Question: I need all the possible process 6. Consider a manufacturing network with 4 processing stations. Each of the stations can be modeled as a system
I need all the possible process
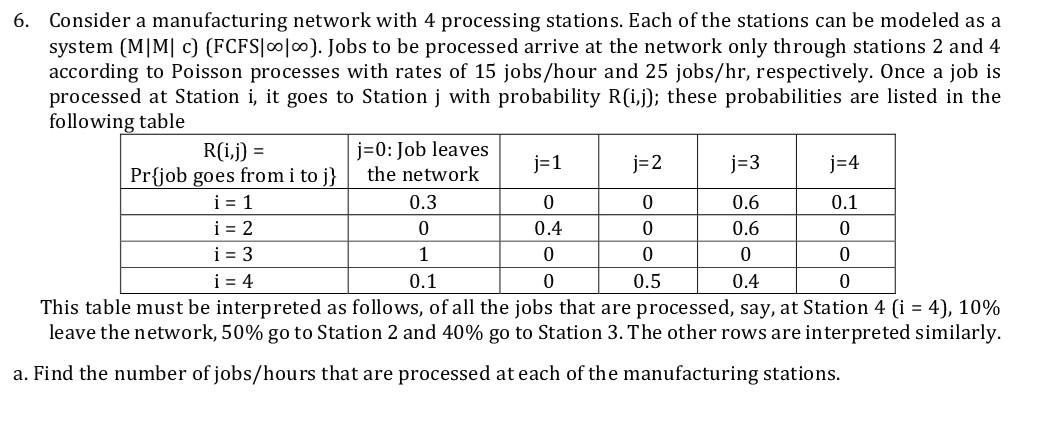
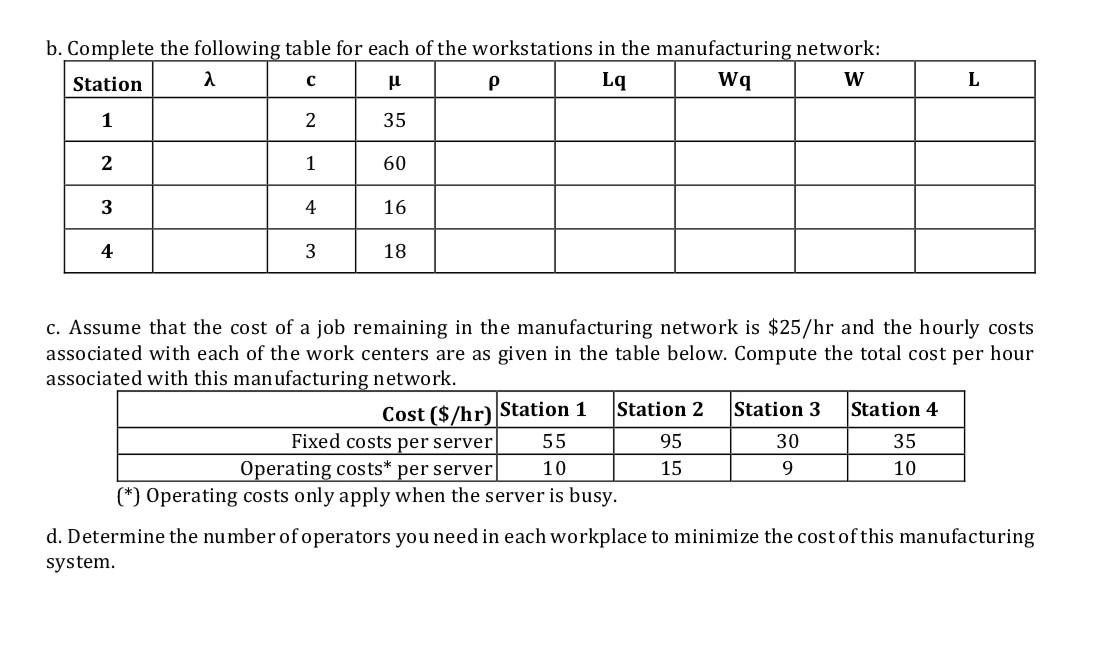
6. Consider a manufacturing network with 4 processing stations. Each of the stations can be modeled as a system (MMC) (FCFS|00|00). Jobs to be processed arrive at the network only through stations 2 and 4 according to Poisson processes with rates of 15 jobs/hour and 25 jobs/hr, respectively. Once a job is processed at Station i, it goes to Station j with probability R[i,j]; these probabilities are listed in the following table R(i,j) = j=0: Job leaves j=1 j=2 j=3 the network j=4 Pr{job goes from i to j} i = 1 0.3 0 0.6 0.1 i = 2 0.4 0.6 i = 3 1 0 0 0 i = 4 0.1 0.5 0.4 0 This table must be interpreted as follows, of all the jobs that are processed, say, at Station 4 (i = 4), 10% leave the network, 50% go to Station 2 and 40% go to Station 3. The other rows are interpreted similarly. a. Find the number of jobs/hours that are processed at each of the manufacturing stations. 0 0 0 0 0 b. Complete the following table for each of the workstations in the manufacturing network: Station u Lq Wq W L 1 2 35 2 1 60 3 4 16 4 3 18 c. Assume that the cost of a job remaining in the manufacturing network is $25/hr and the hourly costs associated with each of the work centers are as given in the table below. Compute the total cost per hour associated with this manufacturing network. Cost ($/hr) Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 Station 4 Fixed costs per server 55 95 30 35 Operating costs* per server 10 15 9 10 *) Operating costs only apply when the server is busy. d. Determine the number of operators you need in each workplace to minimize the cost of this manufacturing system. 6. Consider a manufacturing network with 4 processing stations. Each of the stations can be modeled as a system (MMC) (FCFS|00|00). Jobs to be processed arrive at the network only through stations 2 and 4 according to Poisson processes with rates of 15 jobs/hour and 25 jobs/hr, respectively. Once a job is processed at Station i, it goes to Station j with probability R[i,j]; these probabilities are listed in the following table R(i,j) = j=0: Job leaves j=1 j=2 j=3 the network j=4 Pr{job goes from i to j} i = 1 0.3 0 0.6 0.1 i = 2 0.4 0.6 i = 3 1 0 0 0 i = 4 0.1 0.5 0.4 0 This table must be interpreted as follows, of all the jobs that are processed, say, at Station 4 (i = 4), 10% leave the network, 50% go to Station 2 and 40% go to Station 3. The other rows are interpreted similarly. a. Find the number of jobs/hours that are processed at each of the manufacturing stations. 0 0 0 0 0 b. Complete the following table for each of the workstations in the manufacturing network: Station u Lq Wq W L 1 2 35 2 1 60 3 4 16 4 3 18 c. Assume that the cost of a job remaining in the manufacturing network is $25/hr and the hourly costs associated with each of the work centers are as given in the table below. Compute the total cost per hour associated with this manufacturing network. Cost ($/hr) Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 Station 4 Fixed costs per server 55 95 30 35 Operating costs* per server 10 15 9 10 *) Operating costs only apply when the server is busy. d. Determine the number of operators you need in each workplace to minimize the cost of this manufacturing systemStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


