Question: I used a Binary Search Tree for my Card class. I need help defining the PlayerHand class. Here is my card class code: class Card:
I used a Binary Search Tree for my Card class. I need help defining the PlayerHand class. Here is my card class code:
class Card: suits = ["C", 'D', 'H', 'S'] ranks = ['A', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '10', 'J', 'Q', 'K'] def __init__(self, suit, rank): self.left = None self.right = None self.parent = None self.count = 1 if suit.upper() in Card.suits: self.suit = suit.upper() else: self.suit = 'C' if rank.upper() in Card.ranks: self.rank = rank.upper() else: self.rank = 'A' def setSuit(self, suit): if suit.upper() in Card.suits: self.suit = suit.upper() def getSuit(self): return self.suit def setRank(self,rank): if rank.upper() in Card.ranks: self.rank = rank.upper() def getRank(self): return self.rank def setCount(self, count): self.count = count def getCount(self): return self.count def setParent(self, parent): self.parent = parent def getParent(self): return self.parent def setLeft(self, left): if self.left == None: self.left = Card(left) else: t = Card(left) t.left = self.left self.left = t def getLeft(self): return self.left def setRight(self, right): if self.right == None: self.right = Card(right) else: t = Card(right) t.right = self.right self.right = t def getRight(self): return self.right def __str__(self): return "%s %s | %d"%(self.suit, self.rank, self.count) def __lt__(self, other): rank1_idx = Card.ranks.index(self.rank) rank2_idx = Card.ranks.index(other.rank) if rank1_idx > rank2_idx: return True elif rank1_idx > rank2_idx: return False else: suit_idx1 = Card.suits.index(self.suit) suit_idx2 = Card.suits.index(other.suit) return (suit_idx1 rank2_idx: return True elif rank1_idx suit_idx2) def __eq__(self, other): return self.rank == other.rank and self.suit == other.suit 
 Here is the PlayerHand instructions:
Here is the PlayerHand instructions:
- PlayerHand.py - Defines a PlayerHand (BST) class that is an ordered collection of a Players Cards. You can adapt the BST implementation shown in the textbook supporting the specifications in this lab
![Card: suits = ["C", 'D', 'H', 'S'] ranks = ['A', '2', '3',](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f08666dd81e_07866f0866646a32.jpg)
!['4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '10', 'J', 'Q', 'K'] def __init__(self,](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f08667ad787_07966f086672b061.jpg)
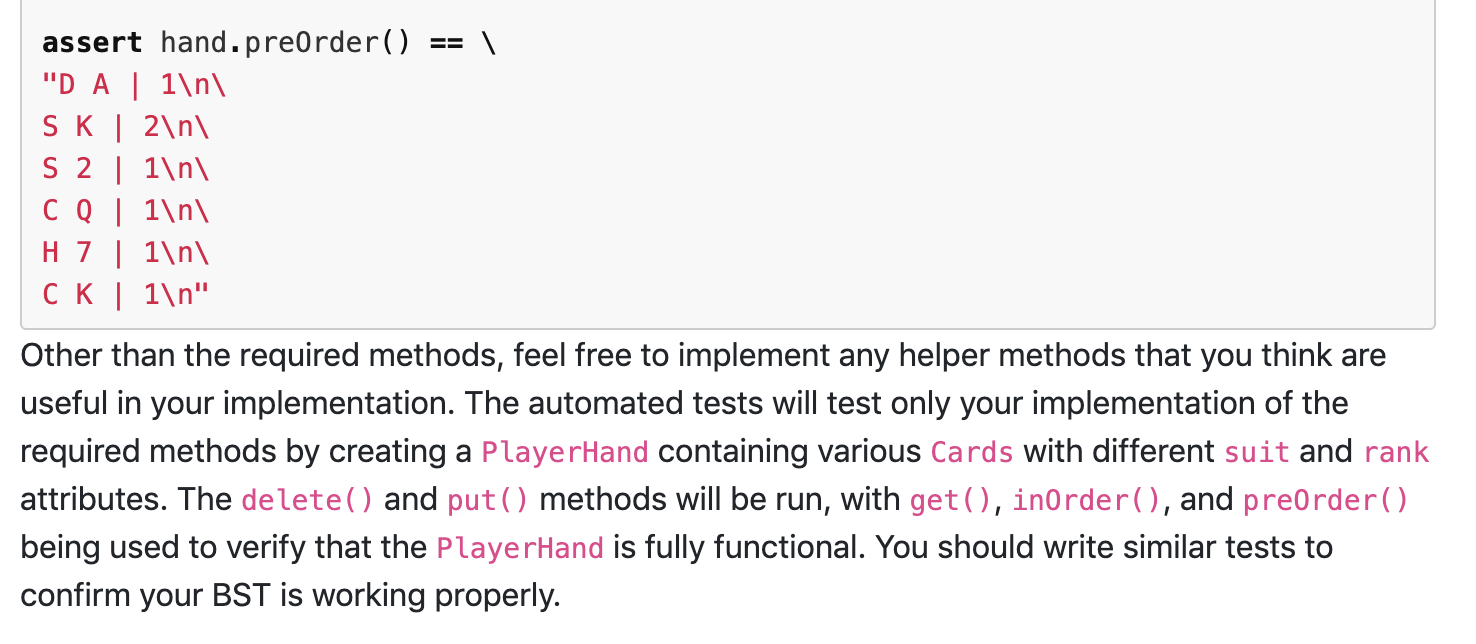
class Card: suits = ["C", 'D', 'H', 'S'] ranks = ['A', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '10', 'd', 'Q', 'K'] def __init__(self, suit, rank): self. left = None self.right = None self.parent = None self.count = 1 if suit.upper() in Card.suits: self.suit = suit.upper() else: self. suit = 'C' if rank.upper() in Card.ranks: self.rank = rank.upper() else: self.rank = 'A' def setSuit(self, suit): if suit.upper() in Card. suits: self.suit = suit.upper() def getSuit(self): return self.suit def setRank(self, rank): if rank.upper() in Card.ranks: self.rank = rank.upper() def getRank(self): return self.rank def setCount(self, count): self.count = count def getCount(self): return self.count def setParent(self, parent): self.parent = parent def getParent(self): return self.parent def setLeft(self, left): if self. left == None: self.left = Card(left) else: t = Card(left) t.left = self.left self.left = t def getLeft(self): return self. left def setRight(self, right): if self.right == None: self.right = Card(right) else: t = Card(right) t.right = self.right self.right = t = def getRight(self): return self.right def -_str__(self): return "%s %s | %d"%(self.suit, self.rank, self.count) def __it__(self, other): rank1_idx = Card.ranks.index(self.rank) rank2_idx = Card.ranks.index(other.rank) if rank1_idx > rank2_idx: return True elif rank1_idx > rank2_idx: return false else: suit_idx1 Card.suits.index(self.suit) suit_idx2 = Card.suits.index(other.suit) return (suit_idx1 rank2_idx: return True elif rank1_idx suit_idx2) def --eq__(self, other): return self.rank == other.rank and self.suit other. suit = == Player Hand.py The PlayerHand.py file will contain the definition of a PlayerHand class. This will keep track of the cards a player has in their hand, implemented as a BST. The PlayerHand will manage Card objects based on their suit and rank. _init__(self) - the constructor for the PlayerHand will simply initialize the empty BST. In addition to the construction of the BST in this class, the following methods are required to be implemented: . . getTotalCards (self) - returns the total number of cards in hand getMin(self) - returns the card with the lowest value from the player's hand. Returns None if there is no card in the hand getSuccessor(self, suit, rank) - attempts to finds the Card with the suit and rank, and returns the card with the next greatest value Returns None if there is no card with the specified suit and rank, or if the Card is the maximum and has no successor put(self, suit, rank) - this adds a card with the specified suit and rank to the BST. If that Card already exists in the BST, increment the count for that Card delete(self, suit, rank) - attempts to find the Card with the specified suit and rank, and decrements the Card count. If the count is o after decrementing the count, remove the node from the BST entirely. Returns True if the Card was successfully removed or decremented, and False if the card is not present in the BST isEmpty(self) - returns True if there are no cards in the BST and returns False otherwise get(self, suit, rank) - attempts to find the Card with the specified suit and rank, and returns the Card object if it exists. Otherwise, return None inOrder(self) - returns a string with the in-order traversal of the BST. Printing the in-order traversal should help check that the cards are in the correct order in the tree preorder(self) - returns a string with the pre-order traversal of the BST. BSTs with the same structure should always have the same pre-order traversal, so this can be used to preorder(self) - returns a string with the pre-order traversal of the BST. BSTs with the same structure should always have the same pre-order traversal, so this can be used to verify that everything was inserted correctly An example of the inOrder() string format is given below: hand = PlayerHand() hand.put('D', 'A') hand.put('s', 'K') hand.put('s', '2') hand.put('C', 'Q') hand.put('H', '7') hand.put('s', 'K') hand.put('C', 'K') assert hand.inOrder() == "DA 1 \ S2 1 \ H7 | 1 \ 0 0 | 1 \ CK 1 \ SK 2 " An example of the preorder() string format is given below: hand = PlayerHand() hand.put('D', 'A') hand.put('s', 'K') hand.put('s', '2') hand.put('C', 'Q') hand.put('H', '7') hand.put('s', 'K') hand.put('C', 'K') assert hand.preorder() == "D A | 1 \ SK | 2 \ S2 | 1 \ Co | 1 \ H7 | 1 \ CK | 1 " Other than the required methods, feel free to implement any helper methods that you think are useful in your implementation. The automated tests will test only your implementation of the required methods by creating a PlayerHand containing various Cards with different suit and rank attributes. The delete() and put() methods will be run, with get(), inOrder(), and preorder() being used to verify that the PlayerHand is fully functional. You should write similar tests to confirm your BST is working properly. class Card: suits = ["C", 'D', 'H', 'S'] ranks = ['A', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '10', 'd', 'Q', 'K'] def __init__(self, suit, rank): self. left = None self.right = None self.parent = None self.count = 1 if suit.upper() in Card.suits: self.suit = suit.upper() else: self. suit = 'C' if rank.upper() in Card.ranks: self.rank = rank.upper() else: self.rank = 'A' def setSuit(self, suit): if suit.upper() in Card. suits: self.suit = suit.upper() def getSuit(self): return self.suit def setRank(self, rank): if rank.upper() in Card.ranks: self.rank = rank.upper() def getRank(self): return self.rank def setCount(self, count): self.count = count def getCount(self): return self.count def setParent(self, parent): self.parent = parent def getParent(self): return self.parent def setLeft(self, left): if self. left == None: self.left = Card(left) else: t = Card(left) t.left = self.left self.left = t def getLeft(self): return self. left def setRight(self, right): if self.right == None: self.right = Card(right) else: t = Card(right) t.right = self.right self.right = t = def getRight(self): return self.right def -_str__(self): return "%s %s | %d"%(self.suit, self.rank, self.count) def __it__(self, other): rank1_idx = Card.ranks.index(self.rank) rank2_idx = Card.ranks.index(other.rank) if rank1_idx > rank2_idx: return True elif rank1_idx > rank2_idx: return false else: suit_idx1 Card.suits.index(self.suit) suit_idx2 = Card.suits.index(other.suit) return (suit_idx1 rank2_idx: return True elif rank1_idx suit_idx2) def --eq__(self, other): return self.rank == other.rank and self.suit other. suit = == Player Hand.py The PlayerHand.py file will contain the definition of a PlayerHand class. This will keep track of the cards a player has in their hand, implemented as a BST. The PlayerHand will manage Card objects based on their suit and rank. _init__(self) - the constructor for the PlayerHand will simply initialize the empty BST. In addition to the construction of the BST in this class, the following methods are required to be implemented: . . getTotalCards (self) - returns the total number of cards in hand getMin(self) - returns the card with the lowest value from the player's hand. Returns None if there is no card in the hand getSuccessor(self, suit, rank) - attempts to finds the Card with the suit and rank, and returns the card with the next greatest value Returns None if there is no card with the specified suit and rank, or if the Card is the maximum and has no successor put(self, suit, rank) - this adds a card with the specified suit and rank to the BST. If that Card already exists in the BST, increment the count for that Card delete(self, suit, rank) - attempts to find the Card with the specified suit and rank, and decrements the Card count. If the count is o after decrementing the count, remove the node from the BST entirely. Returns True if the Card was successfully removed or decremented, and False if the card is not present in the BST isEmpty(self) - returns True if there are no cards in the BST and returns False otherwise get(self, suit, rank) - attempts to find the Card with the specified suit and rank, and returns the Card object if it exists. Otherwise, return None inOrder(self) - returns a string with the in-order traversal of the BST. Printing the in-order traversal should help check that the cards are in the correct order in the tree preorder(self) - returns a string with the pre-order traversal of the BST. BSTs with the same structure should always have the same pre-order traversal, so this can be used to preorder(self) - returns a string with the pre-order traversal of the BST. BSTs with the same structure should always have the same pre-order traversal, so this can be used to verify that everything was inserted correctly An example of the inOrder() string format is given below: hand = PlayerHand() hand.put('D', 'A') hand.put('s', 'K') hand.put('s', '2') hand.put('C', 'Q') hand.put('H', '7') hand.put('s', 'K') hand.put('C', 'K') assert hand.inOrder() == "DA 1 \ S2 1 \ H7 | 1 \ 0 0 | 1 \ CK 1 \ SK 2 " An example of the preorder() string format is given below: hand = PlayerHand() hand.put('D', 'A') hand.put('s', 'K') hand.put('s', '2') hand.put('C', 'Q') hand.put('H', '7') hand.put('s', 'K') hand.put('C', 'K') assert hand.preorder() == "D A | 1 \ SK | 2 \ S2 | 1 \ Co | 1 \ H7 | 1 \ CK | 1 " Other than the required methods, feel free to implement any helper methods that you think are useful in your implementation. The automated tests will test only your implementation of the required methods by creating a PlayerHand containing various Cards with different suit and rank attributes. The delete() and put() methods will be run, with get(), inOrder(), and preorder() being used to verify that the PlayerHand is fully functional. You should write similar tests to confirm your BST is working properly
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


