Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In receiving terminals of petrochemical plants, some of the liquid natural gas (LNG) storage Tanks are designed to be in ground, to avoid receiving

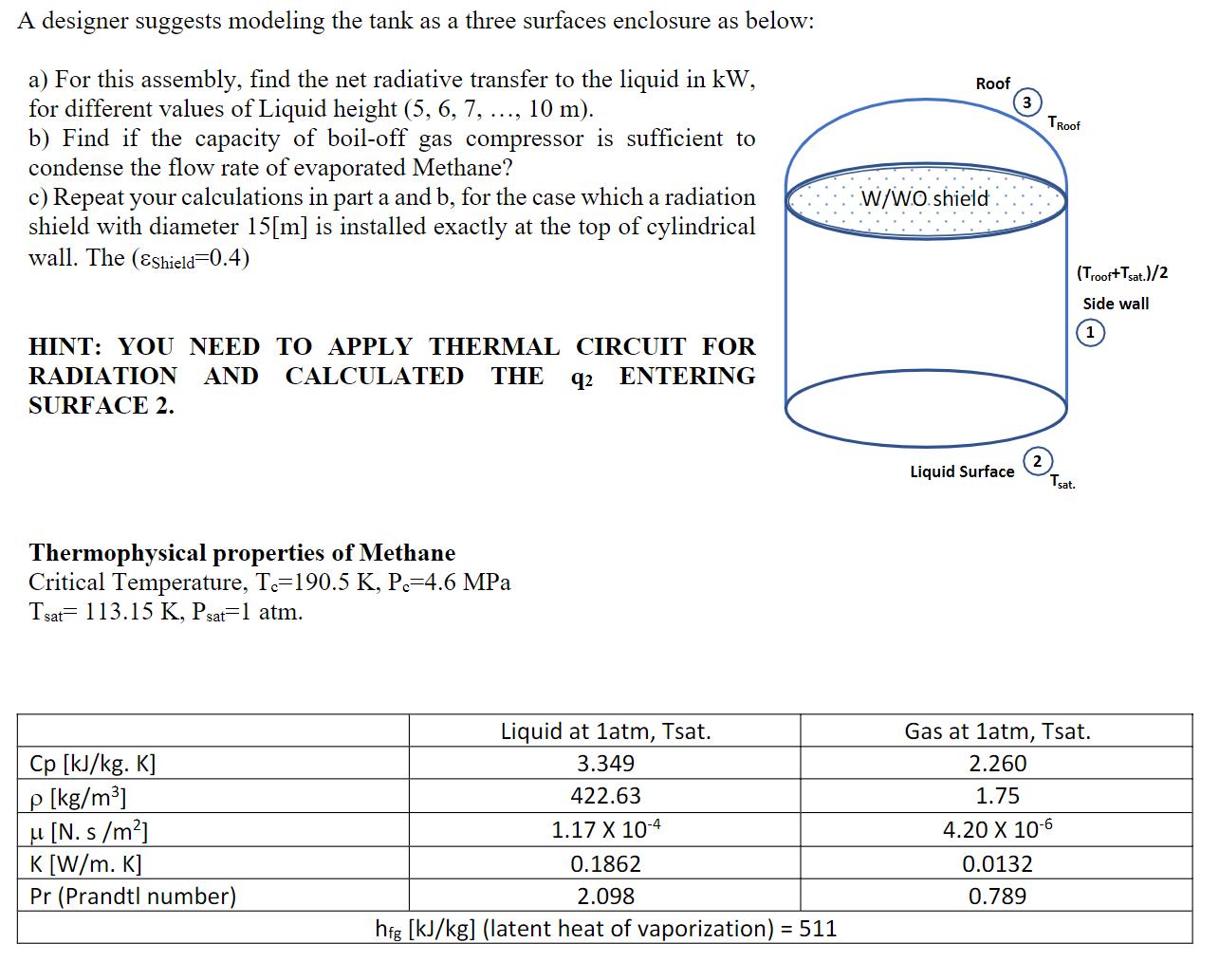
In receiving terminals of petrochemical plants, some of the liquid natural gas (LNG) storage Tanks are designed to be in ground, to avoid receiving radiation from the sun and also being protected from direct hit. Even though, they are buried in the ground the top ceiling is exposed to the environment and can absorb radiation of the sun, sky and surroundings. The absorbed energy by the ceiling can increase the internal energy of the stored liquid methane and at some the liquid methane will evaporate. Evaporated methane will increase the pressure of the tank can cause catastrophe. To avoid any accident a boil-off gas compressor with 0.2% volume full tank capacity per day discharge is installed in a plant. The detail design of the storage tank is as below: Ceiling Tank Diameter = 15 m Tank Height = 15 m Ceiling (Roof) = black body at TRoof Liquid CH4 surface = black body at Tsat Tank diameter Tank height Side wall = gray, diffuse (83=0.6) at T=( TRoof+ TSat)/2 Max. Liquid depth Lmax=10 m TRoof 55C Soil Liquid height in the tank. A designer suggests modeling the tank as a three surfaces enclosure as below: a) For this assembly, find the net radiative transfer to the liquid in kW, for different values of Liquid height (5, 6, 7, ..., 10 m). b) Find if the capacity of boil-off gas compressor is sufficient to condense the flow rate of evaporated Methane? c) Repeat your calculations in part a and b, for the case which a radiation shield with diameter 15[m] is installed exactly at the top of cylindrical wall. The (Eshield=0.4) HINT: YOU NEED TO APPLY THERMAL CIRCUIT FOR RADIATION AND CALCULATED THE 92 ENTERING SURFACE 2. Thermophysical properties of Methane Critical Temperature, T.-190.5 K, P.-4.6 MPa Tsat 113.15 K, Psat=1 atm. Liquid at 1atm, Tsat. 3.349 Cp [kJ/kg. K] p [kg/m] 422.63 u [N. s/m] 1.17 X 10-4 K [W/m. K] 0.1862 Pr (Prandtl number) 2.098 hig [kJ/kg] (latent heat of vaporization) = 511 Roof W/WO shield 3 TRoof 2 (Troof+Tsat.)/2 Side wall Liquid Surface Tsat. Gas at 1atm, Tsat. 2.260 1.75 4.20 X 10-6 0.0132 0.789
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.37 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Given Tsat P I alm Tc1905 K P 46 MPa 160C Assuming Where no shield th...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


