Question: Let F be a pseudorandom function and G be a pseudorandom generator with expansion factor p(n)=n+1. Suppose the shared key is a uniform k{0,1}n. (a)
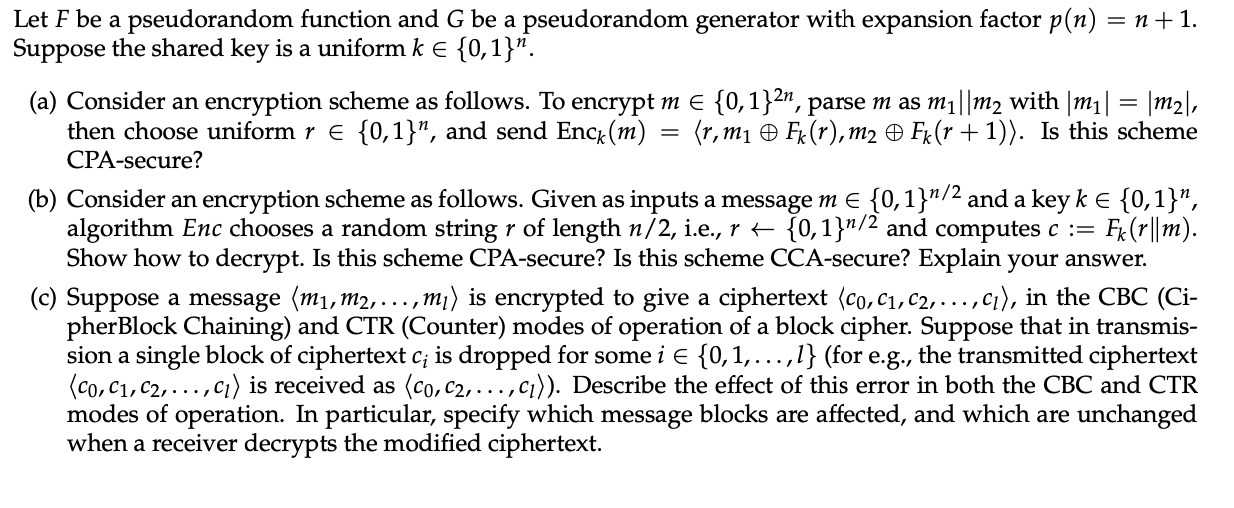
Let F be a pseudorandom function and G be a pseudorandom generator with expansion factor p(n)=n+1. Suppose the shared key is a uniform k{0,1}n. (a) Consider an encryption scheme as follows. To encrypt m{0,1}2n, parse m as m1m2 with m1=m2, then choose uniform r{0,1}n, and send Enck(m)=r,m1Fk(r),m2Fk(r+1). Is this scheme CPA-secure? (b) Consider an encryption scheme as follows. Given as inputs a message m{0,1}n/2 and a key k{0,1}n, algorithm Enc chooses a random string r of length n/2, i.e., r{0,1}n/2 and computes c:=Fk(rm). Show how to decrypt. Is this scheme CPA-secure? Is this scheme CCA-secure? Explain your answer. (c) Suppose a message m1,m2,,ml is encrypted to give a ciphertext c0,c1,c2,,cl, in the CBC (CipherBlock Chaining) and CTR (Counter) modes of operation of a block cipher. Suppose that in transmission a single block of ciphertext ci is dropped for some i{0,1,,l} (for e.g., the transmitted ciphertext c0,c1,c2,,cl is received as c0,c2,,cl). Describe the effect of this error in both the CBC and CTR modes of operation. In particular, specify which message blocks are affected, and which are unchanged when a receiver decrypts the modified ciphertext
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


