Question: Look at the correlations in Table 4. Remember what you know about correlations, are the study variables related? Are the relationships positive and significant as
Look at the correlations in Table 4. Remember what you know about correlations, are the study variables related? Are the relationships positive and significant as hypothesized?
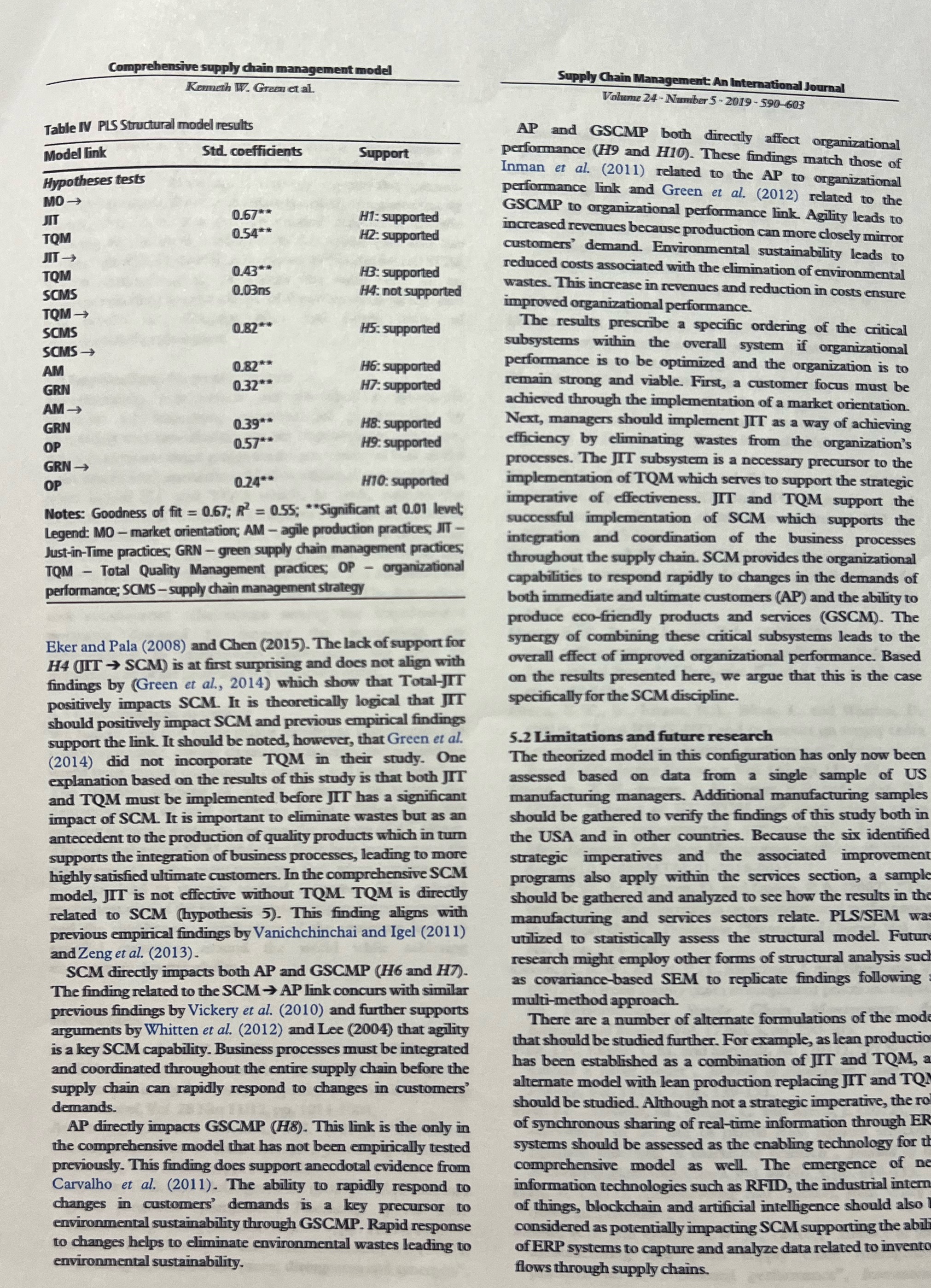
Table IV PLS Structural model results Model link Comprehensive supply chain management model Kenneth W. Green et al. Hypotheses tests MO->>> JIT TQM JIT>> TOM SCMS TQM>> SCMS SCMS AM GRN AM>> GRN OP GRN>> OP Std. coefficients 0.67** 0.54** 0.43** 0.03ns 0.82** 0.82** 0.32** 0.39** 0.57** Support H1: supported HZ: supported HB: supported H4: not supported H5: supported H6:supported H7:supported HB: supported H9: supported 0.24** H10: supported Notes: Goodness of fit = 0.67; R = 0.55; **Significant at 0.01 level; Legend: MO- market orientation; AM-agile production practices; JIT - Just-in-Time practices, GRN - green supply chain management practices; TQM - Total Quality Management practices; OP- organizational performance; SCMS-supply chain management strategy Eker and Pala (2008) and Chen (2015). The lack of support for H4 (JITSCM) is at first surprising and does not align with findings by (Green et al., 2014) which show that Total-JIT positively impacts SCM. It is theoretically logical that JIT should positively impact SCM and previous empirical findings support the link. It should be noted, however, that Green et al. (2014) did not incorporate TQM in their study. One explanation based on the results of this study is that both JIT and TQM must be implemented before JTT has a significant impact of SCM. It is important to eliminate wastes but as an antecedent to the production of quality products which in turn supports the integration of business processes, leading to more highly satisfied ultimate customers. In the comprehensive SCM model, JIT is not effective without TQM TQM is directly related to SCM (hypothesis 5). This finding aligns with previous empirical findings by Vanichchinchai and Igel (2011) and Zeng et al. (2013). SCM directly impacts both AP and GSCMP (H6 and H7). The finding related to the SCM AP link concurs with similar previous findings by Vickery et al. (2010) and further supports arguments by Whitten et al. (2012) and Lee (2004) that agility is a key SCM capability. Business processes must be integrated and coordinated throughout the entire supply chain before the supply chain can rapidly respond to changes in customers' demands. AP directly impacts GSCMP (H8). This link is the only in the comprehensive model that has not been empirically tested previously. This finding does support anecdotal evidence from Carvalho et al. (2011). The ability to rapidly respond to changes in customers' demands is a key precursor to environmental sustainability through GSCMP. Rapid response to changes helps to eliminate environmental wastes leading to environmental sustainability. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal Volume 24-Number 5-2019-590-603 AP and GSCMP both directly affect organizational performance (H9 and H10). These findings match those of Inman et al. (2011) related to the AP to organizational performance link and Green et al. (2012) related to the GSCMP to organizational performance link. Agility leads to increased revenues because production can more closely mirror customers' demand. Environmental sustainability leads to reduced costs associated with the elimination of environmental wastes. This increase in revenues and reduction in costs ensure improved organizational performance. The results prescribe a specific ordering of the critical subsystems within the overall system if organizational performance is to be optimized and the organization is to remain strong and viable. First, a customer focus must be achieved through the implementation of a market orientation. Next, managers should implement JIT as a way of achieving efficiency by eliminating wastes from the organization's processes. The JIT subsystem is a necessary precursor to the implementation of TQM which serves to support the strategic imperative of effectiveness. JIT and TQM support the successful implementation of SCM which supports the integration and coordination of the business processes throughout the supply chain. SCM provides the organizational capabilities to respond rapidly to changes in the demands of both immediate and ultimate customers (AP) and the ability to produce eco-friendly products and services (GSCM). The synergy of combining these critical subsystems leads to the overall effect of improved organizational performance. Based on the results presented here, we argue that this is the case specifically for the SCM discipline. 5.2 Limitations and future research The theorized model in this configuration has only now been assessed based on data from a single sample of US manufacturing managers. Additional manufacturing samples should be gathered to verify the findings of this study both in the USA and in other countries. Because the six identified strategic imperatives and the associated improvement programs also apply within the services section, a sample- should be gathered and analyzed to see how the results in the manufacturing and services sectors relate. PLS/SEM was utilized to statistically assess the structural model. Future research might employ other forms of structural analysis such as covariance-based SEM to replicate findings following multi-method approach. There are a number of alternate formulations of the mode that should be studied further. For example, as lean production has been established as a combination of JIT and TQM, a alternate model with lean production replacing JIT and TOM should be studied. Although not a strategic imperative, the ro of synchronous sharing of real-time information through ER systems should be assessed as the enabling technology for th comprehensive model as well. The emergence of ne information technologies such as RFID, the industrial intern of things, blockchain and artificial intelligence should also considered as potentially impacting SCM supporting the abili of ERP systems to capture and analyze data related to invento flows through supply chains.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Based on the provided correlation results from the PLS structural model lets analyze the relationships between the study variables 1 Market Orientatio... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


