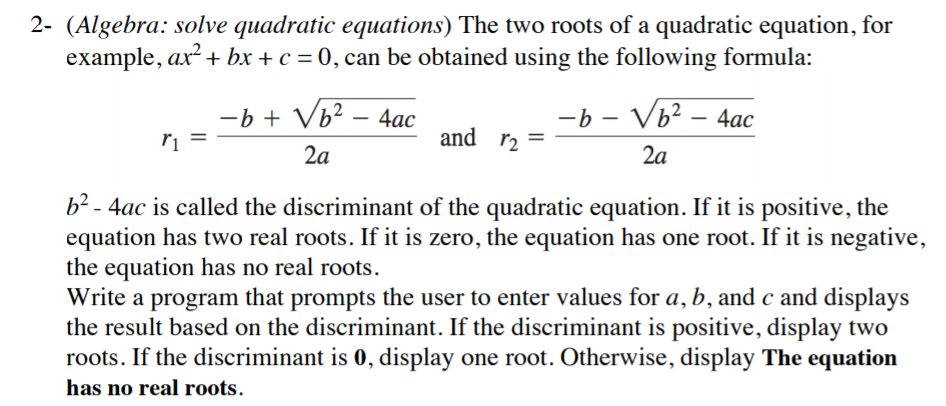
Question: Must be python 3.6 The two roots of a quadratic equation, for example, ax^2 + bx + c = 0, can be obtained using the
 Must be python 3.6
Must be python 3.6
The two roots of a quadratic equation, for example, ax^2 + bx + c = 0, can be obtained using the following formula: r_1 = -b + squareroot b^2 - 4ac/2a and r_2 = -b - squareroot b^2 - 4ac/2a b^2 - 4ac is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation. If it is positive, the equation has two real roots. If it is zero, the equation has one root. If it is negative, the equation has no real roots. Write a program that prompts the user to enter values for a, b, and c and displays the result based on the discriminant. If the discriminant is positive, display two roots. If the discriminant is 0, display one root. Otherwise, display The equation has no real roots
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


