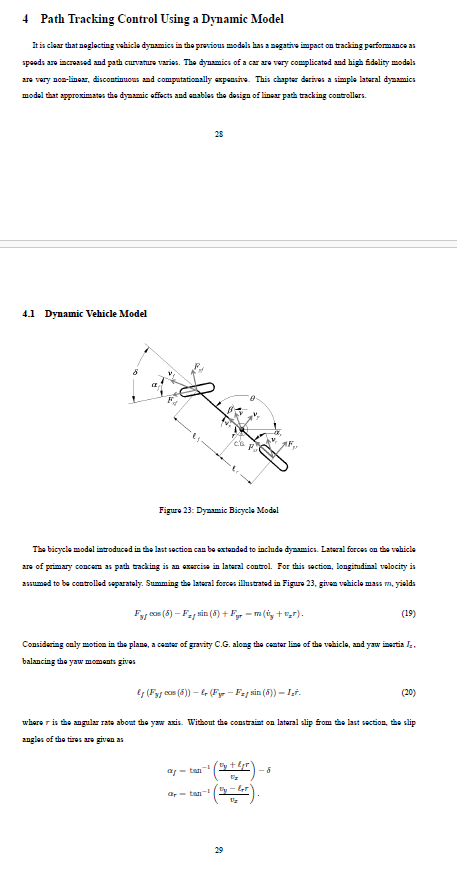
Modelling the force genarated by the wheels as linearly proportionsl to the alip angle, the lateral forces are defined as
Annming a constant longitudinal valocity, allows the simplification
Substituting Eqs. and into Eqz. and and soking for for and
gives the dynamic bicycle model.
Limearized Dymamic Bicycle Model
To apply linear control mathods to the dynamic bicycle modal, the model must be linasrinad. Applying mall angle
assumptions to Eqz. and gives
Collacting torms results in
Finally, the linasr dyuamic bicycle model can be writtan in state space form as
Path Coordinates
Figure : Dyzamic Bicycle Modal in path coordinates
As with the kinematic bicycle modal, it is usafal to axprass the dynamic bicycle model with respact to the path.
With the constant longitudinal valocity asnumption, the yaw rate derived from the path is definad as
Path derived lataral acceleration iy s follow: as
Letting be the orthogonal distance of the CG to the path,
vec
and
where was provioualy dafined as Subatituting into Eqs. and yields
vec
The state space model in tracking error variables is tharafore given by
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


