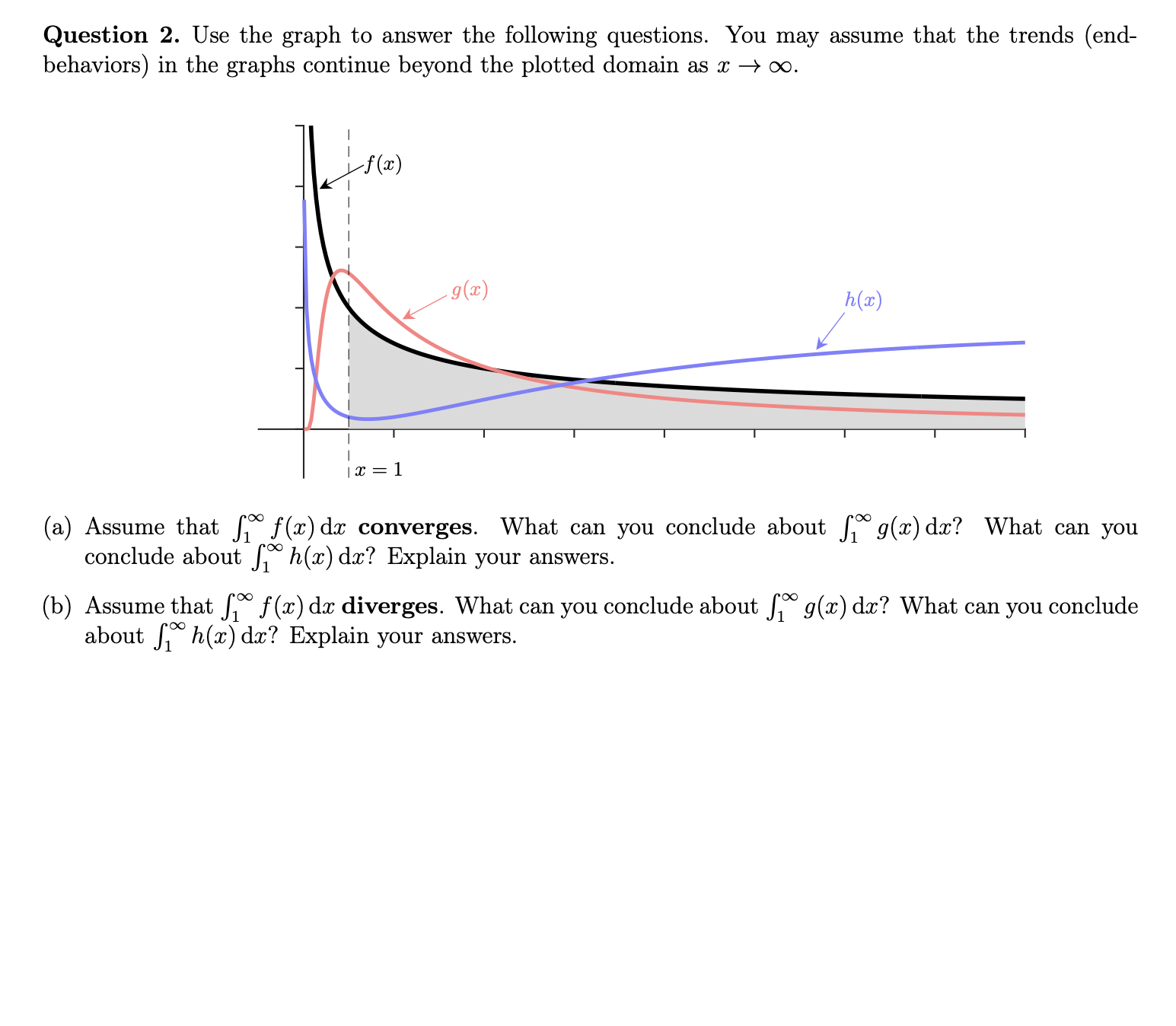
Question: I need help Question 1. Use the integral comparison test to determine if the integral oo -22 / sm(7r:1:)d$ 1 333/2 converges or diverges. Hint:
I need help




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


