Question: Kitchen Electronics has budgeted up to $8000 per week for local advertising. The money is allocated among four promotional media: TV spots, newspaper ads, and
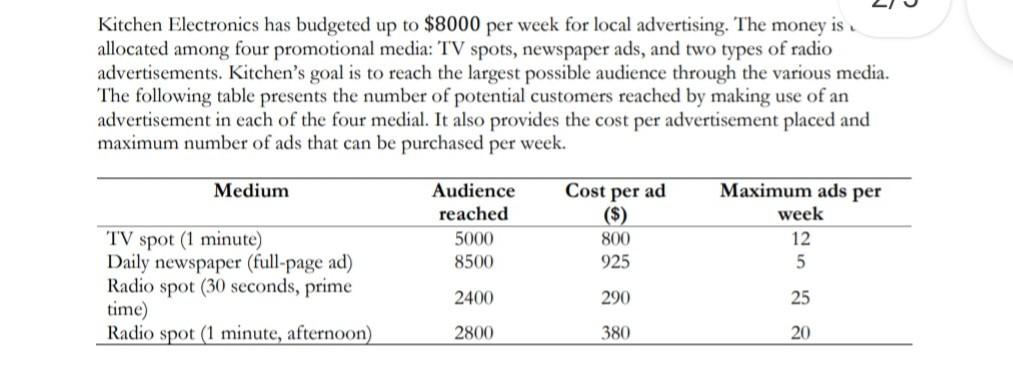

Kitchen Electronics has budgeted up to $8000 per week for local advertising. The money is allocated among four promotional media: TV spots, newspaper ads, and two types of radio advertisements. Kitchen's goal is to reach the largest possible audience through the various media. The following table presents the number of potential customers reached by making use of an advertisement in each of the four medial. It also provides the cost per advertisement placed and maximum number of ads that can be purchased per week. Medium Audience reached 5000 8500 Cost per ad ($) 800 925 Maximum ads per week 12 5 TV spot (1 minute) Daily newspaper (full-page ad) Radio spot (30 seconds, prime time) Radio spot (1 minute, afternoon) 2400 290 25 2800 380 20 Kitchen's contractual arrangements require that at least five radio spots be placed each week. To ensure a broad-scoped promotional camping, management also insists that no more than $1800 be spent on radio advertising every week. The problem is formulated as a LP model below. Maximize audience coverage = 5000T + 8500 N + 2400P + 2800A Subject to: T = 5 (maximum radio spots contracted) 290P + 380A = 0 Use the sensitivity report for this LP model (shown in screenshot below) to answer the following questions. Each question is independent of the others. Note: you are encouraged to use the Excel Solver to solve the model and get the solution report and the sensitivity analysis report (as shown below). Adjustable Cells Final Reduced Objective Allowable Allowable Cell Name Value Cost Coefficient Increase Decrease $B$5 Number of Units TV spots 1.97 0.00 5000.00 1620.69 5000.00 $C$5 Number of Units Newspaper ads 5.00 0.00 8500.00 1E+30 2718.75 $D$5 Number of Units Prime-time radio spots 6.21 0.00 2400.00 1E+30 263.16 $E$5 Number of Units Afternoon radio spots 0.00 -344.83 2800.00 344.83 1E+30 Constraints Cell Name $F$14 Min Radio Spots $F$8 Max TV $F$9 Max Newspaper $F$10 Max Prime-Time Radio $F$11 Max Afternoon Radio $F$12 Budget $F$13 Max Radio $ Final Shadow Constraint Allowable Allowable Value Price R.H. Side Increase Decrease 6.21 0.00 5.00 1.21 1E+30 1.97 0.00 12.00 1E+30 10.03 5.00 2718.75 5.00 1.70 5.00 6.21 0.00 25.00 1E+30 18.79 0.00 0.00 20.00 1E+30 20.00 $8,000.00 $6.25 8000.00 8025.00 1575.00 $1,800.00 $2.03 1800.00 1575.00 350.00 (a) What would be the impact if management approved spending $200 more on radio advertising each week? (b) Would it help Kitchen if it could get out of the contractual agreement to place at least five radio spots each week? (c) The radio station manager agrees to run the afternoon radio spots during some of the more popular programs. He thinks this will increase the audience reached per ad to 3100. Will this change the optimal solution? Why or why not? (d) There is some uncertainty in the audience reached per TV spot. For what range of values of this OFC, will the current solution remain optimal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


