Question: *JAVA ONLY* In my attached java file, I completed the code but need help with the syntax errors? import java.text.DecimalFormat; // Abstract class Shape definition
*JAVA ONLY*
In my attached java file, I completed the code but need help with the syntax errors?
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
// Abstract class Shape definition
public abstract class Shape
{
// To store shape name
String name;
// Decimal format for two decimal places
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
// Abstract method declaration
public abstract double area();
// Default constructor
Shape()
{
// Assigns the class name
name = this.getClass().getName();
}// End of constructor
// Parameterized constructor definition
Shape(String name)
{
// Assign parameter data to instance variable name
this.name = name;
}// End of constructor
// Method to return name
String getName()
{
return name;
}// End of method
// Method to set name
void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}// End of method
// Method to return true if both the objects are equal otherwise return false
public boolean equals(Shape s)
{
// Checks parameter object name is equals to the current object name then return true
if(s.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(name) == 0)
return true;
// Otherwise both are not equal return false
else
return false;
}// End of method
// Overrides toString() to return area
public String toString()
{
return " Shape: " + name + " Area = " + df.format(area());
}// End of function
}// End of class
---------------------------------------------------------
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
// Class Rectangle derived from Shape
class Rectangle extends Shape
{
// Instance variable to store data
double length;
double width;
// Default constructor
Rectangle()
{
// Calls base class parameterized constructor
super("Rectangle");
length = width = 1.0;
}// End of constructor
// Parameterized constructor definition
Rectangle(String name, double len, double wid)
{
// Calls base class parameterized constructor
super(name);
length = len;
width = wid;
}// End of constructor
// Method to return length
double getLength()
{
return length;
}// End of method
// Method to return width
double getWidth()
{
return width;
}// End of method
// Method to set length
void setLength(double len)
{
length = len;
}// End of method
// Method to set width
void setWidth(double wid)
{
width = wid;
}// End of method
// Overrides method to calculate and return area
public double area()
{
return (width * length);
}// End of method
// Override method equals() to return true if both the objects are equal otherwise return false
public boolean equals(Rectangle r)
{
// Checks parameter object name is equals to the current object name then return true
if(r.name.compareToIgnoreCase(name) == 0)
return true;
// Otherwise both are not equal return false
else
return false;
}// End of method
// Overrides toString() to return width, length and area
public String toString()
{
return " Width and Length: " + df.format(width) + ", " + df.format(length) + super.toString();
}// End of method
}// End of class
// Driver class RectangleDriver definition
public class RectangleDriver
{
// main method definition
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Decimal format for two decimal places
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
// Creates an object using default constructor
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle();
// Creates an object using parameterized constructor
Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle("Red Rectangle", 12.3, 23.45);
// Displays name, length and width
System.out.print(" Name: " + r1.getName());
System.out.print(" Length: " + df.format(r1.getLength()));
System.out.print(" Width: " + df.format(r1.getWidth()));
// Sets name
r1.setName("Green Rectangle");
// Displays name
System.out.print(" Name: " + r1.getName());
// Sets length
r1.setLength(22.12);
// Displays length
System.out.print(" Length: " + df.format(r1.getLength()));
// Sets width
r1.setWidth(11.12);
// Displays length
System.out.print(" Width: " + df.format(r1.getWidth()));
// Displays area
System.out.print(" Area: " + df.format(r1.area()));
// Displays rectangle one one two object
System.out.print(" Rectangle 1: " + r1);
System.out.print(" Rectangle 2: " + r2);
// Calls the equals() method to compre the objects and displays result
System.out.print(" Rectangle 1 equals to Rectangle 1: " + r1.equals(r1));
System.out.print(" Rectangle 1 equals to Rectangle 2: " + r1.equals(r2));
System.out.print(" Rectangle 1 equals to New Rectangle: " + r1.equals("New Rectangle"));
}// End of main method
}// End of driver class RectangleDriver
--------------------------------------------------------------
Sample Output:
Name: Rectangle Length: 1.00 Width: 1.00 Name: Green Rectangle Length: 22.12 Width: 11.12 Area: 245.97 Rectangle 1: Width and Length: 11.12, 22.12 Shape: Green Rectangle Area = 245.97 Rectangle 2: Width and Length: 23.45, 12.30 Shape: Red Rectangle Area = 288.44 Rectangle 1 equals to Rectangle 1: true Rectangle 1 equals to Rectangle 2: false Rectangle 1 equals to New Rectangle: false
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
class Circle extends Shape
{
// Instance variable to store data
double radius;
// Default constructor
Circle()
{
// Calls base class parameterized constructor
super("Circle");
radius = 1.0;
}// End of constructor
// Parameterized constructor definition
Circle(String name, double r)
{
// Calls base class parameterized constructor
super(name);
radius = r;
}// End of constructor
// Method to return radius
double getRadius()
{
return radius;
}// End of method
// Method to set radius
void setRadius(double r)
{
radius = r;
}// End of method
// Method to calculate and return area
public double area()
{
return (3.141 * radius * radius);
}// End of method
// Override method equals() to return true if both the objects are equal otherwise return false
public boolean equals(Rectangle r)
{
// Checks parameter object name is equals to the current object name then return true
if(r.name.compareToIgnoreCase(name) == 0)
return true;
// Otherwise both are not equal return false
else
return false;
}// End of method
// Overrides toString() to return radius and area
public String toString()
{
return " Radius: " + df.format(radius) + super.toString();
}// End of method
}// End of class
// Driver class CircleDriver definition
public class CircleDriver
{
// main method definition
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Decimal format for two decimal places
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
// Creates an object using default constructor
Circle c1 = new Circle();
// Creates an object using parameterized constructor
Circle c2 = new Circle("Blue Circle", 1.5);
// Displays name and radius
System.out.print(" Name: " + c1.getName());
System.out.print(" Length: " + df.format(c1.getRadius()));
// Sets name
c1.setName("Green Circle");
// Displays name
System.out.print(" Name: " + c1.getName());
// Sets radius
c1.setRadius(11.15);
// Displays radius
System.out.print(" Length: " + df.format(c1.getRadius()));
// Displays area
System.out.print(" Area: " + df.format(c1.area()));
// Displays two objects
System.out.print(" Circle 1: " + c1);
System.out.print(" Circle 2: " + c2);
// Calls the equals() method to compre the objects and displays result
System.out.print(" Circle 1 equals to Circle 1: " + c1.equals(c1));
System.out.print(" Circle 1 equals to Circle 2: " + c1.equals(c2));
System.out.print(" Circle 1 equals to New Circle: " + c1.equals("New Circle"));
}// End of main method
}// End of driver class CircleDriver
Sample Output:
Name: Circle Length: 1.00 Name: Green Circle Length: 11.15 Area: 390.50 Circle 1: Radius: 11.15 Shape: Green Circle Area = 390.50 Circle 2: Radius: 1.50 Shape: Blue Circle Area = 7.07 Circle 1 equals to Circle 1: true Circle 1 equals to Circle 2: false Circle 1 equals to New Circle: false
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
class Triangle extends Shape
{
// Instance variable to store data
double sideOne;
double sideTwo;
double sideThree;
// Default constructor
Triangle()
{
// Calls base class parameterized constructor
super("Triangle");
sideOne = sideTwo = sideThree = 1.0;
}// End of constructor // Parameterized constructor definition
Triangle(String name, double sOne, double sTwo, double sThree)
{
// Calls base class parameterized constructor
super(name);
try
{
if((sOne + sTwo) > sThree && (sOne + sThree) > sTwo && (sTwo + sThree) > sOne)
{
sideOne = sOne; sideTwo = sTwo; sideThree = sThree;
}// End of if condition
else
throw new InvalidTriangleException("Invalid Triangle");
}// End of try
catch(InvalidTriangleException ex)
{ sideOne = sideTwo = sideThree = 1.0;
ex.printStackTrace();
}// End of catch
catch(Exception ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}// End of catch }// End of constructor // Method to return side one
double getSideOne()
{
return sideOne; }// End of method // Method to return side two
double getSideTwo()
{
return sideTwo;
}// End of method // Method to return side three
double getSideThree()
{
return sideThree;
}// End of method // Method to set side one
void setSideOne(double side)
{
try
{
if((side + sideTwo) > sideThree && (side + sideThree) > sideTwo && (sideTwo + sideThree) > side)
sideOne = side;
else
throw new InvalidTriangleException("Invalid Triangle");
}// End of try
catch(InvalidTriangleException ex)
{
sideOne = sideTwo = sideThree = 1.0;
ex.printStackTrace(); }// End of catch }// End of method // Method to set side two
void setSideTwo(double side)
{
try
{
if((sideOne + side) > sideThree && (sideOne + sideThree) > side && (side + sideThree) > sideOne)
sideTwo = side;
else
throw new InvalidTriangleException("Invalid Triangle");
} // End of try
catch(InvalidTriangleException ex)
{
sideOne = sideTwo = sideThree = 1.0;
ex.printStackTrace(); }// End of catch }// End of method // Method to set side three
void setSideThree(double side)
{
try
{
if((sideOne + sideTwo) > side && (sideOne + side) > sideTwo && (sideTwo + side) > sideOne)
sideThree = side;
else
throw new InvalidTriangleException("Invalid Triangle");
} // End of try
catch(InvalidTriangleException ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}// End of catch }// End of method // Method to calculate and return area
public double area()
{
double s = (sideOne + sideTwo + sideThree);
return (Math.sqrt(s * (s - sideOne) * (s - sideTwo) * (s - sideThree)));
}// End of method // Override method equals() to return true if both the objects are equal otherwise return false
public boolean equals(Triangle t)
{
// Checks parameter object name is equals to the current object name then return true
if(t.name.compareToIgnoreCase(name) == 0)
return true;
// Otherwise both are not equal return false
else
return false;
}// End of method // Overrides toString() to return side one, two, three and area
public String toString()
{
return " Side One: " + df.format(sideOne) + " Side Two: " + df.format(sideTwo) +
" Side Three: " + df.format(sideThree) + super.toString();
}// End of method }// End of class
//Driver class TriangleDriver definition
public class TriangleDriver
{
// main method definition
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Decimal format for two decimal places
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
// Creates an object using parameterized constructor Triangle t1 = new Triangle("Black Triangle", 2.5, 3.5, 7.5); Triangle t2 = new Triangle("Red Triangle", 3.5, 1.5, 3.5); // Displays name, side one, two, and three
System.out.print(" Name: " + t1.getName()); System.out.print(" Side One: " + df.format(t1.getSideOne())); System.out.print(" Side Two: " + df.format(t1.getSideTwo())); System.out.print(" Side Three: " + df.format(t1.getSideThree()));
// Sets name
t1.setName("Green Triangle");
// Displays name
System.out.print(" Name: " + t1.getName());
// Sets side one
t1.setSideOne(1.15);
// Displays side one
System.out.print(" Side One: " + df.format(t1.getSideOne()));
// Sets side one with invalid side
t1.setSideOne(21.15);
// Displays side one
System.out.print(" Side One: " + df.format(t1.getSideOne()));
// Sets side two
t1.setSideTwo(1.25);
// Displays side two
System.out.print(" Side Two: " + df.format(t1.getSideTwo()));
// Sets side one with invalid side
t1.setSideTwo(21.15);
// Displays side two
System.out.print(" Side Two: " + df.format(t1.getSideTwo()));
// Sets side three
t1.setSideThree(2.15);
System.out.print(" Side Three: " + df.format(t1.getSideThree()));
// Sets side one with invalid side
t1.setSideThree(21.15);
// Displays side three
System.out.print(" Side Three: " + df.format(t1.getSideThree()));
// Displays area
System.out.print(" Area: " + df.format(t1.area()));
// Displays two objects System.out.print(" Triangle 1: " + t1);
System.out.print(" Triangle 2: " + t2);
// Calls the equals() method to compare the objects and displays result
System.out.print(" Triangle 1 equals to Triangle 1: " + t1.equals(t1));
System.out.print(" Triangle 1 equals to Triangle 2: " + t1.equals(t2));
System.out.print(" Triangle 1 equals to New Triangle: " + t1.equals("New Circle"));
} // End of main method
} // End of driver class TriangleDriver
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Class InvalidTriangleException derived from class Exception
public class InvalidTriangleException extends Exception
{
// Parameterized constructor to display error message
InvalidTriangleException(String message)
{
// Calls the base class parameterized constructor
super(message);
} // End of constructor
} // End of class
Sample Output:
inheritance.InvalidTriangleException: Invalid Triangle
at inheritance.Triangle.
at inheritance.TriangleDriver.main(TriangleDriver.java:151)
Name: Black Triangle
Side One: 1.00
Side Two: 1.00
Side Three: 1.00
Name: Green Triangle
Side One: 1.15inheritance.InvalidTriangleException: Invalid Triangle
at inheritance.Triangle.setSideOne(TriangleDriver.java:73)
at inheritance.TriangleDriver.main(TriangleDriver.java:171)
Side One: 1.00
Side Two: 1.25inheritance.InvalidTriangleException: Invalid Triangle
at inheritance.Triangle.setSideTwo(TriangleDriver.java:90)
at inheritance.TriangleDriver.main(TriangleDriver.java:181)
Side Two: 1.00inheritance.InvalidTriangleException: Invalid Triangle
at inheritance.Triangle.setSideThree(TriangleDriver.java:107)
at inheritance.TriangleDriver.main(TriangleDriver.java:186)
Side Three: 1.00inheritance.InvalidTriangleException: Invalid Triangle
at inheritance.Triangle.setSideThree(TriangleDriver.java:107)
at inheritance.TriangleDriver.main(TriangleDriver.java:190)
Side Three: 1.00
Area: 4.90
Triangle 1:
Side One: 1.00
Side Two: 1.00
Side Three: 1.00
Shape: Green Triangle Area = 4.90
Triangle 2:
Side One: 3.50
Side Two: 1.50
Side Three: 3.50
Shape: Red Triangle Area = 38.57
Triangle 1 equals to Triangle 1: true
Triangle 1 equals to Triangle 2: false
Triangle 1 equals to New Triangle: false
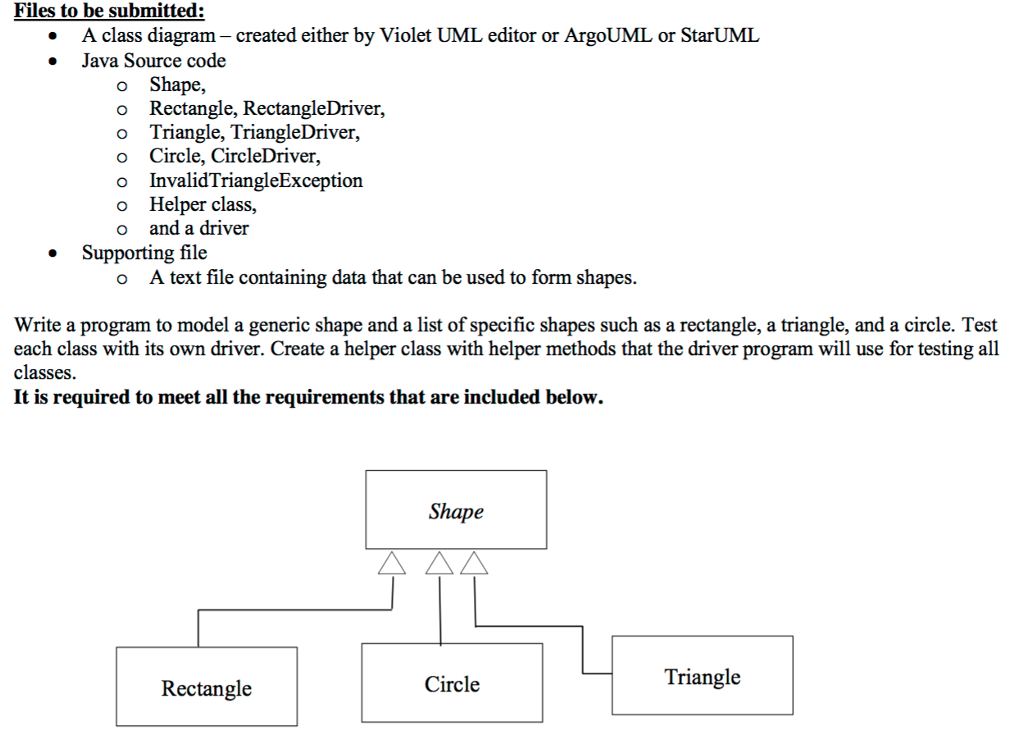
Files to be submitted: . A class diagram - created either by Violet UML editor or ArgoUML or StarUML Java Source code o Shape o Rectangle, RectangleDriver, o Triangle, TriangleDriver, o Circle, CircleDriver, o InvalidTriangleException o Helper class, o and a driver Supporting file o A text file containing data that can be used to form shapes. Write a program to model a generic shape and a list of specific shapes such as a rectangle, a triangle, and a circle. Test each class with its own driver. Create a helper class with helper methods th classes. It is required to meet all the requirements that are included below. at the driver program will use for testing all Shape Triangle Rectangle Circle
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


