Question: Kindle Classic File Edit View Go Tools Help Q Thu Sep 5 12:29 PM ... shauna's Kindle for Mac 2 - Making the Team Library



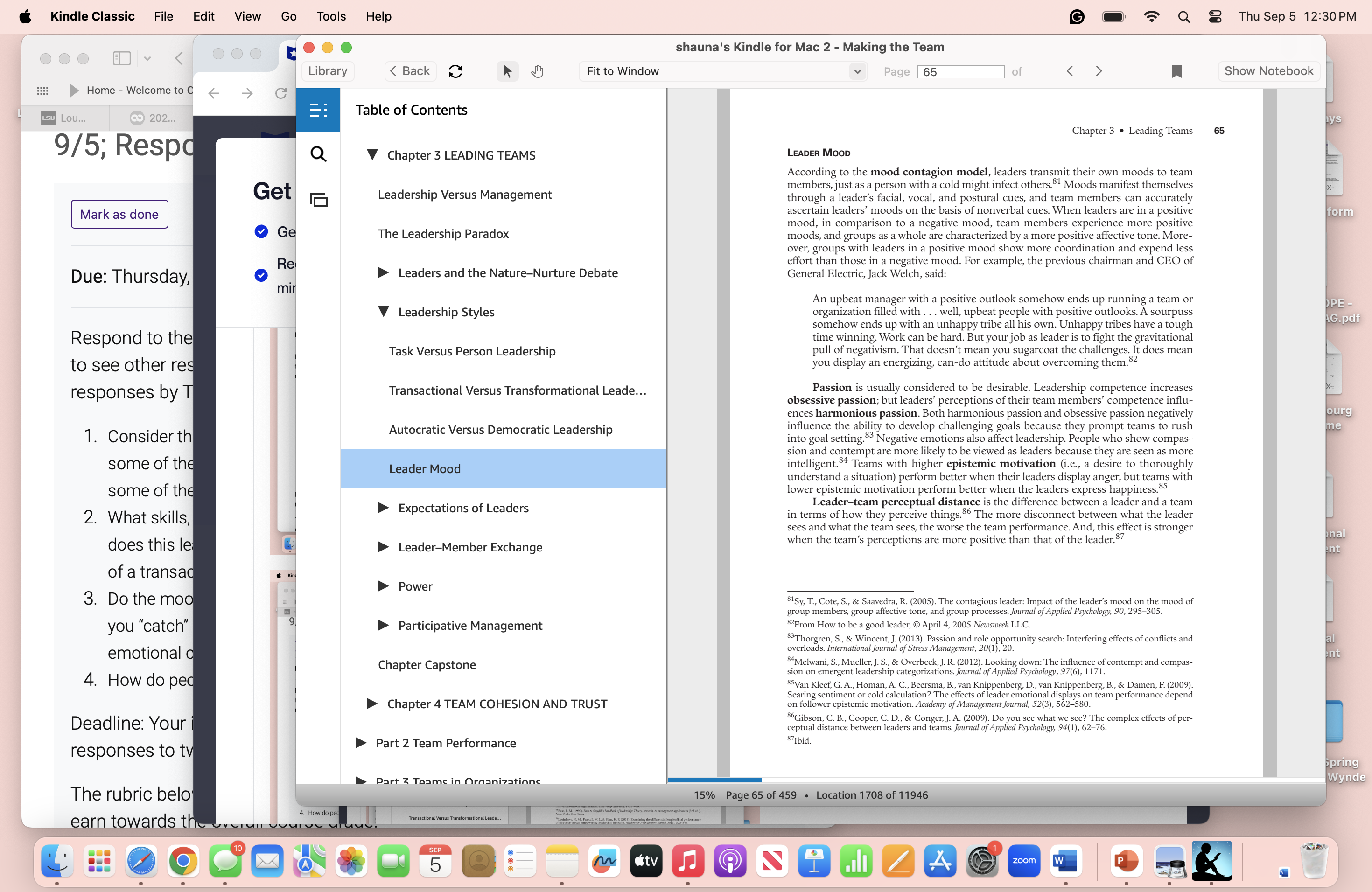
Kindle Classic File Edit View Go Tools Help Q Thu Sep 5 12:29 PM ... shauna's Kindle for Mac 2 - Making the Team Library Show Notebook Home - Welcome to Charter y! Yahoo! LSU Lou .. G 202 ... Module . . E: Table of Contents ys Chapter 3 . Leading Teams 59 9/5; Responses to a Task Focus Types of Team Autonomy Country Club Team HIGH Manager Manager Mark as done (High People - Low Task) High People - High Task) form Observations About Teams and Teamwork Middle of Road Manager What Leaders Tell Us About Their Teams ( Medium People and Task) People Concern Due: Thursday, September 5 Focus on work outpu as well as Developing Your Team-Building Skills employee morale PE - G.pdf Respond to the questions in mpoverished Authority-Obedience A Warning LOW Manager Manager (Low People - Low Task) (Low People - High Task) to see other responses from Chapter Capstone responses by Thursday and Task Concern LOW HIGH Chapter 2 DESIGNING THE TEAM ourg Exhibit 3-3 Managerial Grid me 1. Consider the different lead Based on Blake, R.R., & Mouton, J.S. (1964). The managerial grid. Houston, TX: Gulf, @ Leigh L. Thompson. some of the representativ Chapter 3 LEADING TEAMS transactional. The corporate world and popular business presses have coined even more some of the benefits and varieties of leadership-often branding them with a particularly influential individual's Leadership Versus Management name, such as the "Jack Welch lexicon of leadership" or the "Warren Buffet CEO."48 2. What skills, behaviors, and Consider the following leadership styles as choices leaders can make. The Leadership Paradox TASK VERSUS PERSON LEADERSHIP does this leadership style nal Leaders vary in terms of how much they focus on the people (relationships) and the ent of a transactional leaders task."(See Exhibit 3-3.) Task-oriented leaders focus on accomplishing the objectives Leaders and the Nature-Nurture Debate of the team; relationship-oriented leaders focus on the people. Person-focused leaders 3. Do the moods and emotic allow members of their team more freedom in their work, permit team members to use their own judgment in solving problems, and grant members authority. Conversely dership St you "catch" other people's task-oriented leaders typically act as the spokesperson of their group, push for more work and higher production, and determine what should be done and how it should be accomplished. Ideally, leaders who focus on getting the work done and supporting emotional contagion? Task Versus Person Leadership 4. How do people who work 47Krames, J. A. (2001). The Jack Welch lexicon of leadership: Over 250 terms, concepts, strategies & initiatives of the legendary leader. New York: McGraw-Hill. Transactional Versus Transformational Leade... 48 Miles, R. P., & Osborne, T. (2001). The Warren Buffett CEO: Secrets of the Berkshire Hathaway managers. New York: John Wiley & Sons. Deadline: Your initial respon 49 Blake, R.R., & Mouton, J.S. (1964). The managerial grid. Houston, TX: Gulf. Autocratic Versus Democratic Leadership 50 Sergiovanni, T.J., Metzcus, R., & Burden, L. (1969). Toward a particularistic approach to leadership style: Some finds. American Educational Research Journal, 6, 62-79. responses to two of your cla spring Leader Mood Wynde The rubric below outlines the 14% Page 59 of 459 . Location 1576 of 11946 earn towards the overall course arade. stv 4 zoom w KKindle Classic File Edit View Go Tools Help Q Thu Sep 5 12:30 PM shauna's Kindle for Mac 2 - Making the Team Library Show Notebook Home - Welcome to C C LSU LOU .. 202. Table of Contents ys 60 Part 1 . Building the Team 9/5; Respo Task Focus their people are team leaders. Leaders who are accountable are more team-oriented, particularly when they identify with their team.$1 Get Types of Team Autonomy TRANSACTIONAL VERSUS TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP Mark as done The transactional versus transformational paradigm views leadership as either a matter form Ge Observations About Teams and Teamwork of contingent reinforcement of followers or the moving of followers beyond their self- interests for the good of the team, organization, or society. Transformational leader- ship (TFL) is developmental and usually begins with a transactional approach. At a Re What Leaders Tell Us About Their Teams basic level, leaders and their teams are in an exchange relationship that involves negotia- Due: Thursday tion to establish outcomes and rewards." A psychological contract is a person's belief mir in mutual obligations between that person and another party, such as an employer or Developing Your Team-Building Skills leader. $4 PE In contrast, transactional leadership depends on the leader's power to reinforce subordinates (team members) for their successful completion of the bargain (task). G.pdf Respond to the A Warning However, this type of leadership sets up a competitive relationship: "If you limit yourself 1. Ask to transactional leadership of a follower with rewards of carrots for compliance, or pun- to see other res ishments with a stick for failure to comply with agreed-on work to be done by the fol- Chapter Capstone lower, the follower will continue to feel like a jackass."$5 responses by T B ADVANTAGES Transformational leaders motivate their teams to work toward goals that go beyond immediate self-interest, and motivate their teams to do more than they origi- ourg Chapter 2 DESIGNING THE TEAM nally expected to do as they strive for higher-order outcomes. In an investigation of ne 1. Consider th the performance of 118 R&D project teams from five companies, transformational lead- some of the Chapter 3 LEADING TEAMS ership predicted technical quality, schedule performance, and cost performance 1 year later, and profitability and speed-to-market 5 years later. Teams with transformational leaders have higher teamwork quality and more inter-team collaboration. TFL is asso- some of the ciated with a more positive effect on teams, enhancing resilience, learning goal Leadership Versus Management 2. What skills does this le The Leadership Paradox nal $1 Giessner, S. R., van Knippenberg, D., van Ginkel, W., & Sleebos, E. (2013). Team-oriented leadership: The ent interactive effects of leader group prototypicality, accountability, and team identification. Journal of Applied of a transad Leaders and the Nature-Nurture Debate Psychology, 98(4), 658. $2Bass, B. M. (1985). Leadership and performance beyond expectations. New York: Free Press; Burns, J. M. (1978). 3. Do the moo Leadership. New York: Harper & Row; Hollander, E. P. (1964). Leaders, groups, and influence. New York: Oxford University Press. 53 Hollander, E. P. (1986). On the central role of leadership processes. International Review of Applied Psychology, you "catch" Leadership Styles 35, 39-52. 5Rousseau, D. M., & Tijoriwala, S. A. (1998). Assessing psychological contracts: Issues, alternatives, and emotional a Task Versus Person Leadership measures. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 19, 679-695. $5 From Power, leadership, and the management of stress by Harry Levinson, 1980 Professional Psychology. 4. How do ped Burns, J. M. (1978). Leadership. New York: Harper & Row. Transactional Versus Transformational Leade... 57Keller, R. T. (2006). Transformational leadership, initiating structure, and substitutes for leadership: A lon- gitudinal study of research and development project team performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(1), 202-210. Deadline: Your 58Cha, J., Kim, Y., Lee, J. Y., & Bachrach, D. G. (2015). Transformational leadership and inter-team collabora- Autocratic Versus Democratic Leadership ion exploring the mediating role of teamwork quality and moderating role of team size. Group & Organization Management, 40(6), 715-743. responses to tv spring Leader Mood Wynde The rubric belo 14% Page 60 of 459 . Location 1592 of 11946 earn towards the rerun ceria and drop images or Unload :tv 4 zoom W@& KindleClassic File Edit View Go Tools Help & ThuSep5 12:30PM M~ S ) Home-WelcometoC 5 (3 | B Lou.. 202.. | 9/5; Respd Due: Thursday, Respond to the to see other reg responses by 1. Consider th some of th some of th 2. What skills, does this le of a transad 3. Do the moo =4 you \"catch\" emotional g 4. How do ped Deadline: Your responses to t E.('). Library Observations About Teams and Teamwork P> What Leaders Tell Us About Their Teams P Developing Your Team-Building Skills A Warning Chapter Capstone P> Chapter 2 DESIGNING THE TEAM V Chapter 3 LEADING TEAMS Leadership Versus Management The Leadership Paradox P> Leaders and the Nature-Nurture Debate V Leadership Styles Task Versus Person Leadership Transactional Versus Transformational Leade... Autocratic Versus Democratic Leadership Leader Mood Part 1 o Building the Team agreeableness, extraversion, and greater conscientiousness. Transformational leadership has a positive impact on team performance because teams trust their leaders.\" DISADVANTAGES Group-focused transformational leadership has a positive impact on team innovation, but a negative impact on individual motivation.\"! In some instances, transformational leadership can have a dark side, such as when a charismatic leader, like Jim Jones, motivates people to do something that is lethal.\"? (See Exhibit 3-4.) Leaders who exhibit antinormative behaviors are judged more positively and given more credit relative to antinormative team members, ex-leaders, and established leaders.\" Moreover, under some conditions, charismatic leaders promote disenchantment among team members. The hypocrisy attribution dynamic refers to the tendency for team members to draw sinister conclusions about a leader's behavior.\" This can happen when employees are prompted to engage in sensemaking in strong value-driven organizations. AUTOCRATIC VERSUS DEMOCRATIC LEADERSHIP Another view of leadership focuses on a continuum of behavior ranging from entirely autocratic to purely democratic.\" Also known as vertical leadership (emanating from the top down), this type of leadership stems from an appointed or formal leader of a team, whereas shared leadership is a group process in which leadership is distributed among, and stems from, team members. Autocratic leadership is displayed by leaders who seek sole possession of authority, power, and control, whereas democratic leader- ship is displayed by leaders who share authority, power, and control with their team. Initially, teams led by a directive leader outperform those led by an empowering leader. However over time, empowering leaders instigate more improvement via increased team learning, coordination, and mental model development.\" In one investigation, the effectiveness of 71 change management teams in companies was examined as a function of vertical versus shared leadership.\"\" Shared leadership significantly predicted team 70Schaubroeck, J., Lam, S. S., & Peng, A. C. (2011). Cognition-based and affect-based trust as mediators of leader behavior influences on team performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96(4), 863-871. 7ILi, V., Mitchell, R., & Boyle, B. (2016). The divergent effects of transformational leadership on individual and team innovation. Group & Organization Management, 41(1), 66-97. Hogan, R., Raskin, R., & Fazzini, D. (1990). The dark side of charisma. In K. E. Clark & M. B. Clark (Eds)), Measures of leadership (pp. 343-354). West Orange, NJ: Leadership Library of America. 7Abrams, D., De Moura, G. R., Marques, J. G., & Hutchison, P. (2008). Innovation credit: When can leaders oppose their group's norms? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95(3), 662-678. 74Cha, S. E., & Edmondson, A. C. (2006). When values backfire: Leadership, attribution, and disenchantment in a values-driven organization. Leadership Quarterly, 17, 57-78. 7SBass, B. M. (1990). Bass & Stogdill's handbook of leadership: Theory, research, & management applications (3rd ed.). New York: Free Press. \"SLorinkova, N. M., Pearsall, M. J., & Sims, H. P. (2013). Examining the differential longitudinal performance o directive versus empowering ieadership in teams. Academy of Management Journal, 56(2), 573-596. TPearce, C. L., & Sims, Jr., H. P. (2002). Vertical versus shared leadership as predictors of the effectiveness of change management teams: An examination of aversive, directive, transactional, transformational and empowering leader behaviors. Group Dynamics: Theory, Rescarch, and Practics, 6(2), 172-197. @& KindleClassic File Edit View Go Tools Help [=) o Thu Sep 5 12:30PM M~ S b Eou.. 202 | 9/5; Respd Due: Thursday, Respond to the to see other reg responses by 1. Consider th some of th some of th 2. What skills, does this le of a transad 3. Do the moo you \"catch\" emotional g 4. How do ped Deadline: Your responses to t ) Home - WelcometoC C\" shauna's Kindle for Mac 2 - Making the Team v Page [65 4> N Show Notebook [ o Library Expectations of Leaders P Leader-Member Exchange Power Pai Chapter Capstone P> Chapter 4 TEAM COHESION AND TRUST P> Part 2 Team Performance P> Leaders and the Nature-Nurture Debate pative Management B Dart 2 Taamc in Nraanizatinne Chapter 3 * Leading Teams Leaber Moop According to the mood contagion model, leaders transmit their own moods to team members, just as a person with a cold might infect others.! Moods manifest themselves through a leader's facial, vocal, and postural cues, and team members can accurately ascertain leaders' moods on the basis of nonverbal cues. When leaders are in a positive mood, in comparison to a negative mood, team members experience more positive moods, and groups as a whole are characterized by a more positive affective tone. More- over, groups with leaders in a positive mood show more coordination and expend less effort than those in a negative mood. For example, the previous chairman and CEO of General Electric, Jack Welch, said: An upbeat manager with a positive outlook somehow ends up running a team or organization filled with . . . well, upbeat people with positive outlooks. A sourpuss somehow ends up with an unhappy tribe all his own. Unhappy tribes have a tough time winning. Work can be hard. But your job as leader is to fight the gravitational pull of negativism. That doesn't mean you sugarcoat the challenges. It does mean you display an energizing, can-do attitude about overcoming them.*? Passion is usually considered to be desirable. Leadership competence increases obsessive passion; but leaders' perceptions of their team members' competence influ- ences harmonious passion. Both harmonious passion and obsessive passion negatively influence the ability to develop challenging goals because they prompt teams to rush into goal setting.** Negative emotions also affect leadership. People who show compas- sion and contempt are more likely to be viewed as leaders because they are seen as more intelligent.** Teams with higher epistemic motivation (i.c., a desire to thoroughly understand a situation) perform better when their leaders display anger, but teams with lower epistemic motivation perform better when the leaders express happiness.S Leader-team perceptual distance is the difference between a leader and a team in terms of how they perceive things.3 The more disconnect between what the leader sees and what the team sees, the worse the team performance. And, this effect is stronger when the team's perceptions are more positive than that of the leader.\" 818y, T,, Cote, S., & Saavedra, R. (2005). The contagious leader: Impact of the leader's mood on the mood of 'group members, group affective tone, and group processes. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90, 295-305. $2From How to be a good leader, April 4, 2005 Newsweek LLC. 53Thorgren, S., & Wincent, J. (2013). Passion and role opportunity search: Interfering effects of conflicts and overloads. International Journal of Stress Management, 20(1), 20, $4Melwani, S. ,Mueller, ]. S., & Overbeck, . R. (2012). Looking down: The influence of contempt and compas- sion on emergent leadership categorizations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 97(6), 1171. $5Van Kleef, G. A., Homan, A. C., Beersma, B., van Knippenberg, D., van Knippenberg, B, & Damen, F. (2009). Searing sentiment or cold calculation? The effects of leader emotional displays on team performance depend on follower epistemic motivation. Academy of Management Journal, 52(3), 562-580. 8Gibson, C. B., Cooper, C. D., & Conger, J. A. (2009). Do you see what we see? The complex effects of per- ceptual distance between leaders and teams. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(1), 62-76
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


