Question: import numpy as np np.random.binomial (3, 0.6, size=5) ## array([1, 1, 1, 3, 1]) plt.hist(x) plt.scatter (successes, counts, c=red) fx(x): 1 (log x-u)2 e

![3, 1]) plt.hist(x) plt.scatter (successes, counts, c="red") fx(x): 1 (log x-u)2 e](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/05/6647f06e83363_6386647f06e6f300.jpg)
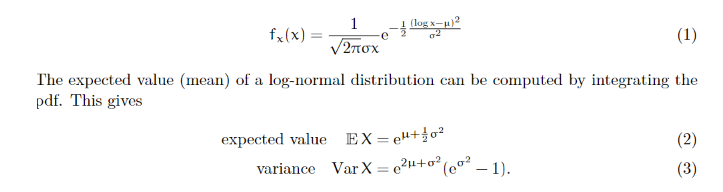
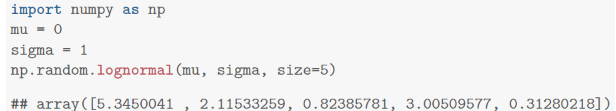
import numpy as np np.random.binomial (3, 0.6, size=5) ## array([1, 1, 1, 3, 1]) plt.hist(x) plt.scatter (successes, counts, c="red") fx(x): 1 (log x-u)2 e 2 2 (1) The expected value (mean) of a log-normal distribution can be computed by integrating the pdf. This gives expected value EX = +0 variance Var X = e+ ( (002 -1). (2) (3) import numpy as np mu - O sigma 1 np.random.lognormal (mu, sigma, size-5) ## array([5.3450041 2.11533259, 0.82385781, 3.00509577, 0.31280218])
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


