Question: Optimisation and Decision Making problem PROBLEM 6: ENERGY PROVISION (20 POINTS) The state of Victoria primarily relies on brown coal sources for electricity generation. Here,
Optimisation and Decision Making problem
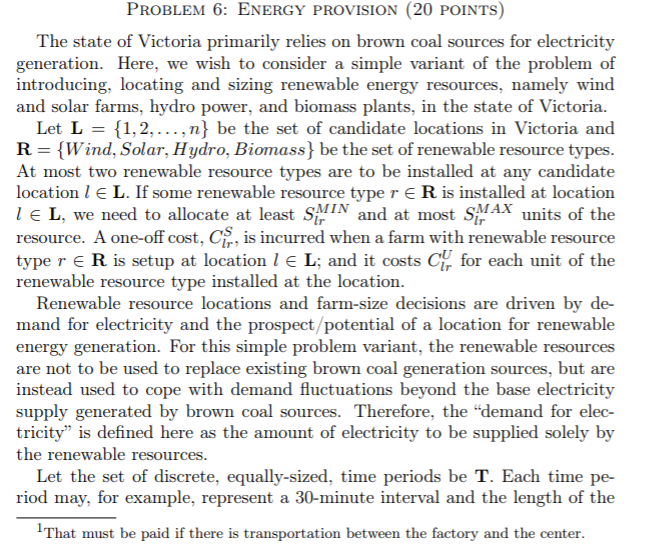
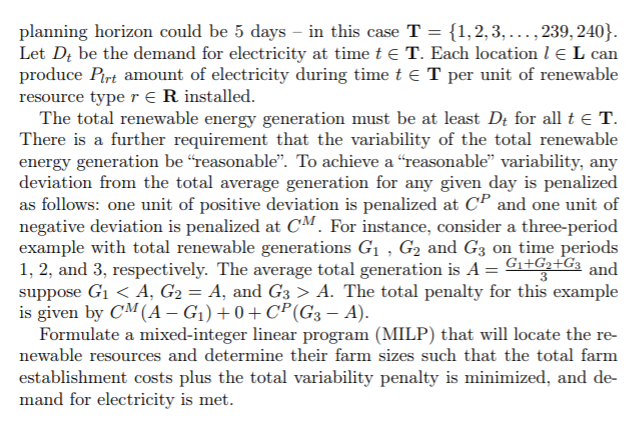
PROBLEM 6: ENERGY PROVISION (20 POINTS) The state of Victoria primarily relies on brown coal sources for electricity generation. Here, we wish to consider a simple variant of the problem of introducing, locating and sizing renewable energy resources, namely wind and solar farms, hydro power, and biomass plants, in the state of Victoria. Let L = {1,2,...,n} be the set of candidate locations in Victoria and R={Wind, Solar, Hydro, Biomass} be the set of renewable resource types. At most two renewable resource types are to be installed at any candidate location l E L. If some renewable resource type r ER is installed at location TEL, we need to allocate at least SW and at most SWAX units of the resource. A one-off cost, Cs, is incurred when a farm with renewable resource type r R is setup at location l e L; and it costs Clfor each unit of the renewable resource type installed at the location. Renewable resource locations and farm-size decisions are driven by de- mand for electricity and the prospect potential of a location for renewable energy generation. For this simple problem variant, the renewable resources are not to be used to replace existing brown coal generation sources, but are instead used to cope with demand fluctuations beyond the base electricity supply generated by brown coal sources. Therefore, the "demand for elec- tricity is defined here as the amount of electricity to be supplied solely by the renewable resources. Let the set of discrete, equally-sized, time periods be T. Each time pe- riod may, for example, represent a 30-minute interval and the length of the That must be paid if there is transportation between the factory and the center. planning horizon could be 5 days - in this case T = {1,2,3,..., 239, 240). Let D be the demand for electricity at time te T. Each location le L can produce Plrt amount of electricity during time tET per unit of renewable resource typer ER installed. The total renewable energy generation must be at least Dt for all t E T. There is a further requirement that the variability of the total renewable energy generation be "reasonable". To achieve a "reasonable" variability, any deviation from the total average generation for any given day is penalized as follows: one unit of positive deviation is penalized at CP and one unit of negative deviation is penalized at CM. For instance, consider a three-period example with total renewable generations G1, G2 and G3 on time periods 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The average total generation is A= GitG2G3 and suppose G1 A. The total penalty for this example is given by CMA-G1) +0+CP (G3 - A). Formulate a mixed-integer linear program (MILP) that will locate the re- newable resources and determine their farm sizes such that the total farm establishment costs plus the total variability penalty is minimized, and de- mand for electricity is met. PROBLEM 6: ENERGY PROVISION (20 POINTS) The state of Victoria primarily relies on brown coal sources for electricity generation. Here, we wish to consider a simple variant of the problem of introducing, locating and sizing renewable energy resources, namely wind and solar farms, hydro power, and biomass plants, in the state of Victoria. Let L = {1,2,...,n} be the set of candidate locations in Victoria and R={Wind, Solar, Hydro, Biomass} be the set of renewable resource types. At most two renewable resource types are to be installed at any candidate location l E L. If some renewable resource type r ER is installed at location TEL, we need to allocate at least SW and at most SWAX units of the resource. A one-off cost, Cs, is incurred when a farm with renewable resource type r R is setup at location l e L; and it costs Clfor each unit of the renewable resource type installed at the location. Renewable resource locations and farm-size decisions are driven by de- mand for electricity and the prospect potential of a location for renewable energy generation. For this simple problem variant, the renewable resources are not to be used to replace existing brown coal generation sources, but are instead used to cope with demand fluctuations beyond the base electricity supply generated by brown coal sources. Therefore, the "demand for elec- tricity is defined here as the amount of electricity to be supplied solely by the renewable resources. Let the set of discrete, equally-sized, time periods be T. Each time pe- riod may, for example, represent a 30-minute interval and the length of the That must be paid if there is transportation between the factory and the center. planning horizon could be 5 days - in this case T = {1,2,3,..., 239, 240). Let D be the demand for electricity at time te T. Each location le L can produce Plrt amount of electricity during time tET per unit of renewable resource typer ER installed. The total renewable energy generation must be at least Dt for all t E T. There is a further requirement that the variability of the total renewable energy generation be "reasonable". To achieve a "reasonable" variability, any deviation from the total average generation for any given day is penalized as follows: one unit of positive deviation is penalized at CP and one unit of negative deviation is penalized at CM. For instance, consider a three-period example with total renewable generations G1, G2 and G3 on time periods 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The average total generation is A= GitG2G3 and suppose G1 A. The total penalty for this example is given by CMA-G1) +0+CP (G3 - A). Formulate a mixed-integer linear program (MILP) that will locate the re- newable resources and determine their farm sizes such that the total farm establishment costs plus the total variability penalty is minimized, and de- mand for electricity is met






