Question: La b Assignments for Chapter 2 We have created six lab assignments for this chapter: Lab2-1 to Lab2-6. We have also included six lab-report sheets,
Lab Assignments for Chapter 2
We have created six lab assignments for this chapter: Lab2-1 to Lab2-6. We have also included six lab-report sheets, which means that each lab assignment needs to be reported in a separate sheet. The six lab assignments are related to six application-layer protocols we discussed in this chapter. The lab assignment for SSH protocol has been moved to Chapter 10 because it involves security issues. It is strongly recommended that the student carefully study and digest the corresponding protocols before working on the related lab assignment. It is necessary that the student carefully study the instructions in the lab assignment for Chapter 1 before starting this assignment.
Lab2-3: TELNET
Using a virtual terminal connection, TELNET provides remote logging, an interactive text-oriented communications between a user and a remote server, over TCP. The best way to capture packets exchanged between your computer and a remote host is to use a client GUI TELNET program. We recommend to use PuTTY, which is a free software and can be downloaded from
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
Save the putty.exe file on your computer (no installation needed). Figure 2.2 shows a sample of PuTTY configuration window.
To access a remote site (which you need to have account and password), type the host name or the IP address of the remote host in the corresponding box and choose Telnet as the connection type (using the corresponding radio button). Then click the
Open button to connect to the site. After the connection has been established, type your username when prompted for it. Then type your password when prompted. When you see the prompt for the Unix or Linux (for example, $), the remote host is ready to accept your commands. There is a long list of Unix or Linux commands, but we give only a few of them in Table 2.2 if you are not familiar with them.
Assignment
Open Wireshark and start capturing.
Start a TELNET client session from PuTTY. Connect to the remote site, login, and execute a few Unix/Linux commands.
Close the TELNET connection (quit) and return to Wireshark. Stop capturing and save the captured file.
Part I: General
Examining the captured file, you will notice several TELNET packets as well as many
TCP packets that are used to establish and terminate TELNET connection.
Questions
Using the captured information, answer the following question in your lab-report sheet.
1. Identify the three TCP packets used for connection establishment.
2. Identify the TCP packets used for connection termination?
Part II: Negotiation
Before (or during) a session the TENET client and server negotiate some options and suboptions. Some common options are Binary, Echo, Terminal type, Terminal speed, and Line mode (Check the Internet to learn about more TELNET options and subop- tions). TELNET allows each party (sender or receiver) to enable or disable an option.
Offer to Enable. The sender can use WILL command to offer enabling an option.
The receiver can agree with DO response or disagree with DONT response.
Request to Enable. The sender can use DO command to request the receiver to enable an option. The receiver can agree with WILL response or disagree with WONT response.
Offer to Disable The sender can use WONT command to offer disabling an option.
The receiver must agree with the DONT command.
Request to Disable The sender can use DONT command to request disabling an option. The receiver must agree with the WONT command.
Some options negotiation require additional information that are called suboptions negotiation. For example, to define the Terminal type or speed, the negotiation must include a string or a number.
Questions
Using the captured information, answer the following question in your lab-report sheet.
1. Check packets that have option negotiation. What options are negotiated?
2. Is the option offered or requested by the sender?
3. What is the response of the receiver to option negotiation?
Part III: Session
After negotiation, the TELNET session starts.
Questions
Using the captured information, answer the following question in your lab-report sheet.
1. How many packets are exchanged for remote login? What is the exchanged infor- mation?
2. Is the user name or password encrypted? What can you say about the security of
TELNET?
3. What packet is used to terminate the TELNET session?
4. Select Analyze from the drop down menu and then click Follow TCP stream.
What are the contents of the Follow TCP stream window?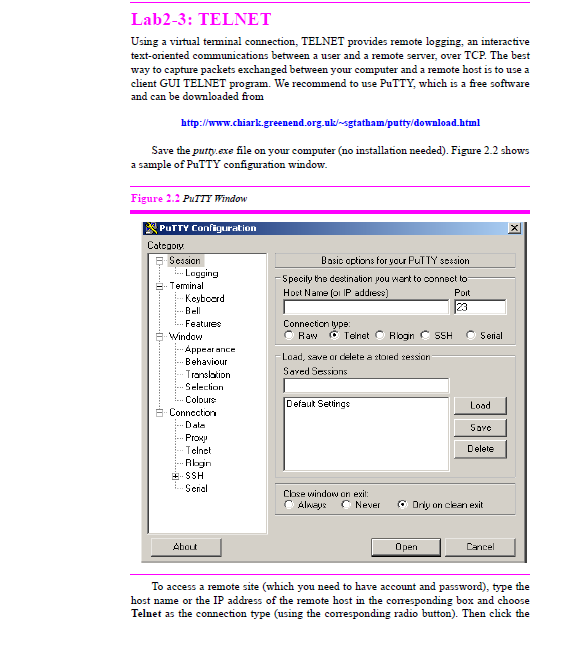
Lab2-3: TELNET Using a virtual terminal connection, TELNET provides remote logging, an interactive text-oriented communications between a user and a remote server, over TCP. The best way to capture packets exchanged between your computer and a remote host is to use a client GUI TELNET program. We recommend to use PuTTY, which is a firee software and can be downloaded from http://www.chiarkgreenend.org.uk-sgtatham/putty/download.html Save the putty exe file on your computer (no installation needed). Figure 2.2 shows a sample of PuTTY configuration window Figure 2.2 PuIII Window PuTTY Configuration Catcooy Basic optizns for your PuTTY session Specily the deetination you wart to connect to Poit 23 Session Logging .. Terminal Hoct Name oi IP addiess Keyboard Bell Features Connectcn type: Window Appear ance Behaviour Translation Seleclion Colours Load, save or delete a xtoied ression Sared Sessions Defaut Settings Load Sarc D elete connecton Dala Prow Telnct E SSH . Senal Close window on exit: Always NeveDrly on cean exit About Open Cancel To access a remote site (which you need to have account and password), type the host name or the IP address of the remote host in the corresponding box and choose Telnet as the connection type (using the corresponding radio button). Then click the Lab2-3: TELNET Using a virtual terminal connection, TELNET provides remote logging, an interactive text-oriented communications between a user and a remote server, over TCP. The best way to capture packets exchanged between your computer and a remote host is to use a client GUI TELNET program. We recommend to use PuTTY, which is a firee software and can be downloaded from http://www.chiarkgreenend.org.uk-sgtatham/putty/download.html Save the putty exe file on your computer (no installation needed). Figure 2.2 shows a sample of PuTTY configuration window Figure 2.2 PuIII Window PuTTY Configuration Catcooy Basic optizns for your PuTTY session Specily the deetination you wart to connect to Poit 23 Session Logging .. Terminal Hoct Name oi IP addiess Keyboard Bell Features Connectcn type: Window Appear ance Behaviour Translation Seleclion Colours Load, save or delete a xtoied ression Sared Sessions Defaut Settings Load Sarc D elete connecton Dala Prow Telnct E SSH . Senal Close window on exit: Always NeveDrly on cean exit About Open Cancel To access a remote site (which you need to have account and password), type the host name or the IP address of the remote host in the corresponding box and choose Telnet as the connection type (using the corresponding radio button). Then click the
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


