Question: Learning Goals use modulo and division operators write a function that is then called in the main program Introduction A common year in the modern
Learning Goals
use modulo and division operators
write a function that is then called in the main program
Introduction
A common year in the modern Gregorian Calendar consists of days. In reality, Earth takes longer to rotate around the sun. To account for the difference in time, every years, a leap year takes place. A leap year is when a year has days: an extra day, February th
The requirements for a given year to be a leap year are:
The year must be divisible by
If the year is a century year etc. the year must be evenly divisible by
Therefore, both and are not leap years. Even though and are divisible by and because they are century years ie divisible by they need to be divisible by to be leap, but and
Some example leap years are and
Instructions
Define the following function, which takes the year as an integer and returns the number of days in February also as an integer for the given input year.
def daysinfebuseryear
Your main program should take in a year, call the function and use its return value to output the number of days in February for that year.
Testing your code
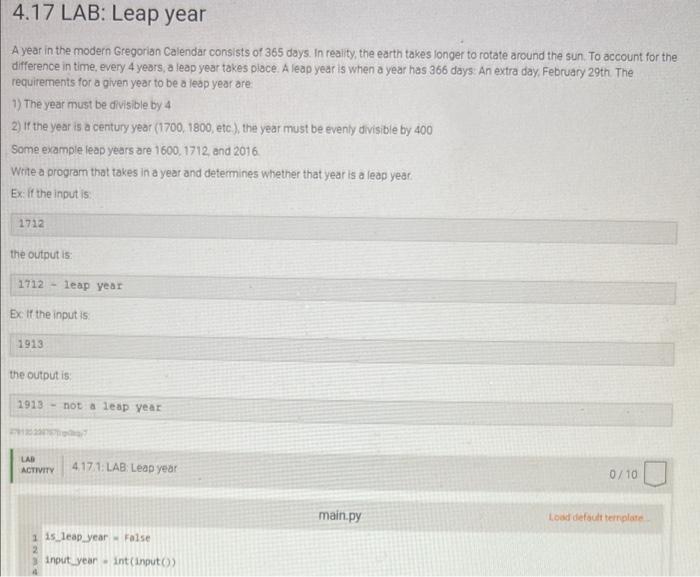
If the input is:
the function returns
the main program output is:
has days in February.
Ex: If the input is:
the function returns
the main program output is:
has days in February.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


