Question: I need help with the attached assignment. I attached the question and completed assigment. I just need help with answering one more question which is
I need help with the attached assignment. I attached the question and completed assigment. I just need help with answering one more question which is which is:
Discuss a strategy that you would use to communicate the status of the project to stakeholders?




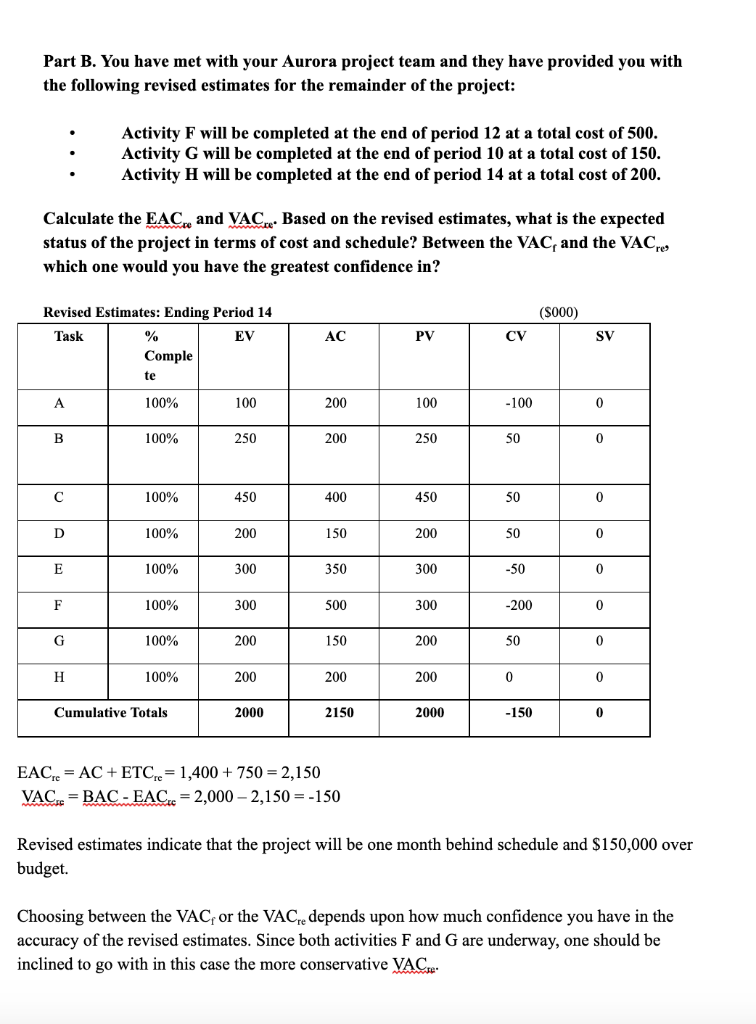
Project Monitoring and Control Assignment Complete the following items for this assignment: 1. Read through the Case 13.1 Tree Trimming Project Case in Larson and Gray. Respond to Questions 1 and 2 of the case. Use Microsoft Excel to complete this item and include all calculations in your Excel file. Note that showing all calculations in Excel is required. 2. Complete Appendix Exercise 2 at end of Chapter 13 in Larson and Gray. Specifically, complete the table on pp. 509-510 in the textbook (note that SPI and CPI can be determined after the table is completed). Assume that cumulative EV, PV, CV, SV, SPI and CPI values are needed. Also, complete the table at the top of p. 511. At the end of Period 5, what is the status of this project (be specific)? 3. Discuss a strategy that you would use to communicate the status of the project to stakeholders. 4. Use Microsoft Excel to complete this item and include all calculations in your Excel file. Note that showing all calculations in Excel is quired. Submit your Microsoft Excel file. Ensure that items 1 and 2 above are in the same Excel file but on different Sheets within the file. While APA style is not required for the body of this assignment, solid academic writing is expected, and in-text citations and references should be presented using APA documentation guidelines, which can be found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center. This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion. You are not required to submit this assignment to Lopeswrite. Tree Trimming Project Wil Fence is a large timber and Christmas tree farmer who is attending a project management class in the spring, his off season. When the class topic came to earned value, he was perplexed. Isn't he using EV? Each summer Wil hires crews to shear fields of Christmas trees for the coming Holiday season. Shearing entails having a worker use a large machete to shear the branches of the tree into a nice, cone-shaped tree. Wil describes his business as follows: A. I count the number of Douglas Fir Christmas trees in the field (24,000). B. Next, I agree on a contract lump sum for shearing with a crew boss for the whole field ($30,000). C. When partial payment for work completed arrives (5 days later), I count or estimate the actual number sheared (6,000 trees). I take the actual as a percent of the total to be sheared, multiply the percent complete by total contract amount for the partial payment [(6,000/$30,000 = 25%), (.25 $30,000 = $7500)]. 1. Is Wil over, on, or below cost and schedule? Is Wil using earned value? 2. How can Wil set up a scheduling variance? 1. Is Wil over, on, or below cost and schedule? Is Wil using earned value? Wil is applying the percent complete to the number of trees sheared (a version of CPIB). His system is always on cost and on schedule. His system does not allow him to really compute cost or schedule variance midway in the project. 2. How can Wil set up a scheduling variance? Earned value requires planned values (PV) of sheared by cost or trees (PV) to be setup on a timeline. This is the major difference from straight accounting or percent complete math. The number of trees or dollars planned must be assigned to time periods over the life cycle of the project. An estimate of percent complete is needed in terms or trees or money. (Refer to pp. 273-274, Why A Time-Phased Budget Baseline is Needed.") In this project the most practical way to setup a schedule variance is to use trees in place of money. Later, tree numbers can be converted to money (dollars). An example is described below. Example Wil's system with added planned value (PV) information needed to compute earned value. Wil counts 24,000 trees in a field. He traditionally to pays $1.25 per tree to shear Douglas Fir trees and assumes a single shearer can shear about 100 trees per eight hour shift. He contracts with a crew of ten to shear the complete field for $30,000. Project through Day 5. (Payday) On Friday evening, after five days of work, Wil estimates 6,000 trees have been sheared. He divides (6,000/24,000 = 25% complete) (.25 x $30,000) = partial payment of $7,500 paid to crew. Computing Variances The numbers suggest the following planned values baseline for trees. (Note: this is a good example to demonstrate that earned value is not limited to using dollars.) Trees Baseline: Planned Value (PV) 1,000 1,000 1,000 1,000 1,000 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 0 1 2 3 4 5 Earned Value Using Trees Wil has estimated that 6,000 trees have been sheared after 5 workdays. This number suggests 1,000 more trees sheared than expected through period five. Percent complete at the end of period 5 is 6,000/5,000 = 1.20 or 120 percent of expected. Cost (tree) Variance: CV = EV AC EV = percent complete x planned value = 1.20% x 5,000 = 6,000 trees sheared CV = 6,000 6,000 actual = 0 (for trees) Schedule (tree) Variance: SV = EV - PV EV = 1.20% x 5,000 = 6,000 trees SV = 6,000 5,000 = +1,000 trees. You are ahead of schedule by 1,000 trees. Earned Value Using Money Wil has estimated that 6,000 trees have actually been sheared after 5 workdays. This number suggests 1,000 more trees sheared than expected through period five. Percent complete at the end of period 5 is 6,000/5,000 = 1.20 or 120%. Computations using the traditional money budget approach: Planned Baseline: Budget Values (PV) $1,250 $1,250 $1,250 $1,250 $1,250 $1,250 $2,500 $3,750 $5,000 $6,250 0 2 3 4 5 Cost Variance: CV = EV AC EV = 1.20% x $6,250 = $7,500 CV = $7,500 $7,500 actual = 0 (on cost) Schedule Variance: SV = EV - PV EV = 1.20% x $6,250 = $7,500 SV = $7,500 $6250 = +$1,250 (ahead of schedule) (Note: $1,250 repreent the value of schedule variance of 1,000 trees above) Part B. You have met with your Aurora project team and they have provided you with the following revised estimates for the remainder of the project: Activity F will be completed at the end of period 12 at a total cost of 500. Activity G will be completed at the end of period 10 at a total cost of 150. Activity H will be completed at the end of period 14 at a total cost of 200. Calculate the EAC and VACre. Based on the revised estimates, what is the expected status of the project in terms of cost and schedule? Between the VAC and the VAC which one would you have the greatest confidence in? (5000) AC PV CV Revised Estimates: Ending Period 14 Task % EV Comple te SV 100% 100 200 100 -100 0 B 100% 250 200 250 50 0 100% 450 400 450 50 0 D 100% 200 150 200 50 0 E 100% 300 350 300 -50 0 F 100% 300 500 300 -200 0 G 100% 200 150 200 50 0 H 100% 200 200 200 0 Cumulative Totals 2000 2150 2000 -150 0 EACE = AC + ETCe = 1,400 + 750 = 2,150 VAC = BAC - EAC = 2,000 - 2,150 = -150 Revised estimates indicate that the project will be one month behind schedule and $150,000 over budget. Choosing between the VAC or the VACre depends upon how much confidence you have in the accuracy of the revised estimates. Since both activities F and G are underway, one should be inclined to go with in this case the more conservative VAC








