Question: In this MATH 336 assignment problem. consider the following figure, which shows a graph G = Each edge ij E E in the figure
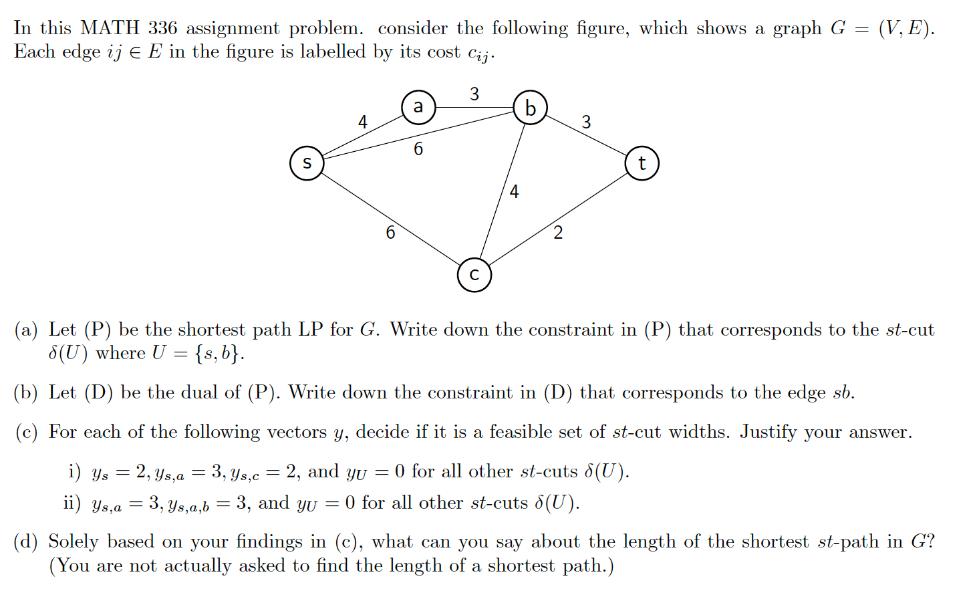
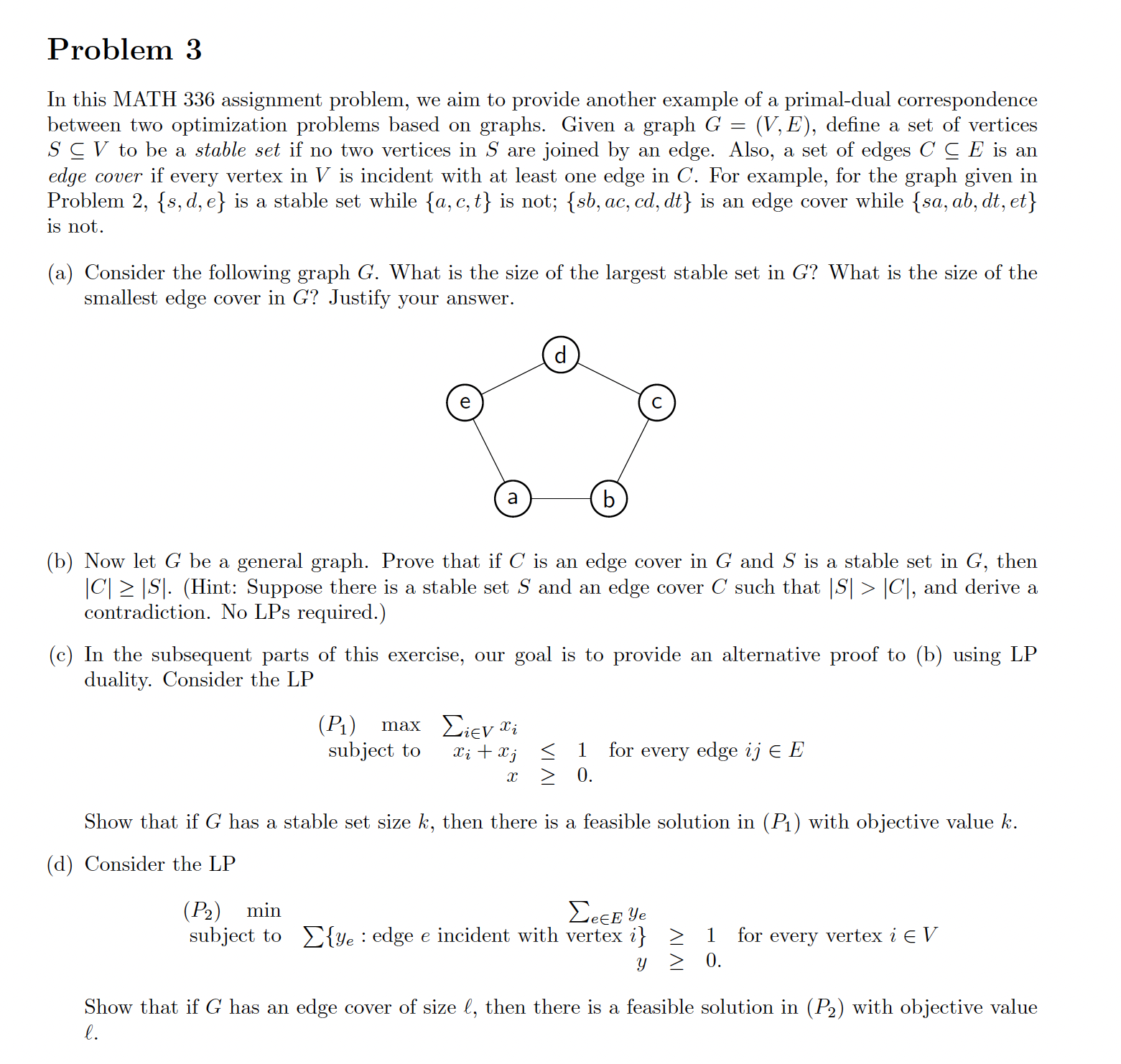

In this MATH 336 assignment problem. consider the following figure, which shows a graph G = Each edge ij E E in the figure is labelled by its cost cij. (V,E). 3 a 4 b 3 6 S t 2 (a) Let (P) be the shortest path LP for G. Write down the constraint in (P) that corresponds to the st-cut 8(U) where U = {s, b}. (b) Let (D) be the dual of (P). Write down the constraint in (D) that corresponds to the edge sb. (c) For each of the following vectors y, decide if it is a feasible set of st-cut widths. Justify your answer. i) ys = 2, ys,a=3, ys,c = 2, and yu = 0 for all other st-cuts (U). = ii) Ys,a 3, Ys,a,b = 3, and yu = 0 for all other st-cuts (U). (d) Solely based on your findings in (c), what can you say about the length of the shortest st-path in G? (You are not actually asked to find the length of a shortest path.) Problem 3 In this MATH 336 assignment problem, we aim to provide another example of a primal-dual correspondence between two optimization problems based on graphs. Given a graph G = (V,E), define a set of vertices SCV to be a stable set if no two vertices in S are joined by an edge. Also, a set of edges C C E is an edge cover if every vertex in V is incident with at least one edge in C. For example, for the graph given in Problem 2, {s, d, e} is a stable set while {a, c,t} is not; {sb, ac, cd, dt} is an edge cover while {sa, ab, dt, et} is not. (a) Consider the following graph G. What is the size of the largest stable set in G? What is the size of the smallest edge cover in G? Justify your answer. d a b (b) Now let G be a general graph. Prove that if C is an edge cover in G and S is a stable set in G, then |C||S|. (Hint: Suppose there is a stable set S and an edge cover C such that |S| > |C|, and derive a contradiction. No LPs required.) (c) In the subsequent parts of this exercise, our goal is to provide an alternative proof to (b) using LP duality. Consider the LP (P1) max iev xi subject to Xixi 1 for every edge ij E X 0. Show that if G has a stable set size k, then there is a feasible solution in (P) with objective value k. (d) Consider the LP (P2) min eE Ye subject to {ye edge e incident with vertex i} > 1 for every vertex i V > 0. Show that if G has an edge cover of size l, then there is a feasible solution in (P2) with objective value l. Show that (P2) is the dual LP of (P1). (Hint: Define matrix A and vectors b, c such that (P1) can be written as and (P2) can be written as max {ex: Ax < b, x>0}, min {by: Arc, y 0}.) (f) Using observations from (c), (d) and (e), give an alternative proof to the statement in (b).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


