Question: #include #include #include int count; int turn = 0; // Shared variable used to implement strict alternation void* myFunction(void* arg) { int actual_arg = *((int*)
#include
int count; int turn = 0; // Shared variable used to implement strict alternation
void* myFunction(void* arg) { int actual_arg = *((int*) arg); for(unsigned int i = 0; i
// Random wait - This code is just to ensure that the threads // show data sharing problems int max = rand() % 100000; for (int x = 0; x
} pthread_exit(NULL); }
// HINT: It is not necessary to make any changes in main() int main() { int rc[2]; pthread_t ids[2]; int args[2]; count = 0; for(unsigned int i = 0; i
i have to write code in area where the have the TODO and the instructions in below
-
A file named pthread-data-sharing-mutex-strict-alternation.cpp has been provided to you in the same project.
-
Compile the program and make sure that it executes.
-
Examine the program code. Note that except for some minor changes, this program is identical to the one you used in Part 2 of this assignment.
-
Modify the program to implement the strict alternation solution to achieve mutual exclusion (refer back to the relevant prep work video/slides if you need to; IMPORTANT NOTE: the outer, infinite while loop in the prep work video/slides is just an example and is not part of the strict alternation solution; only the empty while loop before the call to the critical region and the line immediately following the call to the critical region are part of the strict alternation solution).
Build and execute the updated program several times. Expected Output: Your program should produce the following output (Note: it does not matter whether Thread #0 goes first or Thread #1, but it is important that the threads strictly alternate):
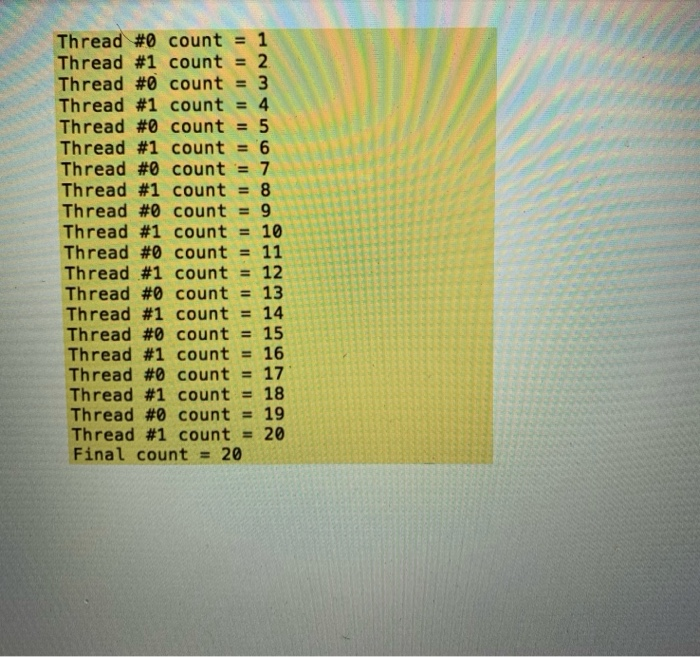
AWN Thread #0 count = Thread #1 count = 2 Thread #0 count = 3 Thread #1 count = 4 Thread #0 count = 5 Thread #1 count = '6 Thread #0 count = 7 Thread #1 count = 8 Thread #0 count = 9 Thread #1 count = Thread #0 count = 11 Thread #1 count = 12 Thread #0 count Thread #1 count = Thread #0 count Thread #1 count Thread #0 count = 17 Thread #1 count = 18 Thread #0 count = 19 Thread #1 count = 20 Final count = 20 || | || | || | || | ||
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


