Question: idd I need SOWT analysis for Target corp with recomndation for future strategy CASE ana a Nassive Data Breach Alan N. Hotiman Bentey Ciniveraty and
 idd
idd






 I need SOWT analysis for Target corp with recomndation for future strategy
I need SOWT analysis for Target corp with recomndation for future strategy
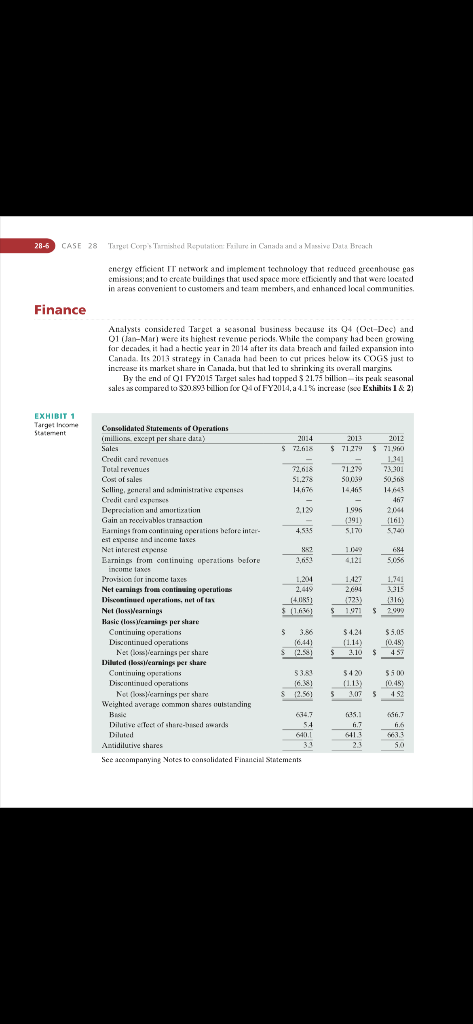
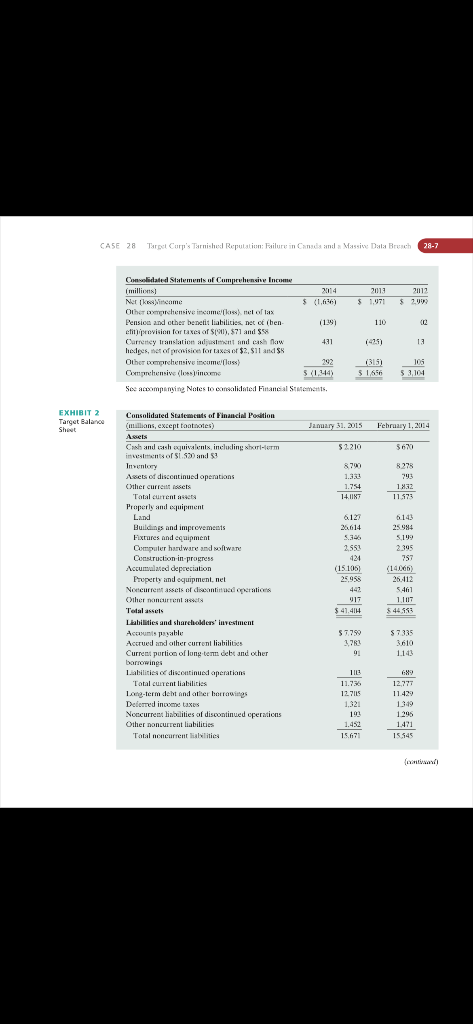
CASE ana a Nassive Data Breach Alan N. Hotiman Bentey Ciniveraty and Natalia Gold Northewsern Liniversiry Company Background Target Corporation's vision was to offer sastocners exeryday cssentials and Cashionable, differestiated merchandise at discount prices, includine apparel and acces50ries, home dcor and fumiture, electronics, office supplies, toys, health and henuty products, fond, pet supplies, and pharmacy products and services " Traditionally, Target sald its own brands as well as specialixed merchandise through periodic exclusive design and creative partnerships. The company alss generated revenue Irom in-slore amenties such as Targel Pholo, and leased or licensedi departnunts. such as Targe! Optical and Slarbucks. Fur the fiscal year entng January 31, 2015, the company geterated orer $72.6 bylion in anual fevenue trom continuine operations at its 1,794 stores spread acmass all 50 states in the United States, a figure that represented an increase of $134 bill oo or 1.9\% over the previous fiseal year's revenueDedzkia, Tejawini Raco, Sounya Shetry and Laderg Therisuit tor their resespeth ard ocnitieutions to this 175 Funca Sinsi, Waliham, X1A [C4 oc Di. Nlan N. Hofinan. asking shopeets if they were interested in partikipating in Taget's REDeatd program. In a bid to reseue its image and its business, Target announced plans to iavest $5 million in nea security measures and offered custoners a free year of eredit monitoring and jdentity' theft protection. W'hile Target's management thid not expect the incident to have a long-term impact on the compiny 's relationahip with its custumers, the breach nevertheless had a negative impati on Target's reputation andi sales. In March 2015 . Target agreet to a 510 million dollar settlement with the victims of the data breach, aho stood 10 tolloct up to $10,000 cach in damages. The Disastrous Canadian Expansion (2011-2014) Target also met with disastrous results in its expansion into the Canadian market. In 2011. Target accuired 133Z Zllers sales acrues Canada that it reopened as Target stores in 2013. However, the stores tailed to meet demand due to inventory 50 ofware constraints and other expansion issues. A mnjor reison for the operational failure was the company's entering into the Canadian market by purchasing all the stores of a failed retailer. a move that seemed prudent but actually saddled the Canadian unit with inconveniently lecated stares that weren't built for Target's well-knona layout. Opening so many stores at once in a brand new market strained the company's legisties intrastruxture and left Canadians staring at cenpty shelses At the same time. this incresse in operational scale mate it diftede fot the company to sale dewn during times of slowing sales. Target's najor operational tailare in Canada rurned out to be a huge loss tor the sotmpany Aftet cateful fevicw of all options, the company was unable to find a realistic scenario that coukd get Target Canada to profitahility hefore 2021 and decisod instead to close al] 139 of ts Canadian stores in January 2015.4 Strategic Direction 'Target's brand promise, "Expect More. Pay Less" succinetly expressed its masiou to hecome customers' preferred shopping destination by offering high quality affordable products and services, continuous innosation, and exceptional customer experiences to satisfy custamer needs, simplify their lives, and leeliver outstanding value. To do so in the face of stiff competition, Target differentiated itself by combining the better quality Gashion aspect of a ligher-end retailer with the low prices of a discouat slore. It also atfered price matching and an additional 5 is savings when customers ased its RElkard loralty program as part of its commitbent to making sure customers got "note for theif money" ewery time they shopped. To further distinguish itself, Target prioritioed innovative design, positive employeri employee relations for positive employee attitubes, diversity, and strong communily relations through coenmunity giving. Its slore layouls acre designed to create a fun, energetie, and inviting atmosphere to engage shoppers and its employees were encouraged to see themselves as "1eant members" to cnbance customet experience by providing friendly and efficient service, In addition, the company strove to foster an inclusise cultare, liring a diserse aboktonee snd making sure everyooe felt welcome. alued, and respected. Tenm membets were supported with training and development apportunities, and encouraged to innovate, contrihute idens, and discover salutions to improwe customer experience. Diversity was viewed as intrinsic to every aspect af Tar get's business, from team anembership, to those in its stapply chain, to the eommunities in waich the oompany operaled, importan! [or developing lasling relationships and leveragitig partnes' talents to drise innovation and suecess Finally, community giving a'fo CASE 28 Targel Cop e Trmished Repalation: Fallune in Canada and a Mnsive Dala Broach taudamental to the company ethos: Targer regalarly pledged 5% of st ibcome to lecal groups and encouraged enployees to doaate theit time, talent, and busaness srecengths. to various community initiatives." At a recent investors meting, Target Chairman and CEO Brian Cornell and his leadership team presented the vision and strategies they hoped would transform Target 's cormpetitive sdge in the near future with renewed emphasis on anawation and putling tustamers first. They planned to increase focus oa the company's amni channel evolution; fut ther deweloge merchandise sategories that would ditwerentiale'Target frota its cetapetitors: taikor a mare personal appronch for individual customers; and implement more flexible store formats such as 'lagetexpress and City Target, A thoreugh strategie analysis of the business revealed that customers who shopped hoth in Target stores and on Target's website generated three times as many sales as those who shopoed only in the srores. . n response, the company becided to take a channel aeutral spproach to growing its business, Uriving a tolal Target experietse atruss stotes, oaline, and on tadaile platforms Houever, 'Taget's perhaps appropriarely ageressive sales objections-to groa in-store sales lyy 2 to Dampany's technology, supply chain, and imentroy manngement systeme. In 2014, four merchandise categories (style, baby, kids, and wellness) accounted for mose than 25% of Target's sales. Moving forward. Thrget planned to invest more resources in those key areas, focusing on newness and dilferentiation for greater consumer value. Another corporate objeclive was to create a more customercentric experience by asing detaographics, dimate, loestion, and othet shistemer-led tactors to drive store and online purchasing, and build up its data analytics to deliver a more personalized digital experience ly tailoring promotional offerings to specific customers, The company also planned store expansimas that woald focus on new, more flexible famnats to cater to rapidly growing dense urban populations, testing new layouts to ensare that each store opened was the right fit for each community. Target hoped to realine cost savings of 32 billioa over the Two yeats 20152016 by establishing leanet operations to make the oxmpany more agile. even while planning to invest $1 billion in tochnology and sapply chain improvements in 2015 , get's Competitors Target's prime competitses in the dixcount retail chain market acre Wal-Mart Stores Its., Cosreo Wholesale Corporation, Sears Holdings, and. Amsoonsom.'The company's. competitors in related indestries such as electronics, grocery; drug, lepartmen1. and home furnishings stores aere Macy's, Burlington Stores, Willard's Inc, Dollar General Comooration, Dollar Tree Ine. Family Dollar Stores, IC Penneg; and Kahl's. As of 20 15, Target was the second largest discount store chain in the Wnited States, with a market share of about 2.5% in the rutail category. l-Mart Inc. In the fiscal year 2014 Wal-Mart, a top conperitor in the discount stores segment, genterated revenue of $485.65B. Prior to 2014 , Wal- Mart had seen its revenues rise hy 16% while Target's revenues anly inerensed by 12,9%. Like Target, Wal-Mart maintained a regutation for convenjence, value for money; and offering a ajde range of products all in ode stere. Its core competentivs in anlormaLive systems and eds1 deadership strategy were used very efectively to identafy belter weys to pertotem tasks, manage stores, and sroek the shelwes, Its size allowed Wat-Mant 10 exereise poner it relacion to suppliers by denanding lowet priess; fand its best praetices allowed it the tlexibility to improvise its inventory atd sapply chait management ahenever nexessary, Wal-Mart's international success and Target's failure in Canada posed a huge threat to Target's future operations. Amazon Inc. Tatger azs slow to provide customers with a satisfying oaline retail shopaing erpetienec: Amazon, its biggest cotapetitot in that tealm. teported revenues of $88.50B, constanty edging our Wal-Wart and Target in online sales for a variery of producrs (though it whe necessary for shoppers te keep close talos ton Amaxon's fluctuating prices). Amaxan had had the foresight to huild its fulfillment centers near aiports which proved a highly suceessiul stralegy for providing expediled shipping. While Amazoa's major weaknesx jts lack of protit on its tnancia] statements, taised soncerns for its ityestors. jts stellaf record of innovation and reshaping the consumer experience on line assared its number ane place in online retailing Barriers to Entry/lmitation Tistorically, three major harriers to entry into the discounted retail segment indesitycurstomer captivity, proprietary lechnology, and econcanies of stale-lamped donn conperition a the conpanies already oceopying this segment had daunting conperitike advastages it these sategorive. Fot example, Amazon and Wal-Matt were ahead in deploying technology for iwventory management and supply chain: Target had the advantage of providing customers with relatively highr-quality producr at low priees. Ihe companies in this segment are huge, yet their operating marpins were low. A company could enter this market only if it sould wumpets wilh the prices that were offered by: these retail giants, which would require massive capital investment and access to prime Jecalions. Target bad stronget product quality than its main oumpetitors, and exclusive partnerships with designers. Its ditferentiation strategy of ofterine designet brands owned hrands, and signature national hrands had proved very suceessful. Twenty percent of the hrands sold in Target Stores were prisate; and 22 of those brands were sald exclusively at Target. For example, Target parinered with Peter Plootto for appareh, Chris March for Halloween wigs, and Justin 'Timburlake for his special edition CD. 'Targel's inage. compared to Lhat of Amazon and Wal-mart, was that ol an upscale discount relailer. 'Target's streag casromef setwice componeat also distangaished it. Fot example, 43% of Target's customers wete parents with children, tbus Target designed its new shopping carts with huilt in haby seats for custemer convenience. Target also gained substantial PR frum its huge number of f ullyeers on Instagram and YouTube. Sustainability In recent years, critics, investors, and customers have bocome increasingly concermed aith all companies' angoing environmental sustainability efforts. Wal-Mart took the lead in this important area. Rising demand for organie and aco-friendly products required conpanies to abide by lavs regulating sastainability, follow sustainable practiecs, and snsure their suppliors foldowed onvironmwntally friendly practices. Targel made comemitmests to ersure its packaging inchuded ferycled and tenewable coorent; to lyaid an energy efficient IT' netaotk and implement technology that redueed greenhouse gas emissiots; and to create buildings that uscd space moce etbeiently and that were located in areas convenient to customers and team members, and enhanced local commanities. Analysts considered Target a seasonal business because its Q4 (Oct-Dec) and Q1 (Jan-Mar) were its highest revenue periods, While the compang had been growing for decades, it had a hectic year in 2014 after its data breach and failed expansion into Canada. Irs 2D13 strategy in Canada had heen to cat prices helow its COGS just to increase its market share in Canada. hut that led to shrinking its werall margins By the end of Q [ Fr2015 Target sales had tapped 321.75 billion-its peak seasonal See aceampanying Notes to cansalidated Finatcinl Statements CA5E 28 Target Curp's Tarnished Repuistien: Failure in Canuela and n Massive Data Breach Sec acoompanging Nutes to earvalidated Financial Stanements. Jonary 31, 2015 or Fetraary 1, 2014. even as pressure Lrom tbe matsel for low priees during peak seasons had forced Target to cat its priess, Annual growth from FY2014 to FY2D15 wa5 11% \%. Its net operating margin incrme margins fell to 1.34% in 02FY2D15, ompared to 42% in O2FY2013. However, the company predicted margins would recover after it shut down its Canadian srores, and the day Target annoxanced the termination of its Canadian aperations its stock price rose 37% Grom $50 bo $82. In fiseal zI14, Target Corporation spent \$1.7 billion on advertising, $.3 billion more than the $1,4 billion spent in tiscal 2013 , Neaspaper circulars, Internet ads, and broadcast media made up the majority of the company's advertising costs. Target aas facing increasesi donawar pressure on prices from online retailers, particularly Amanon, and also had to adapt to the "shorsmoming" that occurred when customers boruwsed items in Tatget stores thea used their smartphenes to clwek prices and buy from cheapet oaline sites. 'To shy competitive, Target decided to makch Amazon's prives and offered tree wi-Hi in it 5 stoves in-store pickup of oaline orders and in-stare eoceterges offering tip recammendations, and other enhanced customer services. Target further committed to improving its own online customer expenence, launching a pilot program. Target Subsciptions, and eslablishing an innovation center in San Francisco to foster online and mobile business grou'th. In its odvertising the company increasiagly emphasized the value pricing promised in its slogan, "Expect Mare, Pay Less," over its earlier emphasis on differentiation. This shiff of focus to pricing atud value sucececed in improving the eampany's competitiveaess, eabbling the eampany to tap the constantly growing marker of customers opting for lower priced merchandise. Targut's website was redesigned to include product recommendations, enhanced regis tries and lists, integrated community features, and social networking integration. Target also focused on increasing its oaline presenes through acquisitions. The key to Target's success was its strategy of positioning itself as a high style brand despite its low pricxs to atiract shoppers who would otthinanly asoid discount retailerx It did this with clever, eye-eatehing marketing and a series of partoerships with high-profile design-ofiented suppliers. Targer Corp pronided an ercelleat example ot a couteut-based strategy with "A. Aulleye View." Revamped and re-launched, its wehsite told "a deeper CA5E 28 Target Curp's Tarnishud Ropulatien: Failure in Canula and n Massive Dala Breach ba-9 stoty" about "Targer to nedia nembers and other infiueneers, siguiticant in terms of anlite marketing ss many brands were ealy just beginting to focas oa oonteat, where:s Target was ahead of the curve in presenting its a dience with innovative content. With celebrity assets such as Jay Leno. Solange Knowles, and Maria Sharapova, Target's Inter net marketing sarntegy generated about 40 million-plus uniue monthly visitars and its website betame the fourth nost-visited retail uebsite in the United Statex. Target also applied an integrated design phikasophy to everything from visually appealing building exteriors and an award-winning mobile ape, to inothatise lools and systems such that all aspecrs of the Target interface cohered to create a satisfying castomer experienec The lafget mobile app was very sucesstul in atfering persoual, essy. and convenient optiona for customers to shop ahenever and however they wanted. Target's marke ling 2015 campaign featured three of its solutions-focused initiationssubscriptions, store pickup, and Cartwheel, which was designed to help cestomers save lime abd modey and stay organisod-which wete highlighted in TV spots and online educational videos explaining how they worked. Also ke' for Target was its "REDeand," jts proptietary eredit and debir cand, that encouraged customer kayalty and drove sales by offering cust omers 5%s discaunt every time they used their REDxards. perations and Logistics Target hat alaays combenned great leadership and operational savvy mth cuttingedge technologies to aptimixe its supply chain network. A fter its operational failure in Canada., Target's primaty objective was to operate as a single segment throughout the Linied States. The company decided that the leadership team for each store woald inchade at least seven executive level managers eounting the Store Tean Leader ot General Manager. and ench woald be nesigned a strategic department of expertise: Soft I.ines Hard I ines, Asser Protection, Guest Services)Front End, Logistics, Human Resouroes and StoreTeam Leader. Iligh volume and SuperTarget stores would have at least noe additional Logistics' Roplenishment Executioe Team Leader, an Exccutive Operatiocrs Team Leader, and an Exccutive Food Team Leader. The tompany also turnedi its altention to its business-tebusiness sobsidiary. Target Commercial literions (TCD). which operated about a balf-docen showrocals in Illitois, Minncsota, and Wiscunsin previding oflies products and serviecs. The interior design oompany, whose clients included some of Amenca's largest pompanies. ainted to expand hy marketing its products and services to small and midsixe companies Through store level data analysis techniques. Thrget identified opportunities that were Jost ahen data aras aggregated at the chain level rather than store by stare - opportunities 1bat. the company predicted, could substantially improve its wees-its'week-out ability 10 [orocast sales, plan promotions. and optimize its supply chain. Logistic epetationa] experts, who went on to work for the Copital Lnder Advisary Groap, were hired to streamlite the early morning logistie proeess at Tafget to bele the sompany increase profitability and deliver a clean, clutter-free experience to customers every day. The success of this parinership effectively saved Target $475 mallion in expenses vwer the threu years from 2012 through 2014 . Target continued to focier its greatest sirength - its ability to do outbound logisties - which helped i1 to difterentiate from other low sust lesders by emphasixing its brand as more upstale and treadier, and to capilalize on the weaknesses ot other low cost keaders by ereating a higher scale it-store atmosphete, and more spaec: Target also realized it needed to build on relationships alrendy established with suppliers rather than abasing rhem from a price'profit standpoint simply becase they could, a strategy that wouldn't foster long-term relationships or even fit its partnership philosephy. However, it became inereasingly clear Lhal Targel neveled to beter 5 E 28 Targel Cop e Tnmided Repulation: Falun in Canada and a Mnsive Dala Broch understand its own sysrems sucl as ' TCO and POL; even its supely chain experts bad a bate time understanding bos to fix opportatities. Target sutfered a huge decline in owerall net profit growth during the financial crisis that hegan in 2008 , partly hecause its sperational sixe could not be szaled Lawn fast enough. While the thausands af Wal-Mart stores operated 24 hours a day, Target stares did not, a disadivantage in times af crisis. Logistic prowesses were the hest of Target Slore operations, and accounted for muth of the operational effectiveness of any given store. If the logistic process was hroken, the chain's entire oceetation was also broket. The leadership teams knew opetations ooud be fixed, tat that it would take increased proficiency' levels to achieve operational saecssz and respond to custouner demand more effectively. Dhe weak spot for Target was its inventory system software whose main function whs to fuel the logistics processes. The ocmpany itself seemed to recognize the sysrem's deficiencies, as it added an In-Stocks procesx The flared inventory system saftaare alko auded to employment and labor oosks, espectally as the logistics work ounter lecame the souree of the highest rate of attrition at Targer, The insentory and logistics proeesses simply did not operate the way they should have, hurting the company's overall itet profit. In short Target's scalability left it more vulnerahle to drantums in the ecanomy than Wal-Mart. Target had made it a goal to affer a wide variety of job opportunities throughout its sperations, fram its retail stores to its distribution centers and comparate affecs Oyer the 20 years priot 102015 , Tatget scaled stores to achiew levels of productivity outlined by executive level managers. Based on the eperaticnal demands of the average Target slore, 'Target determined that the appropriate mix of full-tince atd part-time employees. was a 6.337 split in favor of full-time employees. This tatio of full to part time was amone the retail industry's highest. In addition, Target implemented many important human resource policies from its hiring practices and diversity efforts, to the benefits odered exployees. Targel defoned diswroity as indisjudality inootporating dillerences of race, gender. sexual orientation. education and life experiences, and physical ability; and instituted specific recruiting etforts to hire teams characteriasd by disersiry on ail of cliese tronts. Target was always known as a repurable company and fun place to work with good benefits. yielding very high employee sztisfaction. Ms one of its most effective benefits, Target prowided educatianal opportunities for emplayees to haild on their skilk, thereby attracting a significan! number of zaung college graduates as an appesaliag stepping stone tor those just starting theit earecrs. At the same time, larget's hiring pailosopay consisted of not only hiting rocant grads bot seasoacd retail managenent tenn leaders from outside the company as well. Whereas Wal-Mart hined botls graduates and noo-graduates with equisalent managethent expetience as keaderalup persottnel for their stares, anly 10% of Target's Fxecutive Team leadership were promoted frun within without four-year college degrees, landing it amoang the bottom 15% of Fortune 500 companies shen it eame to promoting from within. Nevertheless, Target's hiring practices resulted in tonefit to the oxansumer, as the average Target Executive 'Team Leater was much more cuslomer focused than the average W'd-Mart Executive' Assistant managet. The downside of Target's large organizational structure was that it required a lot of neetings and red tape. Decisions often needed to go throagh many lnyers, and unless an employee was specifically on a sirategy team or at the director level, strategic wision was CA5E 28 Target Curp's Tarnished Repulatiun: Failure in Cansela and n Massive Dala Breach 2811 thpically not a ptimary tocus. Rising labor costs also became a major eoncern tor thode fospansible fot Target's botcoen line: the foderal minimum wage, which had femained at S5.15 per hour since 198 , increased to 55,85 per hour in 2008,56.55 per hour in 2014 , and $7.25 per hour in 2010 . with further hikes projected. and many states and municipalities had minimum wage rates even higher than $7.25 per hout in response to higher costs of living. Rising wage and healthcare cosls had the potential to hold denn profit margins. In addition, Target's failed expansion into Canada had signfecant ane-time costs. Tatgel Canada had 133 stores actoss the country and employod approximately 12600 people. To ensure fair treatment of Target Canada employees, the Target Coeporation sought the Coatt's approsal to make voluntary cash contributions of Cs7o million (approximately 11$59 million) to an Fmployee Trust that would provide Target Canada-based employess not reuired for the full wind-donn poriod a minimum af 16 areks' exampensation, inclucting wage and benefits coverage while Target Canada stores fomained open during the liquidation process This operational failure resulted in a huge financial loss for the company, e Competencies First and foremost, Target made sare its hrand was wiely recegnieed in the US. market. hy utilizing strategic placement of its logo on all merchandise, media communications, and eveats Aexording to a recen1 survey conducted by Targel. 95 \$ of Anericans recognized the' la get bullseye logo, At the same time. 'Aarger traditionally differentined itself by providing exchusiwe private brands and designef produces along with exeryday essentials at atractive prices, capitalizing on cuality products and affordable prices. The company iatruduced its first design partnership in 1999. in collaboration with the architect Michael Graves. By 2015, Target had ser $1 hillion of owned and exclusive hands. The company also formed partnerships with high-profals, design-oriented suppliers including Neiman Martus, Lally Puliteer, Burt's Beex, Massimo, Isaac Mizarhi. Liz Lange, Kashi. and many more, launching these brands and pattbetships through linted cdition lincs ar by straking the brands for a limited rime. These designer brands generally yiekded higher margins than cquivalent national brands nnd represented a significant portiou of Target's overall sales. The company further enhanded the value oxi these brands by using celehrities such as Jay Ieno, Solange Knowles and Maria Sharapova to promote them. Ultimately. Target struck an effective bulance betaven fashion and prive, and its strong productiserviou assottment bexame one of its key oompetitioe advan1ages Target had always positioned joself ax an upscale tiscount cin with a bright and attractive enviroument, know tor carrying discount designet clothes and hate decat andet the same monf as detergent and dishwashing liuid. Target thus preitioned itself to attract customers from a wide spectrum of demographics, and as the 1LS. economy exited ane of its axarst slosadowns consumers evidenced more ajllingness to spend on Target's quality and evclusive porducta. Anolher aspect wITargel's sucxess was its goal of providiag a more pleasing shopping experience than that of its contpetitors 'Target rocognized that many customers preferted wider aisles, less crowding, easjer checkouts, with pticing that remained competitive. In addition, the company provided effective on-foor assistance (such as ptice checkers, ou-floor customer service representates, ete. J, as well as sasings programs through options such as the RFDeard. Acconding to industry analysts, new REDearud holders spent 50% to 1.0% more than typital customers, and mate 810 more visits per year, evidence custemers were satisitied with the program and benefiting froult it. Target's Challenges Going Forward Expecially after the Canath debacle, it became clear that Target had challenges that had to be met. Its inwentory managetent system was incticieat and costly, leading to empry sbulves, ahich had a dired negative impact on customers and thus on brand pereeption. The flawed investory system sottware also added to enploynent and labor oasts for Target. The company saw the greatest attrition from the logistis work center. The in-stocks team process was designed to cover every shelf space and SKU in the store. The team aimed to skan every SKL during the course af a week to monitur shelved product levels so that in stack products could to he brixaght to the sales flowr from the backroom should the shelved product be low or out, and aut of stuck products could be te-ordered. However. the in-srock process essentially tuplicated the eftorts of the logisties processes. Unfortunately, tbe inwentory aystem employed by Target was prone to errors and created artificial holes in the lopistic process that the in-stock tenm aimed to fill. The logistic process was supposed to fill the shelves according to the inventory system solware that dictated what was needed on the sales floor and what should be sent directly to the tackroom when it arrived on the daily 53' trailer, but it tid not. Further, the company's inability to seale tbe inventory up or down depenting on ecocomic conditions and denand was a primary reason why Target failed in its expansion efforts in Canada. The improvements needed required not only investment in technology bat also investment in centralixed teams assigned to assess and monitor current systems and recommend changes as needed. Target's ealine presenee war another area of weakness. While the company bad made sone improvements in its website and mobile applications, it struggled to attract and retain a base of online sbeppers. As coline shopping was so presalen1, it became increasingly important that Target innovate in this area to keep its market share on a par with competitors such as Wal-Mart and Amazota. Finally Target had difficulty accurately forecasting consumer demand. From the company's earliest days as an apparel eximpany; it kept its inventory lean to poeserve prosits in in indusiry knosa for kw margins. II wever, the bownside of lean imventary was misaing eut an sales and disappointing custorers whe got to tbe store only to find emply shelves. An example of keeping the inventory tos lean undertul Target's recent parinership with Lilly Pulitact, an American fsshion brand teaturing bright, colottul, tlocal prints. It was wildly successiul: Lilly for Target items sold cut within hours of the hrand's dehut an Target 's website. Loyal Tarpet customers were frustrated and woiced their opinion that faulty insight into consumer demand was indieative of larger prohlems at Target. Even with a robust inventory management system in place, Target ran out of products and could not meet consumer demand. The situation was particularly problematic for Target because it prevented the oompany from fultilling its core mission: if items were out-ot-stock, Target was bot able to inoel cusloeners' expectations, and customers woukd bea leave lae sore emply-handod and trustrated. The situation was complicated by an inefficient imventory manapement systen that required manual fixes by in-stare teams to comhat system errors, which resulted in higher labor, storage and transpartation oosts than those incurred by Target's competitors. REFERENCES 2. hitpsilicorporate.tiageleom:abouthiniotyi Targot-through-the-yars 6. hitpilitinance yahoo eomitewatarpot-xianes-radmaptransione-tusines-21 310005 , teml - target-remenberizg soug dyy-n
 idd
idd








 I need SOWT analysis for Target corp with recomndation for future strategy
I need SOWT analysis for Target corp with recomndation for future strategy



