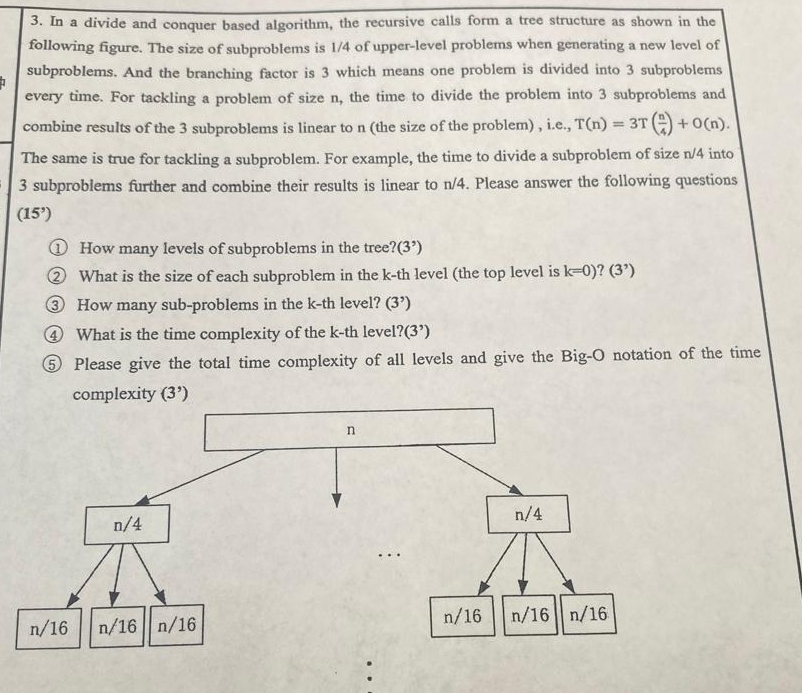
Question: In a divide and conquer based algorithm, the recursive calls form a tree structure as shown in the following figure. The size of subproblems is
In a divide and conquer based algorithm, the recursive calls form a tree structure as shown in the following figure. The size of subproblems is of upperlevel problems when generating a new level of subproblems. And the branching factor is which means one problem is divided into subproblems every time. For tackling a problem of size the time to divide the problem into subproblems and combine results of the subproblems is linear to the size of the problem ie The same is true for tackling a subproblem. For example, the time to divide a subproblem of size into subproblems further and combine their results is linear to Please answer the following questions
How many levels of subproblems in the tree? :
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


