Question: In both Question 1 and Question 2, we will study the reversible expansion of 1mol(n=1) of a monatomic ideal gas from: State I with P1=1.23atm,V1=20.0L
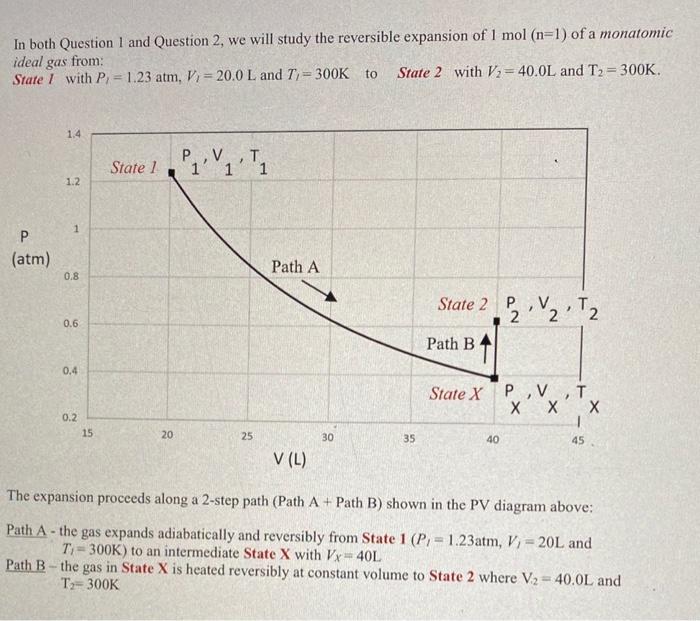


In both Question 1 and Question 2, we will study the reversible expansion of 1mol(n=1) of a monatomic ideal gas from: State I with P1=1.23atm,V1=20.0L and T1=300K to State 2 with V2=40.0L and T2=300K. The expansion proceeds along a 2 -step path (Path A + Path B) shown in the PV diagram above: Path A - the gas expands adiabatically and reversibly from State 1(Pl=1.23atm,V1=20L and Ti=300K ) to an intermediate State X with VX=40L Path B - the gas in State X is heated reversibly at constant volume to State 2 where V2=40.0L and T2=300K 2a. ( 5pts) Path B in the PV diagram is a constant volume process. In lectures, we learned that at constant volume the heat is: qV=CVdT, and for n moles of a monatomic ideal gas, CY=3/2nR The entropy increase when a pure substance is heated from an initial temperature T1 to a final temperature TF at constant volume is: S=Tdqrev=TITFTcVdT Use this to show that going from State X to State 2, the entropy change of the ideal gas is: S=23nRln(TxT2) Calculate the entropy change (in units of J/K ). Note: the entropy of the gas should increase when its temperature is increased. 2b. (4pts) Explain why the entropy change for the ideal gas from State 1 to State X along path A is: S=0 2b. (6pts) Without doing any calculations (but perhaps using diagrams ...) determine if the absolute value of the reversible work, Wrev done along Path A+PathB - is larger or smaller than (or the same as!) the reversible work if the gas had been expanded reversibly and isothermally from State 1 to State 2 Note: the wres should be
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


