Question: In this homework, you will implement a factory simulator program with object-oriented approach. In the UML diagrams below, access (getter) and modifier (setter) methods are





In this homework, you will implement a factory simulator program with object-oriented approach. In the UML diagrams below, access (getter) and modifier (setter) methods are not shown for simplicity. However, you are supposed to implement these methods for each class as well.
// Declared Item class public class Item { // Private data members private int id; public static int numberOfItems;
// Parameterized constructor public Item(int id) { this.setId(id); numberOfItems++; }
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } }
// Declared Payroll class
public class Payroll { // Private data members private int workHour; private int itemCount;
// Parameterized constructor public Payroll(int workHour, int itemCount) { this.workHour = workHour; this.itemCount = itemCount; }
// Public method to calculate salary public int calculateSalary() { int workingHourSalary = workHour * 3; int itemsProducedSalary = itemCount * 2; return workingHourSalary + itemsProducedSalary; }
// String representation of the object public String toString() { return "The work hour is " + workHour + " and the produced item count is " + itemCount + "."; } }
// Declared Employee class
public class Employee { // Private data members private int id; private String name; private String surname; private int workHour; private int speed; private Item[] items; private Payroll payroll;
// Parameterized constructor public Employee(int id, String name, String surname, int workHour, int speed) { this.id = id; this.setName(name); this.setSurname(surname); this.workHour = workHour; this.speed = speed; }
// Public method to generate items public Item[] startShift() { int numberOfItems = speed * workHour; items = new Item[numberOfItems]; for(int i = 0; i
// Public method to calculate payroll public Payroll endShift() { int numberOfItems = speed * workHour; payroll = new Payroll(workHour, numberOfItems); return payroll; }
// String representation of the object public String toString() { return "This is the employee with id " + id + " speed " + speed + ". The work hour is " + workHour + " and the produced item count is " + speed * workHour; }
// Public getter for private data member id public int getId() { return id; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String getSurname() { return surname; }
public void setSurname(String surname) { this.surname = surname; } }
// Declared Storage class
public class Storage { // Private data member private int capacity; private Item[] items; private int numberOfItems;
// Parameterized constructor public Storage(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; this.numberOfItems = 0; this.items = new Item[this.capacity]; }
// Public method to add item to items array public void addItem(Item item) { items[numberOfItems] = item; numberOfItems++; }
// Public method to get number of items in storage public int getNumberOfItems() { return numberOfItems; } }
Declared Factory class
public class Factory { // Private data members private String name; private Employee[] employees; private int capacity; private Storage storage; private Payroll[] payrolls; private double itemPrice;
// Parameterized constructor public Factory(String name, int capacity, double itemPrice) { this.setName(name); this.setCapacity(capacity); this.itemPrice = itemPrice; }
// Public method to calculate revenue public double getRevenue() { return storage.getNumberOfItems()* itemPrice; }
// Public method to calculate salary public double getPaidSalaries() { double salary = 0; for(Payroll payroll: payrolls) { salary += payroll.calculateSalary(); } return salary; }
// Public method to add employee public void addEmployee(Employee employee) { if(employees == null) { employees = new Employee[1]; employees[0] = employee; } else { employees = Arrays.copyOf(employees, employees.length + 1); } Item[] items = employees[employees.length - 1].startShift(); for(Item item: items) { storage.addItem(item); } }
// Public method to remove employee public Employee removeEmployee(int id) { if(employees.length == 0) { System.out.println("There are no employees!"); return null; } int employeeIndex = -1; for(int i = 0; i
// Private method to add payroll private void addPayroll(Payroll payroll) { if(payrolls == null) { payrolls = new Payroll[1]; } else { payrolls = Arrays.copyOf(payrolls, payrolls.length + 1); } payrolls[payrolls.length - 1] = payroll; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public int getCapacity() { return capacity; }
public void setCapacity(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; } }
But i can't print the output with Testing.java class how can i fix this
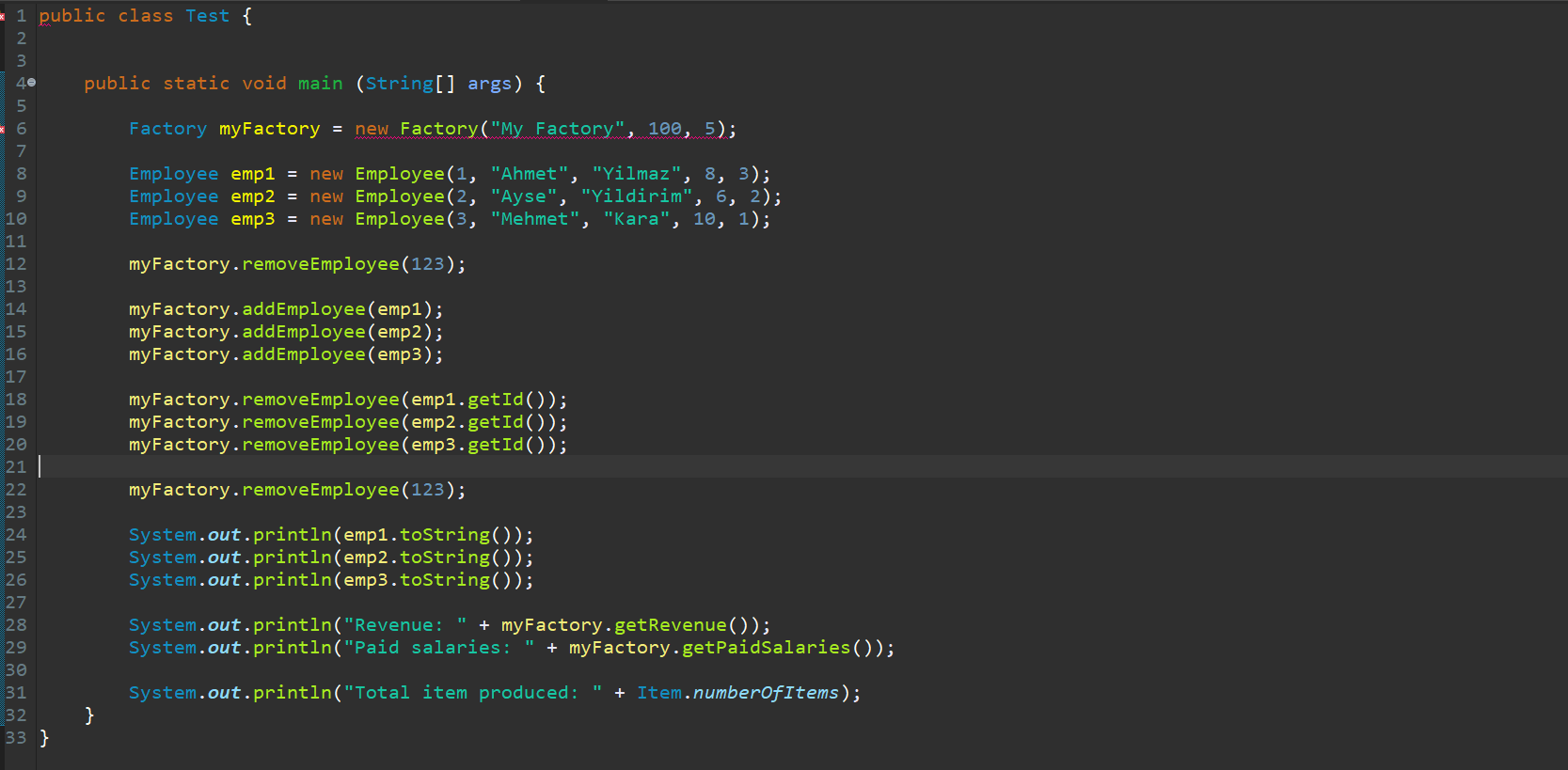
In this homework, you will implement a factory simulator program with object-oriented approach. In the UML diagrams below, access (getter) and modifier (setter) methods are not shown for simplicity. However, you are supposed to implement these methods for each class as well. 1. Implement an Item class with the following UML diagram. Item id : int numberOfItems: int + + Item (id: int) An Item object represents an item generated by the employees working for the factory. Data field id keeps the id of the item object created. Static data field numberOfItems keeps the number of item objects created. An item is created with an id data field. You have to use this keyword in the implementation of the constructor. In the constructor, you also need to increment numberOfItems data field. Consider the following example which demonstrates the creation of Item object. Item item = new Item (10); O 0 O 2. Implement a Payroll class with the following UML diagram. Payroll workHour : int itemCount : int Payroll (workHour:int, itemCount:int) calculateSalary() : int toString(): String + + + A Payroll object represents the payroll of the employees. Data field workHour keeps the number of hours an employee has worked. Data field itemCount keeps the number of items an employee has produced. A Payroll object is created with a given workHour and itemCount. You have to use this keyword in the implementation of the constructor. Consider the following example which demonstrates the creation of Payroll object. O 0 Payroll payroll = new Payroll (8,15); o Here, the payroll will be created for the 8 hours of working and 15 produced items. calculateSalary() method calculates salary of the employee according to the number of hours an employee has worked and the number of items s/he produced. For each hour an employee works, s/he earns 3 liras and for each item s/he produces s/he additionally earns 2 liras. o As an example, an employee will earn 8*3=24 liras for the working hours and 15*2=30 liras for the items produced with the sample Payroll above; hence a total of 54 liras should be calculated. toString() method returns a String containing information about the work hour and the item count of the payroll. An example string is as following: o The work hour is 8 and the produced item count is 15. 3. Implement an Employee class with the following UML diagram. Employee id : int name : String surname : String workHour : int speed : int items : Item [] payroll : Payroll + Employee (id:int, name: String, surname:String, workHour:int, speed:int) + startShift(): Item [] endShift(): Payroll toString(): String + + . . . An Employee object represents an employee working for the factory. Data field id keeps the id number of the Employee object created. Data fields name and surname keeps the name and the surname of the employee, respectively. Data field workHour keeps the number of hours an employee will work. Data field speed keeps the number of items that the employee can produce in an hour. Data field items array holds the items produced by the employee. Data field payroll keeps the payroll of the employee. An employee is created with an id, name, surname, workhour, and speed values. o You have to use this keyword in the implementation of the constructor. Consider the following example which demonstrates the creation of Employee object. . O Employee employee = new Employee (1, "Ahmet", "Yilmaz", 8, 3); o Here, an employee has an id of 1, name of "Ahmet", surname of "Yilmaz", working hour of 8, and speed of 3. Here, speed represents that the employee can produce 3 items in an hour. startShift() method finds how many items this employee should produce according to speed and workHour values. After that, it creates appropriate number of items with randomly generated ids between 1-100 and put them into items array. It then returns items array endShift() method creates a Payroll object with employee's work hour and the number of items s/he creates. It assigns this object to payroll data field. It then returns payroll object. toString() method returns a String with employee's id and the return value of the payroll object's toString() method. An example string is as following: o This is the employee with id 1 speed 3. The work hour is 8 and the produced item count is 24. 4. Implement a Storage class with the following UML diagram. Storage capacity : int items : Item [] Storage (capacity:int) addItem (item:Item) : void + . A Storage object represents a storage area for the factory. Data field id capacity keeps the capacity (the maximum number of items that can be stored) of the Storage object created. Data fields items array keeps the items put inside the storage. A storage is created with a given capacity value. o You have to use this keyword in the implementation of the constructor. o Consider the following example which demonstrates the creation of Storage object. Storage storage = new Storage (100); addItem(item:Item) method adds the item passed as the parameter to the items data field. Note that you need to resize the items array for this. 5. Implement a Factory class with the following UML diagram. Factory name : String employees : Employee [] storage : Storage - payrolls : Payroll[] itemPrice : double + Factory( name:String, capacity:int, itemPrice:double) getrevenue () : double get PaidSalaries () : double addEmployee (employee: Employee) : void removeEmployee (id:int) : Employee addPayroll (payroll:Payroll) : void + + + + + . A Factory object represents a factory with employees. Data field name represents the name of the factory. Data field employees represents employees working for the factory. Data field storage represents the storage area of the factory. Data field payrolls represents the payrolls belonging to the employees. Data field itemPrice represents the price for one item (Suppose that all items have the same price). A factory is created with a given name, capacity, and itemPrice value. o You have to use this keyword in the implementation of the constructor. o In the constructor, you also need to create a Storage object with the given capacity and assign it to storage data field. o Consider the following example which demonstrates the creation of Factory object. Factory factory = new Factory ("My Factory", 100, 5); getRevenue() method returns the revenue according to the number of items in the storage data field and itemPrice data field. get PaidSalaries() method calculates the paid salaries of the employees according to the payrolls array. Note that you need to use calculateSalary() method of payroll objects in payrolls array. addEmployee (employee: Employee) method adds an employee to the employees array. o Note that you need to resize the employees array for this. Then, you need to call startShift() method of the newly added employee and add all the items returned from startShift() method to storage, using addItem(item:Item) method of storage data field. removeEmployee (id:int) method removes the employee from employees array. . O 0 0 O . O If there are no employees, it prints an appropriate error message. If the employee with a given id is not found, it prints an appropriate error message. If the employee is found, it removes employee from the employees array. Note that you need to resize the employees array for this. Then, you need to call endShift() method of the newly removed employee and call addPayroll (payroll: Payroll) method with the returned payroll by the endShift() method. At the end, you need to return the removed employee. addPayroll (payroll: Payroll) method adds the payroll passed as the parameter to the payrolls data field. Note that you need to resize the payrolls array for this. 0 You are given a simple scenario (Test.java) to test your class implementations. Note that the output of the example test class is as the following: There are no employees! Employee does not exist! This is the employee with id 1 speed 3. The work hour is 8 and the produced item count is 24. This is the employee with id 2 speed 2. The work hour is 6 and the produced item count is 12. This is the employee with id 3 speed 1. The work hour is 10 and the produced item count is 10. Revenue: 230.0 Paid salaries: 164.0 Total item produced: 46 There might be other test cases too. Therefore, please pay attention to use the same class, method and variable names in your implementations. You are allowed to increase the number of methods in the classes; however, you cannot decrease the number of them. You are not allowed to use ArrayLists in the homework! You can only use Arrays. The produced output should be identical to that of this example as your programs will be graded by an auto-grader. 6 1 public class Test { 2 3 40 public static void main (String[] args) { 5 Factory myFactory = new Factory("My Factory", 100, 5); 7 8 Employee emp1 = new Employee(1, "Ahmet". "Yilmaz", 8, 3); 9 Employee emp2 = new Employee(2, "Ayse", "Yildirim", 6, 2); 10 Employee emp3 = new Employee(3, "Mehmet", "Kara", 10, 1); 11 12 myFactory.removeEmployee(123); 13 14 myFactory.addEmployee (emp1); 15 myFactory.addEmployee (emp2); 16 myFactory.addEmployee (emp3); 17 18 myFactory.removeEmployee (emp1.getId()); 19 myFactory.remove Employee (emp2.getId()); 20 myFactory.removeEmployee (emp3.getId()); 21 22 myFactory.removeEmployee (123); 23 24 System.out.println(emp1.toString()); 25 System.out.println(emp2.toString()); 26 System.out.println(emp3.toString()); 27 28 System.out.println("Revenue: + my Factory.getRevenue()); 29 System.out.println("Paid salaries: + myFactory.getPaidsalaries()); 30 31 System.out.println("Total item produced: + Item.numberofitems); 32 } 33 }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


