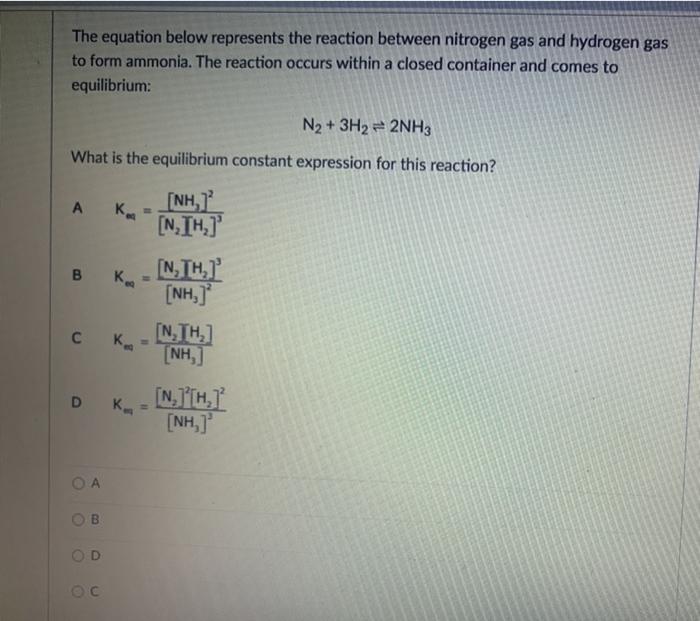
Question: i need help The equation below represents the reaction between nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas to form ammonia. The reaction occurs within a closed container

![[NIH] , K [NH, [NTH) K [NH, D K. [N] [HI [NH,](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f93c9f9dfa8_01566f93c9f3e885.jpg)
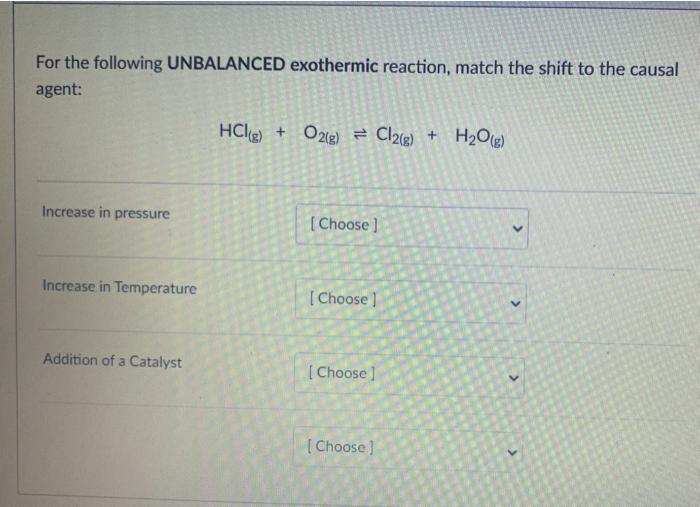
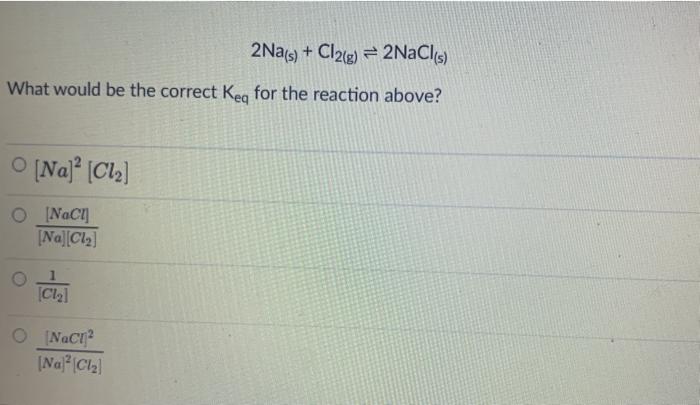
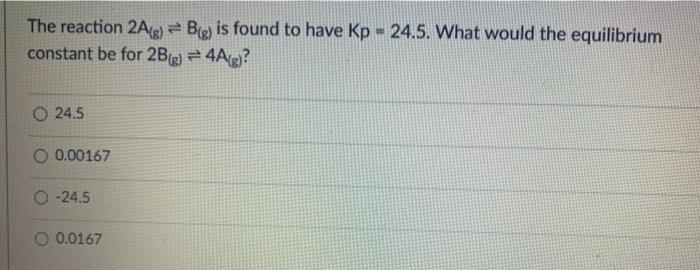
The equation below represents the reaction between nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas to form ammonia. The reaction occurs within a closed container and comes to equilibrium: N2 + 3H2 + 2NH3 What is the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction? A B [NH, Ka [NIH] , K [NH, [NTH) K [NH, D K. [N] [HI [NH, B D N2(g) + 3H2(g) = 2NH3(g) Calculate the Keg for the reaction if at equilibrium, the reaction above contains the following concentrations: ammonia = 1.866 M nitrogen = 1.066 M hydrogen = 3.200 M 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) = 2NaCl(s) What would be the correct Key for the reaction above? O [Na] [C12] 0 [NCI] [Na][Cl] Clal (NaCI (NaCl2 The reaction 2A(g) = B(e) is found to have Kp - 24.5. What would the equilibrium constant be for 2B(g) = 4A(g)? 0 24.5 0.00167 0 -24.5 O 0.0167 CO2(g) + 3FeO3) = Fe3O4(s) + CO2) If the volume of the above reaction at equilibrium was increased, what would be the change in equilibrium? O shift to reactants - increasing volume increases direction of more moles O shift to reactants - increasing volume increases direction of less moles O no shift in equilibrium O shift to products - increasing volume increases direction of loss moles O shift to products - increasing volume increases direction of more moles For the following UNBALANCED exothermic reaction, match the shift to the causal agent: HCLg) + O2(g) = O2(g) + Cl2(g) + H2O(g) Increase in pressure [Choose ] > Increase in Temperature [ Choose ] Addition of a Catalyst [ Choose [Choose]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


