Question: it is desirable to have a comparison between two regenerative engines, one using a rotating matrix, one using a stationary heat exchanger. to make this
it is desirable to have a comparison between two regenerative engines, one using a rotating matrix, one using a stationary heat exchanger. to make this comparison, calculated the net work, thermal efficiency, and specific fuel consumption for two cycles described. Known Values Pi P P4 P6 P T T Regenerator Effectiveness Compressor Efficiency Rotating Regenerator 14.7 psia (101.3 kPa) 73.5 psia (505.6 kPa) 73.1 psia (503.7 kPa) 72.6 psia (500.3 kPa) 15.3 psia (105.4 kPa) 14.7 psia (101.3 kPa) 519R (288 K) 2160R (1200 K) Stationary Regenerator 14.7 psia (101.3 kPa) 73.5 psia (505.6 kPa) 72.5 psia (499.6 kPa) 72.0 psia (496.2 kPa) 15.8 psia (108.9 kPa) 14.7 psia (101.3 kPa) 519R (288 K) 2160R (1200 K) 75% 85% 90% 90% 0.00% 84% 85% Turbine T, Efficiency 90% 90% Turbine T, Efficiency Leakage 2.5% Turbine T drives the compressor, turbine T delivers power to an external system.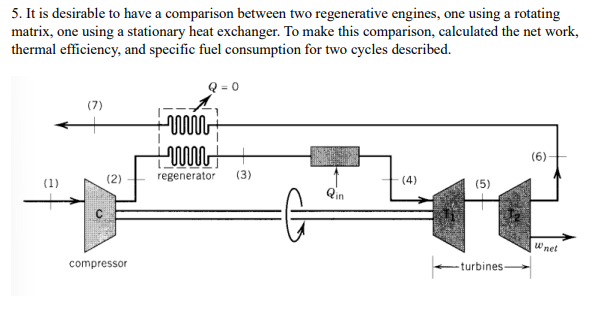
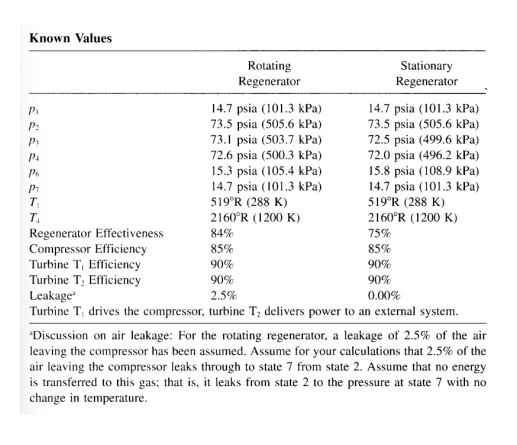
5. It is desirable to have a comparison between two regenerative engines, one using a rotating matrix, one using a stationary heat exchanger. To make this comparison, calculated the net work, thermal efficiency, and specific fuel consumption for two cycles described. 'Discussion on air leakage: For the rotating regenerator, a leakage of 2.5% of the air leaving the compressor has been assumed. Assume for your calculations that 2.5% of the air leaving the compressor leaks through to state 7 from state 2. Assume that no energy is transferred to this gas; that is, it leaks from state 2 to the pressure at state 7 with no change in temperature
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


