Question: In each compound below, two protons are color-coded (red and blue). Determine which of the two protons is more acidic, and explain your choice: OH



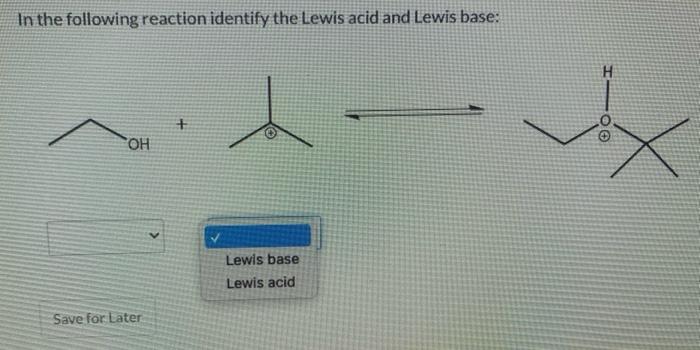
In each compound below, two protons are color-coded (red and blue). Determine which of the two protons is more acidic, and explain your choice: OH H The red proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is more stable, with a negative charge that is delocalized by resonance The red proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is more stable, with a negative charge associated with an sp? hybrid orbital. The blue proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is more stable, with a negative charge associated with an sp? hybrid orbital. The blue proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is more stable with a negative charge that is delocalized by resonance O The red proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is more stable, with a negative charge that is delocalized by resonance over multiple atoms, including two electronegative oxygen atoms. The blue proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is less stable, with a negative charge that is delocalized over a carbon atom and an electronegative oxygen atom. The red proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is less stable, with a negative charge that is delocalized by resonance over multiple atoms, including an electronegative oxygen atom. The blue proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is more stable, with a negative charge that is delocalized over a carbon atom and an electronegative oxygen atom. NH2 HO N a O hered proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is more stable, with a negative charge that is delocalized by resonance over two electronegative oxygen atoms. The red proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is less stable, with a negative charge that is delocalized by resonance over two electronegative oxygen atoms. The blue proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is more stable, with a negative charge that is delocalized by resonance over two less electronegative nitrogen atoms. The blue proton is more acidic because its conjugate base is less stable, with a negative charge that is de localized by resonance over two less electronegative nitrogen atoms. In the following reaction identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base: I-OO + OH Lewis base Lewis acid Save for Later
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


