Question: In Java simulate a simple CPU. The simulator takes in a simplified text based object file (full of TAC instructions encoded as decimal bytes) and
In Java simulate a simple CPU. The simulator takes in a simplified text based object file (full of TAC instructions encoded as decimal bytes) and then simulates the execution of a CPU.
This program's task is simple: to simulate the execution of a single program in memory, one instruction at a time. The input to the program is a text file with object codes and data with one byte per line. This is chosen for this exercise to keep the project simple. I dont want you getting bogged down in how to read binary file formats. The simulator, tacsim, will first load the instructions from the program into a simulated memory. Then, it will start the main loop that simulates the CPU: fetch, decode, execute. It will continue to do this until it reaches the special instruction HLT, that we will use to indicate the program should be finished. To simulate a CPU, you'll have to keep track of these things: register state (i.e., what's in each of the CPU registers, such as ACC, X, etc.), memory state (what's in each byte of memory), and a few other things (e.g., the branching condition code). Each instruction just updates some subset of machine state. Because the simulated computer is rather simple, you wont have to spend too much effort decoding the instructions. Each instruction is represented by two bytes, the first is the opcode, the second is the operand. Lets start by taking a look at the CPU instruction set.
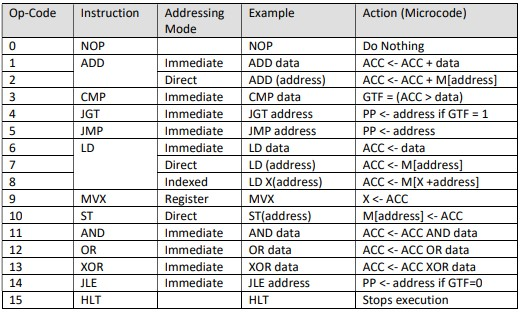




Op-Code Instruction Addressing Mode Example Action (Microcode) 0 NOP ADD CMP IGT JMP ID Immediate Direct Immediate Immediate Immediate Immediate Direct Indexed Register Direct Immediate Immediate Immediate Immediate NOP ADD data ADD (address) CMP data JGT address JMP address LD data LD (address) LD X(address) MVX ST(address) AND data OR data XOR data JLE address HLT Do Nothing ACC data) PP data) PP
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


