Question: Part A (4 polnta): Implement the function sit powers. b) such that Assume a and bare Integers, and assume a cb (no need to check

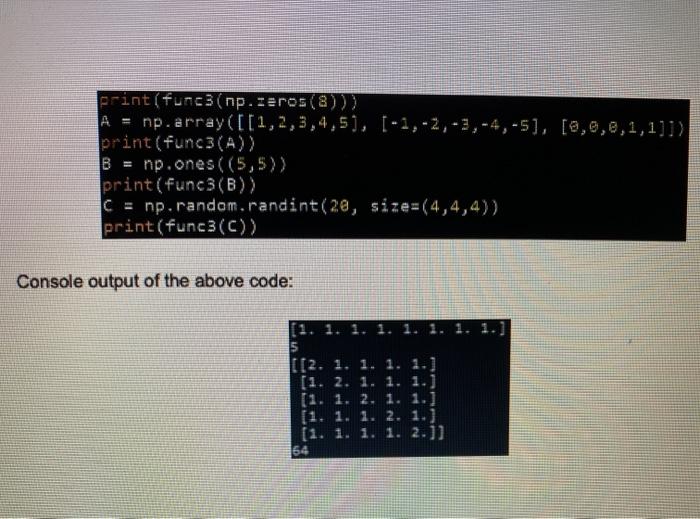
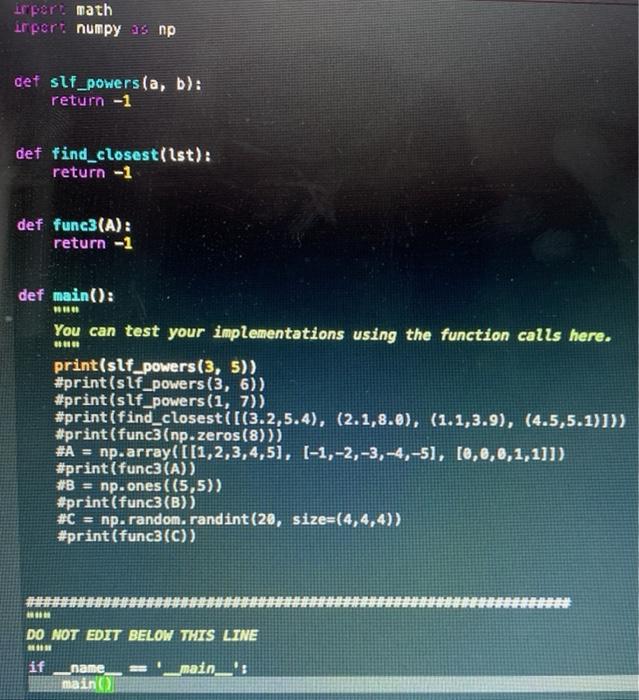
Part A (4 polnta): Implement the function sit powers. b) such that Assume a and bare Integers, and assume a cb (no need to check for erroneous Inputs sif powers should calculate and retum the result of: k=b kra Part B (8 polnts): Implement the function find closest(i sl) such that Ist is a list of tuples, e.g.: [(3.2,5.4), (2.1,8.0), (1.1,3.9). (4.5,5.1)] Each tuple is a point in two-dimensional space: (x coordinate, y coordinate) find_closest returns the pair of tuples that are closest to each other in terms of Pythagorean distance. o Two retum values: tuple1, tuple2 Calculating Pythagorean distance of two points (xy) and (x,y): Part C (points): Implement the function func3(1) such that func3 has 1 input: Numpy ndarray A func3 behaves as follows: Of A is 1-dimensional, add 1 to each element of A and return the result of A is 2-dimensional: If A is N by N (square matrix), then add the Identity Matrix of the same size to A and return the result. Recall that the identity Matrix contains t's in its diagonal and all remaining entries are 0 If A is not a square matrix, return the maximum entry in A of A is 3-dimensional, return the total number of elements in A o. If A is of any other dimension, return A Here are some sample executions of func3 and their corresponding outputs. Code 1 print(func(np.zeros(&))) A = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5), (-1,-2, -3, -4,-5), [0,0,0,1,1]]) print (func3(A)) np.ones((5,5)) print(func3(B)) C = np.random.randint(2e, size=(4,4,4)) print(func3(C)) Console output of the above code: 1 [[2. 1. 1. (1. 2. 1 (1. 1. 2. 1. 1.) (1. 1. 1. 2. 1.) (1. 1. 1. 1. 2.)] 64 impert math irport numpy as np cef slf_powers(a, b): return -1 def find_closest(lst): return -1 def func3(A): return -1 def main(): WHO 03 You can test your implementations using the function calls here. print(slf_powers(3, 5)) #print(slf_powers(3, 6)) #print(slf_powers(1, 7)) #print(find_closest([(3.2,5.4), (2.1,8.0), (1.1,3.9), (4.5,5.1)))) #print(func3(np.zeros(8))) #A = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5), (-1,-2,-3, -4,-5), [0,0,0,1,1]]) #print(func3(A)) #B = np.ones((5,5)) #print(func3(B)) # = np.random.randint(29, size=(4,4,4)) #print(func3(C)) #*** 233 DO NOT EDIT BELOW THIS LINE M if name main_'s main (
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


