Question: import numpy as np; import pylab as pl N-len(x) a=np. linspace(0,0,N) A-np.zeros(N,N) for k in range (O,N): Alk,0]-1 for j in range (1,N) a=np. linalg.

![A-np.zeros(N,N) for k in range (O,N): Alk,0]-1 for j in range (1,N)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3990422750_45166f39903c65bc.jpg)

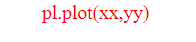

![yy[k]-P(xx[k],a,N-1) pl.grid(b-True) pl.plot(xx,yy import numpy as np import pylab as pl pje4%](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3990649f61_45366f39905eda25.jpg)
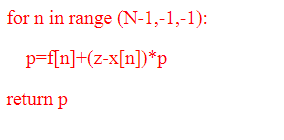

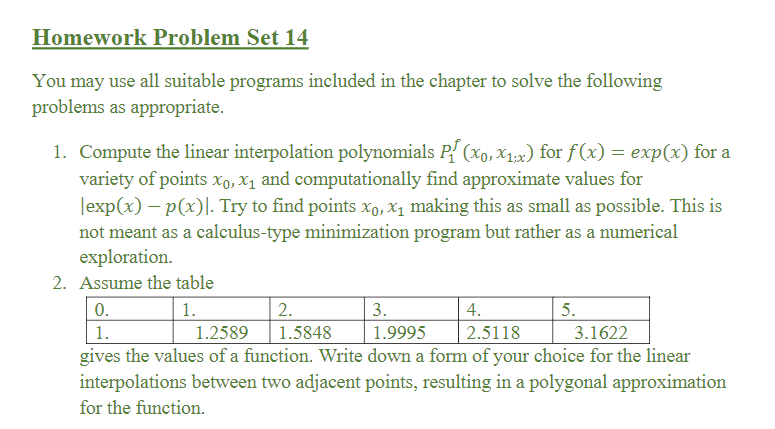
import numpy as np; import pylab as pl N-len(x) a=np. linspace(0,0,N) A-np.zeros(N,N) for k in range (O,N): Alk,0]-1 for j in range (1,N) a=np. linalg. solve(A,y) #Here the computation of the coefficients is finished, the rest is just plotting the polynomial def P(x,a,M: for n in range (M-1,-1,-1) return p c-np.amax(x) d-np.amin(x) xx=np.linspacec.d.200) yy-np.linspace(c,d,200) for k in range (0,200): yy[k]-P(xx[k],a,N-1) pl.grid(b-True) pl.plot(xx,yy import numpy as np import pylab as pl pje4% parctan( 1 .0) N-5 a--2 b-2 x=np.linspace(a,b,N+1) f=np. linspace(0,0,N+1 ) def F(x): y-np.arctan(x) return y for k in range (0,N+1): #This computes the divided differences for k in range (0,N): for j in range (N,k,-1): f i-fi-1/x-x[i-k-1]) #This is the def P(z,f,N) p-IN] modified Homer scheme for n in range (N-1,-1,-1): return p #This plots the function and the interpolation polynomial xx-np.linspace(a,b,200) yy-np.linspace(a,.b,200) zz-np.linspace(a,b,200) for k in range (0,200): pl.grid(b- True pl.plot(xx,yy pl.plot(xx,zz) g11 Homework Problem Set 14 You may use all suitable programs included in the chapter to solve the following problems as appropriate. 1. Compute the linear interpolation polynomials P (o,1x for fx) exp(x) for a variety of points xo,x1 and computationally find approximate values for lexp(x)-p(x). Try to find points xo, X1 making this as small as possible. This is not meant as a calculus-type minimization program but rather as a numerical exploration. 2. Assume the table 0. 1. 1. 2. 4. 1.25891.5848 1.9995 2.5118 3.1622 the values of a function. Write down a form of your choice for the linear interpolations between two adjacent points, resulting in a polygonal approximation for the function import numpy as np; import pylab as pl N-len(x) a=np. linspace(0,0,N) A-np.zeros(N,N) for k in range (O,N): Alk,0]-1 for j in range (1,N) a=np. linalg. solve(A,y) #Here the computation of the coefficients is finished, the rest is just plotting the polynomial def P(x,a,M: for n in range (M-1,-1,-1) return p c-np.amax(x) d-np.amin(x) xx=np.linspacec.d.200) yy-np.linspace(c,d,200) for k in range (0,200): yy[k]-P(xx[k],a,N-1) pl.grid(b-True) pl.plot(xx,yy import numpy as np import pylab as pl pje4% parctan( 1 .0) N-5 a--2 b-2 x=np.linspace(a,b,N+1) f=np. linspace(0,0,N+1 ) def F(x): y-np.arctan(x) return y for k in range (0,N+1): #This computes the divided differences for k in range (0,N): for j in range (N,k,-1): f i-fi-1/x-x[i-k-1]) #This is the def P(z,f,N) p-IN] modified Homer scheme for n in range (N-1,-1,-1): return p #This plots the function and the interpolation polynomial xx-np.linspace(a,b,200) yy-np.linspace(a,.b,200) zz-np.linspace(a,b,200) for k in range (0,200): pl.grid(b- True pl.plot(xx,yy pl.plot(xx,zz) g11 Homework Problem Set 14 You may use all suitable programs included in the chapter to solve the following problems as appropriate. 1. Compute the linear interpolation polynomials P (o,1x for fx) exp(x) for a variety of points xo,x1 and computationally find approximate values for lexp(x)-p(x). Try to find points xo, X1 making this as small as possible. This is not meant as a calculus-type minimization program but rather as a numerical exploration. 2. Assume the table 0. 1. 1. 2. 4. 1.25891.5848 1.9995 2.5118 3.1622 the values of a function. Write down a form of your choice for the linear interpolations between two adjacent points, resulting in a polygonal approximation for the function
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


