Question: II. Probability P(AUB) = P(A) + P(B) - P(An B) P(AB) = P(An B) P(B) E(X) = Ux = Expi Var(X) = 0; = _(x

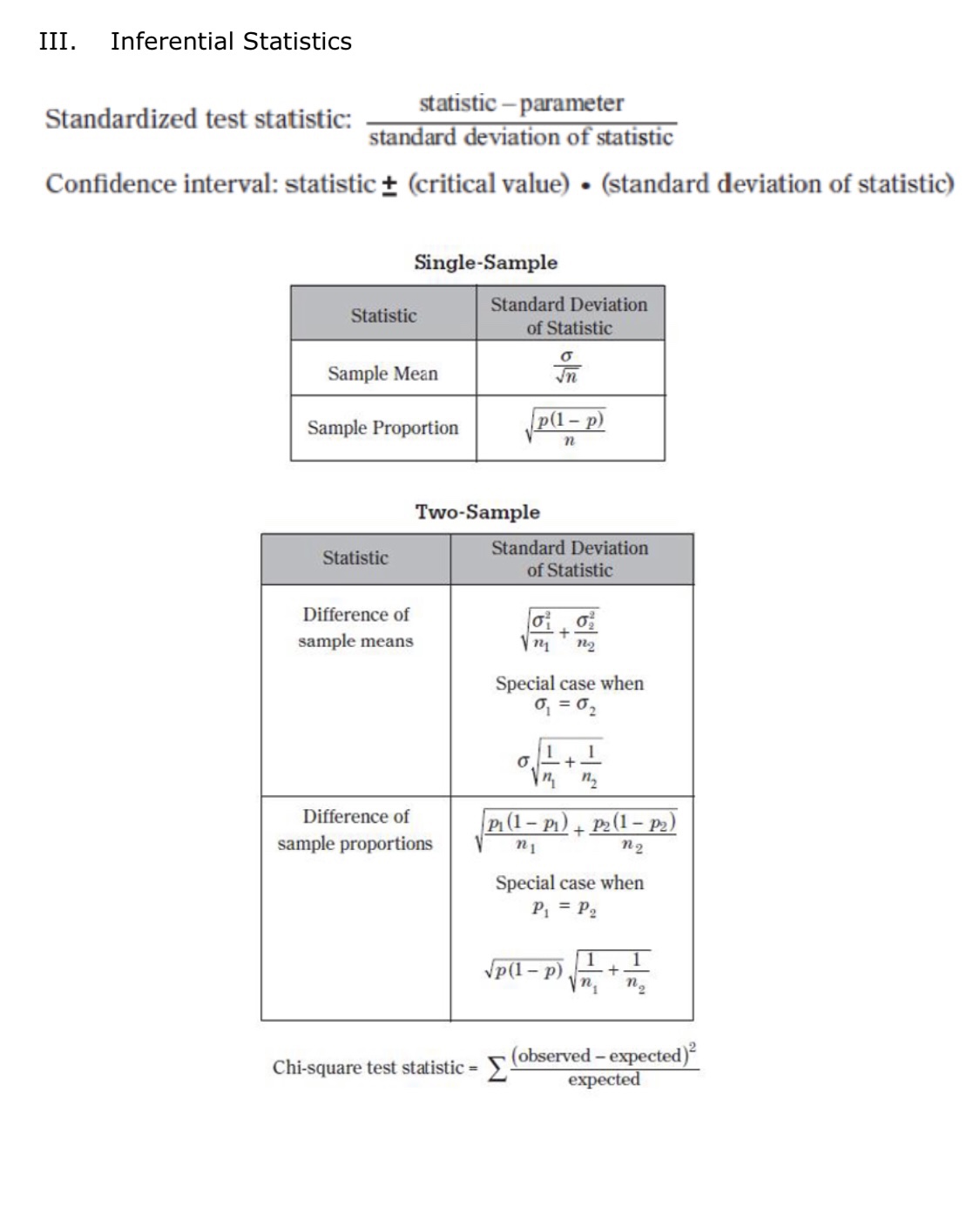
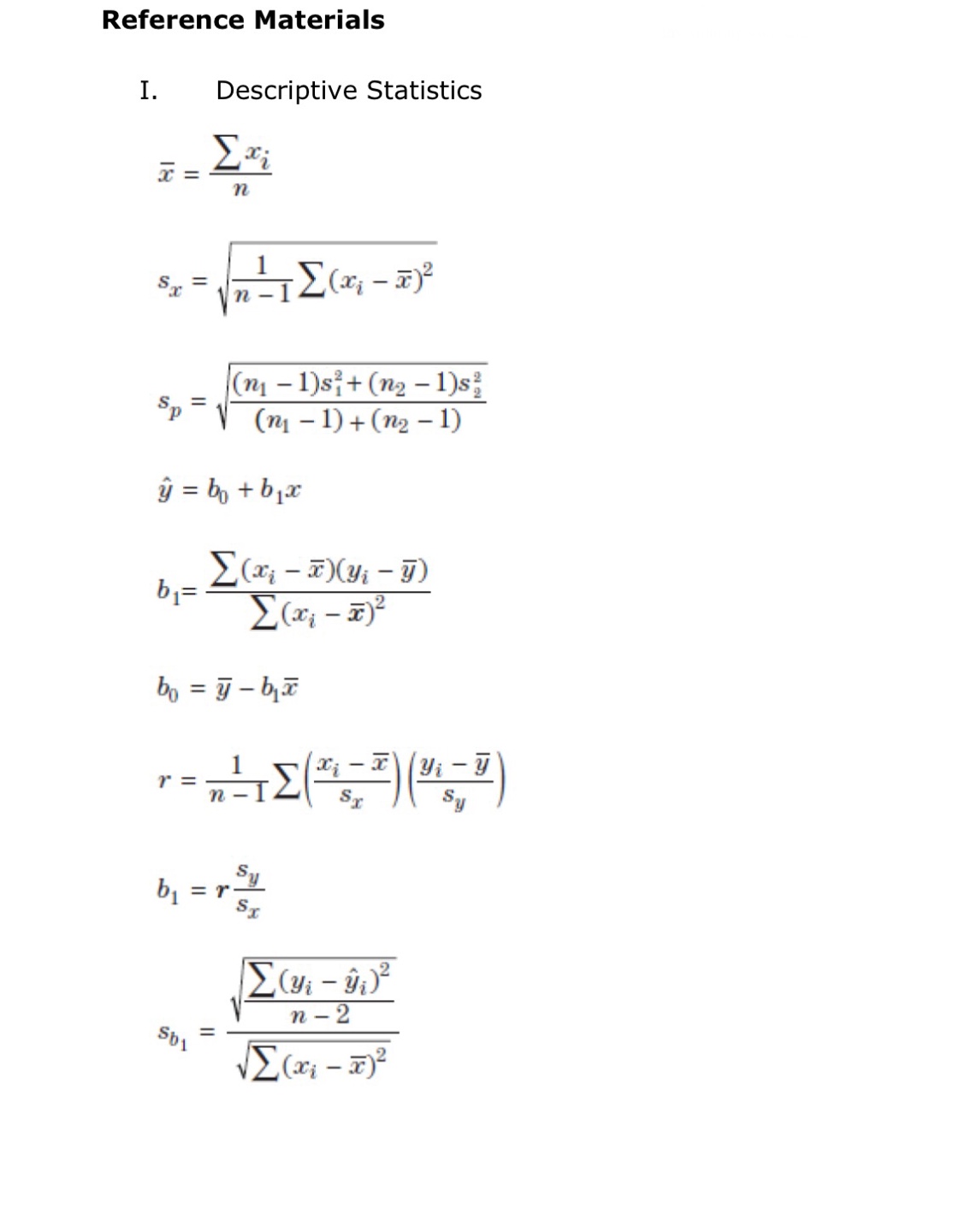

II. Probability P(AUB) = P(A) + P(B) - P(An B) P(AB) = P(An B) P(B) E(X) = Ux = Expi Var(X) = 0; = _(x - ux)2pi If X has a binomial distribution with parameters n and p, then: P(X = k) = k) p* (1 - p)" -* HI = np Or = Vnp(1 - p) Ho = P Op = P(1- p n If x is the mean of a random sample of size n from an infinite population with mean u and standard deviation O, then: MY = HIII. Inferential Statistics Standardized test statistic: statistic - parameter standard deviation of statistic Confidence interval: statistic + (critical value) . (standard deviation of statistic) Single-Sample Statistic Standard Deviation of Statistic Sample Mean Sample Proportion p(1 - p) n Two-Sample Statistic Standard Deviation of Statistic Difference of sample means 722 Special case when 61 =02 ol+1 n2 Difference of PI (1 - PI) + P2 (1 - P2) sample proportions n1 n2 Special case when P1 = P2 Jp(1 - P) 1 + 1 Vn, n2 Chi-square test statistic = \\ (observed - expected) expected\fD Question 38 1 pts Suppose you wish to test the hypothesis that Ho: p= 0.25. Based on a random sample of 100 participants you find that the sample proportion, p is 0.29. Which of these expressions represents the standard error of p for this test? O (0.25) (0.75) (100) O (0.25) (0.29) 100 0 100 (0.25) (0.75) O 1 + 0.25 0.29 O (0.25) (0.75) (0.29) (0.71) 100 100
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


