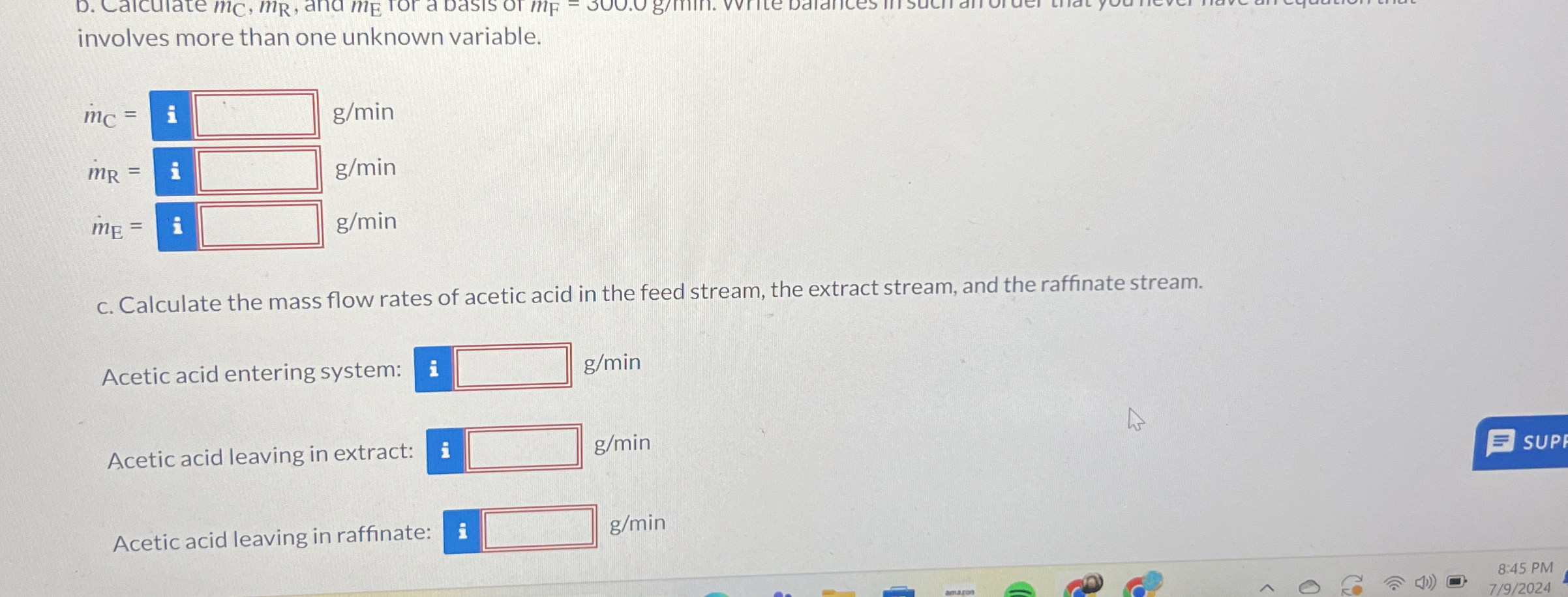
Question: Liquid extraction is an operation used to separate the components of a liquid mixture of two or more species. In the simplest case, the mixture
Liquid extraction is an operation used to separate the components of a liquid mixture of two or more species.
In the simplest case, the mixture contains two components: a solute A and a liquid solvent B
The mixture is contacted in an agitated vessle with a second liquid solvent that has two key properties: A dissolves in it and is immiscible or nearly immiscible with it
For example, B may be water, a hydrocarbon oil, and a species that has significant solubility in both water and oil. Some of the A transfers from to and then the rich phase the raffinate and the rich phase the extract separate from each other in a settling tank.
If the raffinate is then contacted with fresh in another stage, more A will be transferred from it This process can be repeated until essentially all of the A has been extracted from the B
Shown below is a flowchart of a process in which acetic acid aa is extracted from a mixture of acetic acid and water into hexanol h a liquid immiscible with water.
Stream Compositions mass fractions
tableStreamComponentSolvent CFeed Raffinate Extract EtableAcetic Acid aa
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


