Question: In a laboratory experiment, air ) = 1 . 2 k g m 3 , = ( 0 . 0 0 0 0 1 5
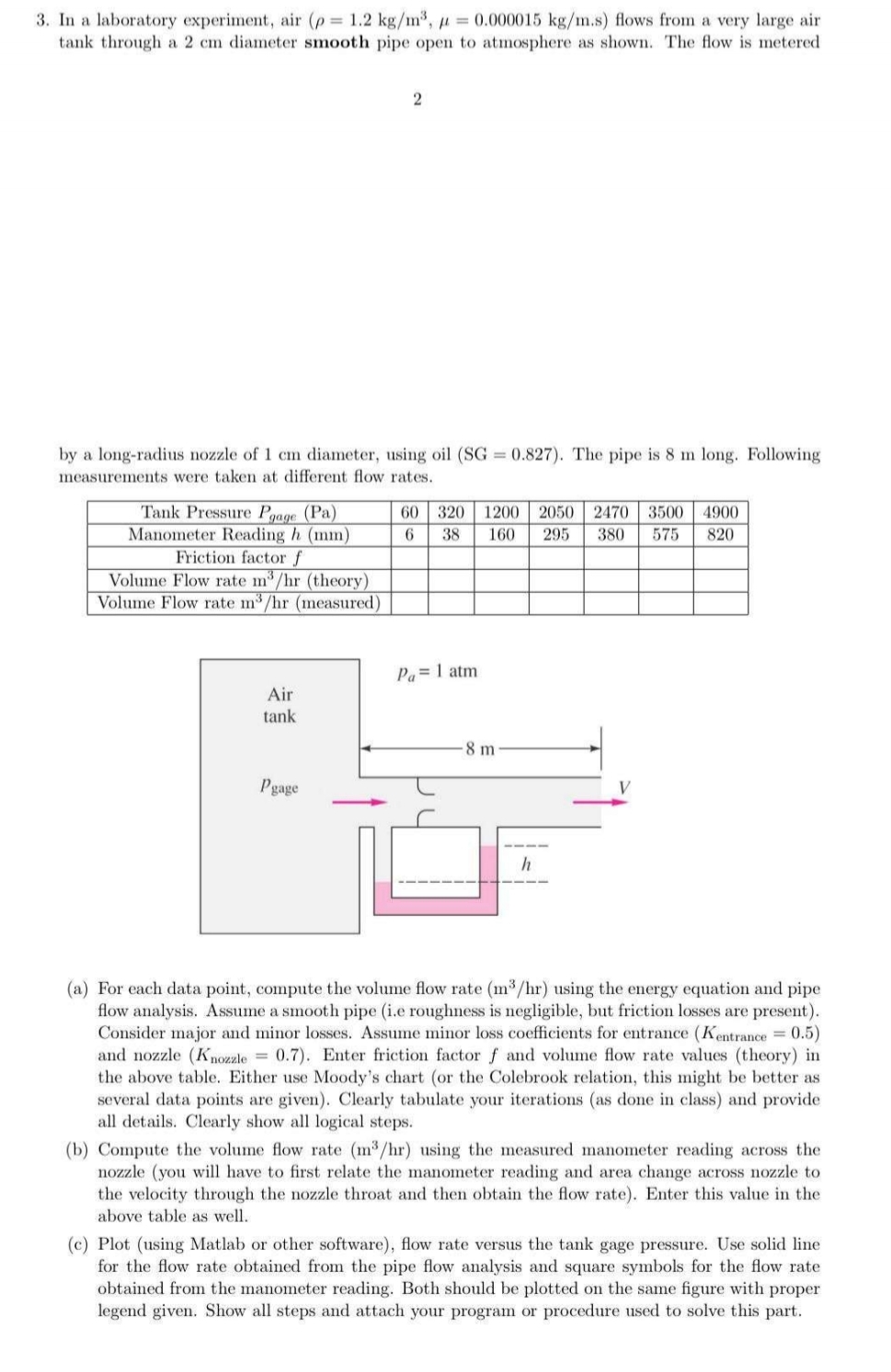
In a laboratory experiment, air flows from a very large air tank through a diameter smooth pipe open to atmosphere as shown. The flow is metered
by a longradius nozzle of diameter, using oil The pipe is long. Following measurements were taken at different flow rates.
tableTank Pressure Manometer Reading Friction factor Volume Flow rate theoryVolume Flow rate measured
a For each data point, compute the volume flow rate using the energy equation and pipe flow analysis. Assume a smooth pipe ie roughness is negligible, but friction losses are present Consider major and minor losses. Assume minor loss coefficients for entrance and nozzle Enter friction factor and volume flow rate values theory in the above table. Either use Moody's chart or the Colebrook relation, this might be better as several data points are given Clearly tabulate your iterations as done in class and provide all details. Clearly show all logical steps.
b Compute the volume flow rate using the measured manometer reading across the nozzle you will have to first relate the manometer reading and area change across nozzle to the velocity through the nozzle throat and then obtain the flow rate Enter this value in the above table as well.
c Plot using Matlab or other software flow rate versus the tank gage pressure. Use solid line for the flow rate obtained from the pipe flow analysis and square symbols for the flow rate obtained from the manometer reading. Both should be plotted on the same figure with proper legend given. Show all steps and attach your program or procedure used to solve this part.
please answer as soon as possible
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


