Question: Note : Please skip if you don't know how to answer. Don't spam i swear you will receive the most unlikes here. Based on the
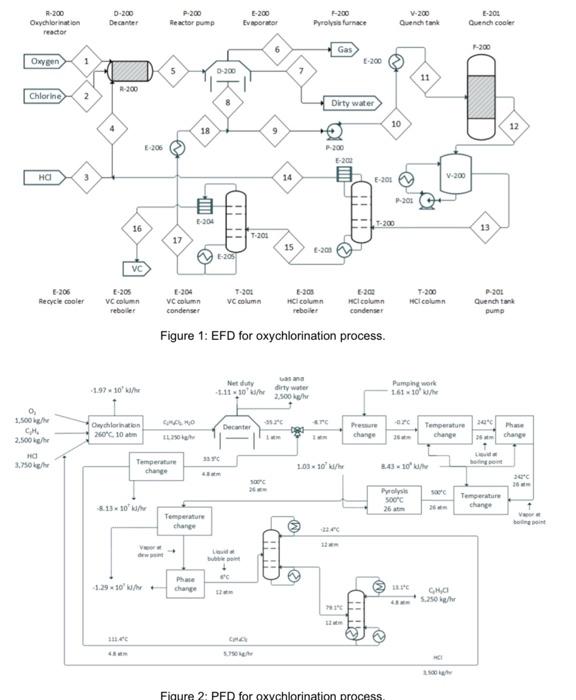

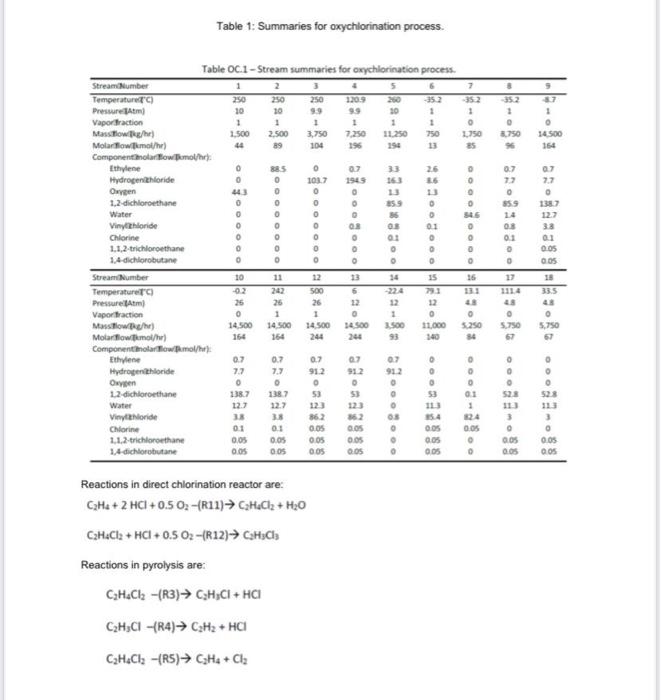
P-200 R-200 Oxychlorination reactor 0-200 Decanter Reactor -200 Pyrolysis furnace V-200 Quench tank 201 Quench cooler Evaporator Gas -200 Oxygen 1 0-200 7 -200 Chlorine 2 Dirty water 10 12 18 9 E206 - 200 3 14 V-200 w E-201 201 204 !!! T-200 16 13 17 T-201 15 205 VC Recycle cooler VC column reboller T-20 VC column VC column condenser -200 HCI Column reboiler 30 HCl.com condenser T-200 HCl column P-201 Quench tak pump Figure 1: EFD for oxychlorination process. 1.97.10 Netty 1.1110 dirty water 2.500 Pumping word 16110 0 1.500 CH 2,500 NANO er - sec Olychlorination 26.10 Decanter Temperature change change change ra 3.750 33 Temperature 10310/ 3.43 10' SOME Polis SOC Temperature change 8.13.10 Temperature change VE Ph 129 10' CHO 20 CI Figure 2: PFD for oxychlorination process 3.0 DESCRIPTION The oxychlorination process design is highly comparable to the direct chlorination method, with many shared downstream operations (Benyahia, 2005). It begins with preheated (from storage at 25C) near-stoichiometric feeds of pure ethylene, oxygen, and hydrogen chloride (streams 1,2, and 3; stream 3 joins with a recycle stream to form stream 4) entering an oxychlorination reactor (R-200). Oxychlorination reactors are gas phase reactors, which avoid corrosion by aqueous acid solutions (a classic pitfall of direct chlorination reactors) (Magistro & Cowfer, 1986). To maintain a vapor fraction of 1, the reactor is held at 260C and 10 atm. The oxychlorination products (stream 5) are flown to a decanter (D-200), which removes gas (stream 6) and water (stream 7). The bottoms stream from the decanter, stream 8, is joined by a recycle (to form stream 9) before entering a centrifugal pump and heating system in preparation for pyrolysis (F-200; streams 10 and 11). As with the direct chlorination method, the pyrolysis furnace runs at 500C and 26 atm before opening into a quench tank (V-200; stream 12) at 12 bar and 6C. The quench tank temperature is maintained by continuous material circulation in contact with a refrigerant stream. After cooling, the products travel to distillation columns that are essentially identical to those in the direct chlorination process (T-200 and T-201; streams 13 and 15), which one major deviation. In the oxychlorination model, the distillate HCl from T-200 (stream 14) is recycled upstream to enter the oxychlorination reactor alongside the pure components. Similar to the direct chlorination process, the distillate from T-201 (stream 16) is 98% pure vinyl chloride at 13C and 4.8 atm while the bottoms (stream 17), which is primarily water and 1,2-dichloroethane, is recycled to merge with the enriched 1,2-dichloroethane exiting the bottom of the decanter. The EFD and PFD for oxychlorination process is given in Figure 1 and 2, respectively. Summaries for all the process is given in Table 1. Table 1: Summaries for oxychlorination process. 250 250 GOGO Table C.1 - Stream summaries for oxychlorination process. Stream Number 5 7 Temperature) 250 1203 -352 -352 Pressure 10 30 30 1 1 1 1 Vapor fraction 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 Mass flow 1.500 2.500 2.750 7.250 11.250 750 2150 3750 14 500 Molar flowmoth 44 89 104 254 13 25 96 154 Component olarowemol/hr): Ethylene 0 85 . 07 33 26 0.7 07 Hydrogen chloride 0 0 103.7 1949 7.7 Oxygen 43 . . 1,2-dichloroethane 0 0 0 15 . Water 1387 0 0 0 55 0 546 14 127 Vinythloride 0 0 0 08 01 08 33 Chlorine 0 0 0 o 0.1 01 1.1.2-trichloroethane 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.05 14-dichlorobutane 0 0 0 O 0 0 DOS Strean Number 10 11 12 14 15 16 17 18 Temperaturer 242 500 791 33.5 Pressure Atm 26 26 26 12 12 43 43 Vapor fraction 0 1 1 0 1 0 . Maslower) 14.500 14.500 14.500 34.500 3.500 11.000 5.250 5.750 5.750 Molar flow mol/h) 164 164 244 244 93 140 Componentinolarowemol/hr) Ethylene 0.7 0.7 0.7 07 07 0 0 0 0 Hydrogenloride 77 7.7 91.2 912 912 0 Owen 0 o o 12-dichloroethane 138.7 138.7 53 53 O 53 01 528 Water 12.7 123 1 Vinyloride 1 38 862 2 3 Chlorine 01 0.1 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0 . 1.1.2-trichloroethane 0.05 0.05 0.05 DOS . QOS o QOS OOS 1.4 dichlorobutane 0.05 005 0.05 O DOS 0 0.05 Qos ||. . . . 127 Dos Reactions in direct chlorination reactor are: CH2 + 2HCI+0.5 0:-(R11) HeCl2 + H20 CzH4Cl2 + HCl + 0.5 02 (12) CH3Cl2 Reactions in pyrolysis are: CzH4Cl2 -(R3) C3H,Cl + HCI CzH;CI -(R4) C2H2 + HCI + CzH4Cl2 -(R5) CH4 + Cla
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


