Question: Need matlab code, green is instructions. Use the vector and rotation functions you created above to find the endpoints of the links in a 3D
Need matlab code, green is instructions.
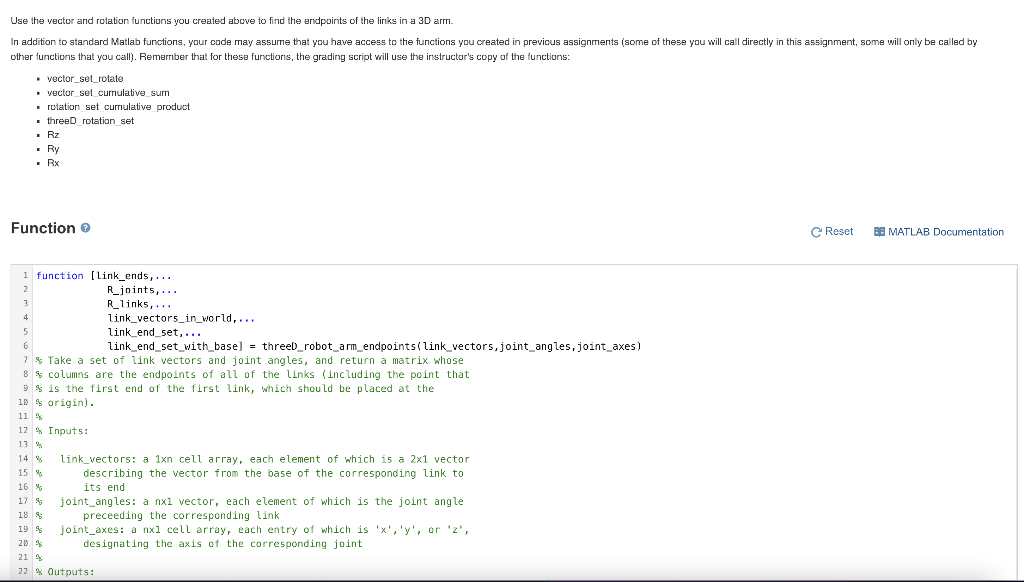
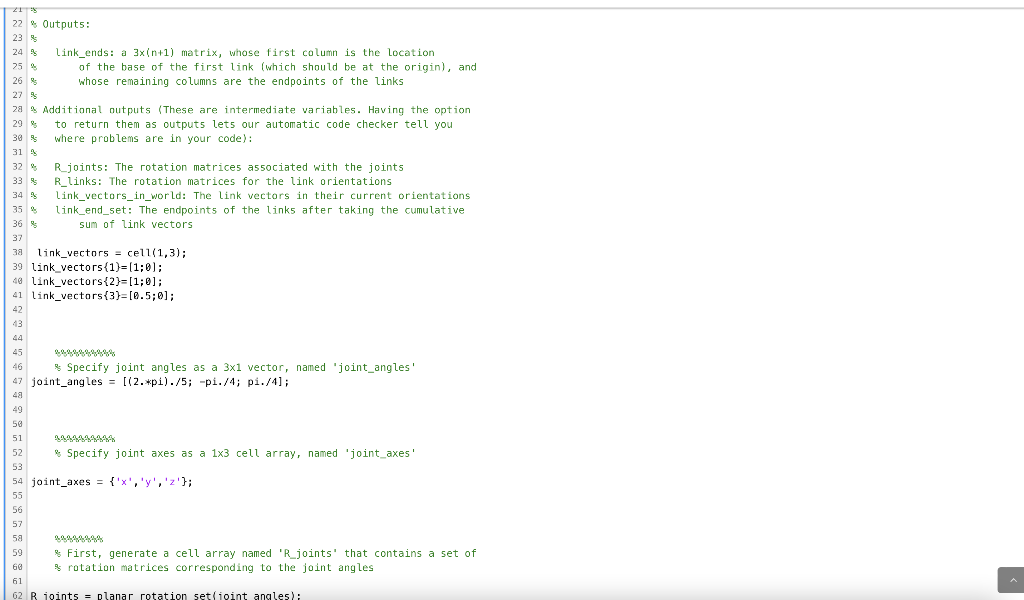
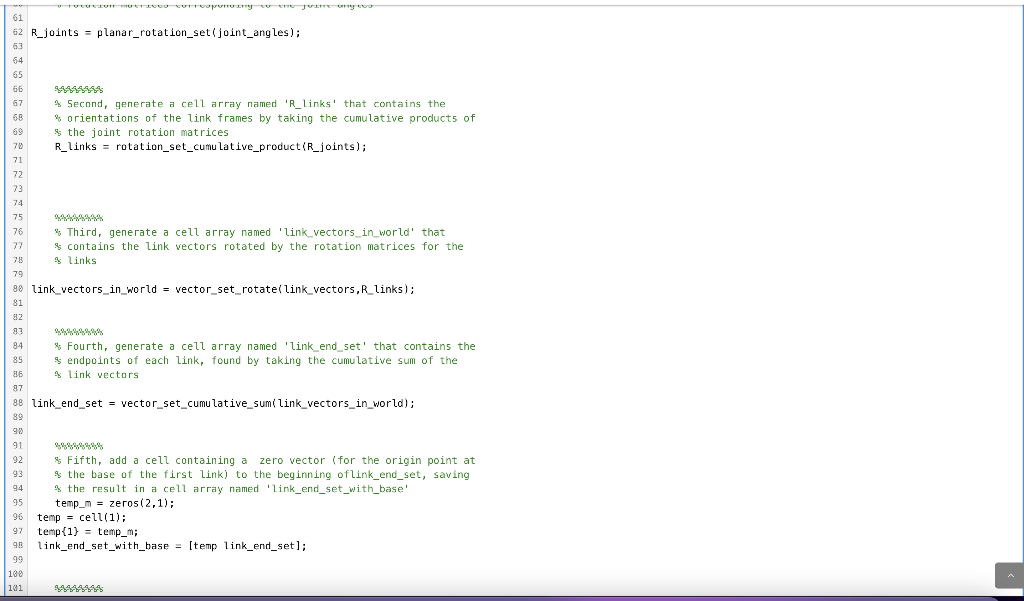
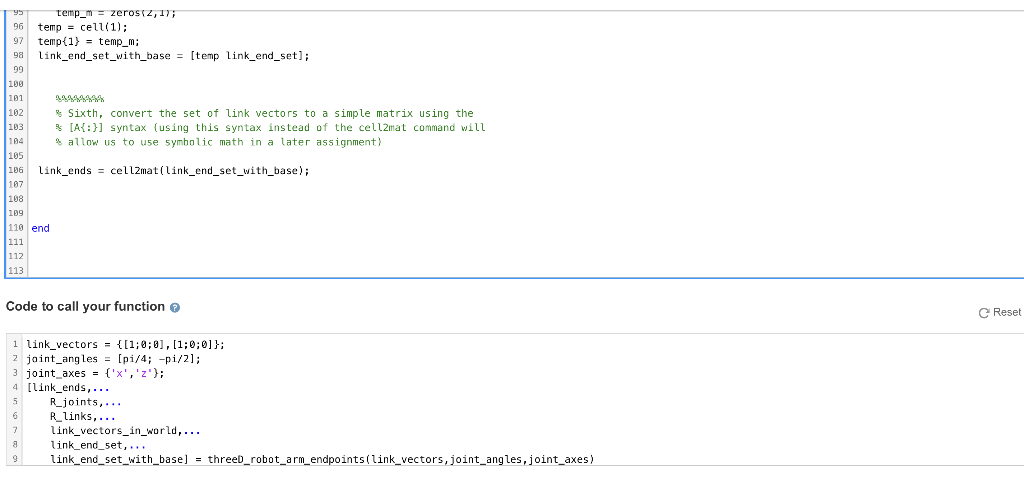
Use the vector and rotation functions you created above to find the endpoints of the links in a 3D arm. In addition to standard Matlab functions, your code may assume that you have access to the functions you created in previous assignments (some of these you will call directly in this assignment, some will only be called by other functions that you call). Remember that for these functions, the grading script will use the instructor's copy of the functions: vector set rotate vector set currulative sum rotation set cumulative product threeD rotation set Rz Ry Rx Function Reset BE MATLAB Documentation 1 function [link_ends,... 2 R_joints,... 3 R_links, ... 4 link_vectors_in_world,... 5 link_end_set,... 6 link_end_set_with_base) = threeD_robot_arm_endpoints(link_vectors, joint_angles, joint_axes) 7 % Take a set of link vectors and joint angles, and return a matrix whose 8 $ columns are the endpoints of all of the links (including the point that 9 $ is the first end of the first link, which should be placed at the 10 % origin). 11 12 Inputs: 13 % 14 % link_vectors: a 1xn cell array, each element of which is a 2x1 vector 15 % describing the vector from the base of the corresponding link to 16 % its end joint_angles: a nx1 vector, each element of which is the joint angle 18 9 preceeding the corresponding link 19 s joint_axes: a nxl cell array, each entry of which is 'x', 'y', or 'z', 20 s designating the axis of the corresponding joint 21 % 22 % Outputs: 17 21 S 22 % Outputs: 23 24 link_ends: a 3x(n+1) matrix, whose first column is the location 25 of the base of the first link (which should be at the origin), and 26 whose remaining columns are the endpoints of the links 27 28 Additional outputs (These are intermediate variables. Having the option 29 to return them as outputs lets our automatic code checker tell you 30 where problems are in your code): 31 32 Rjoints: The rotation matrices associated with the joints 33 R_links: The rotation matrices for the link orientations 34 Link_vectors_in_world: The link vectors in their current orientations 35 % link_end_set: The endpoints of the links after taking the cumulative 36 sum of link vectors 37 38 link_vectors = cell(1,3); 39 link_vectors{1}=(1; 0); 48 link_vectors(2)=[1;0); 41 link_vectors{3}=[0.5;0]; 42 43 44 45 46 Specify joint angles as a 3x1 vector, named 'joint_angles' 47 joint_angles = [(2.*pi)./5; -pi./4; pi./4]; 49 50 51 52 Specify joint axes as a 1x3 cell array, named 'joint_axes' 53 54 joint_axes = {'X', 'y', 'z'}; 55 56 57 58 59 First, generate a cell array named 'R_joints' that contains a set of 60 rotation matrices corresponding to the joint angles 61 62 R joints = planar rotation set joint angles); 61 62 R_joints = planar_rotation_set(joint_angles); 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 4 Second, generate a cell array named 'R_links' that contains the * orientations of the link frames by taking the cumulative products of the joint rotation matrices R_links = rotation_set_cumulative_product (R_joints); 71 72 73 74 75 78 76 % Third, generate a cell array named 'link_vectors_in_world' that 77 $ contains the link vectors rotated by the rotation matrices for the links 79 90 link_vectors_in_world = vector_set_rotate(link_vectors, R_links); 81 82 83 84 * Fourth, generate a cell array named 'link_end_set' that contains the 85 % endpoints of each link, found by taking the cumulative sum of the 86 % link vectors 87 88 link_end_set = vector_set_cumulative_sumi link_vectors_in_world); 89 9 91 92 $ Fifth, add a cell containing a zero vector (for the origin point at , 93 % the base of the first link) to the beginning of link_end_set, saving 94 % the result in a cell array named 'link_end_set_with_base' 95 temp_m = zeros(2,1); 96 temp = cell(1); = (1) 97 temp{1} = temp_m; 96 link_end_set_with_base = [temp link_end_set); 99 100 101 temp_m = zeros 2,1); 96 temp = cell(1); 97 temp(1) = temp_m; 9 link_end_set_with_base = [temp link_end_set); 99 100 181 182 Sixth, convert the set of link vectors to a simple matrix using the 103 [A{:}] syntax (using this syntax instead of the cell2mat command will 164 allow us to use symbolic math in a later assignment) 105 106 link_ends = cellzmat(link_end_set_with_base); 187 108 109 110 end 111 112 113 Code to call your function Reset 1 link_vectors = {(1;0;0], [1;0;0]}; 2 joint_angles = [pi/4; -pi/2); 3 joint_axes = {'X','z'}; 4 [link_ends,... R_joints,... R_links,... link_vectors_in_world, ... link_end_set, ... 9 link_end_set_with_base] = threeD_robot_arm_endpoints(link_vectors, joint_angles,joint_axes) 8
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


