Question: Let V C R be a subspace. Define VI = (u e R : u is orthogonal to V). In other words, V = (u
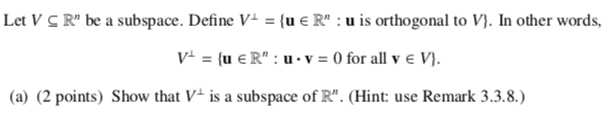
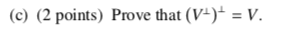
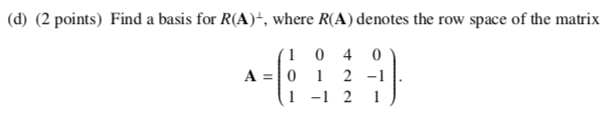
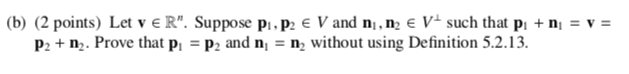

Let V C R" be a subspace. Define VI = (u e R" : u is orthogonal to V). In other words, V = (u ER" : u . v = 0 for all v E V). (a) (2 points) Show that Vis a subspace of R". (Hint: use Remark 3.3.8.)\f(d) (2 points) Find a basis for R(A), where R(A) denotes the row space of the matrix 0 A = 2 -1(b) (2 points) Let v E R". Suppose pi, p2 E V and m, n2 E V- such that pi + n) = V = P2 + 12. Prove that p, = p2 and n, = ny without using Definition 5.2.13.Remark 3.3.8 Let V be a non-empty subset of R". Then V is a subspace of R" if and only if for all u, v E V and c, d ER, cu + du E V
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


