Question: Part C - Case Study XYZ Pty Ltd is a company selling computers and accessories to the clients. You are the accountant of XYZ Pty

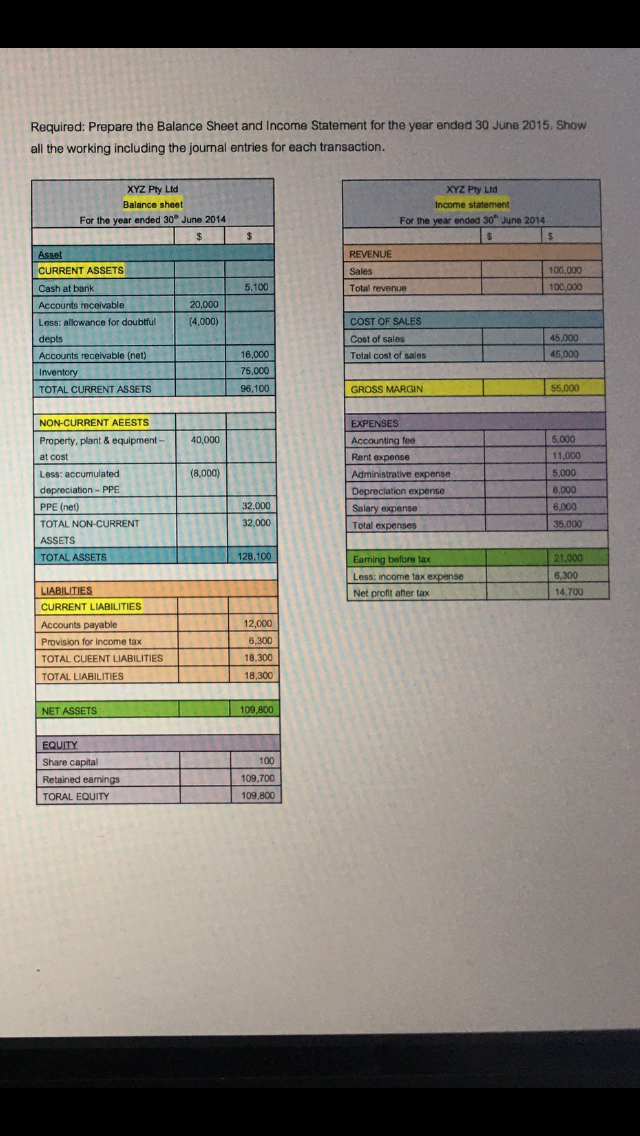
Part C - Case Study XYZ Pty Ltd is a company selling computers and accessories to the clients. You are the accountant of XYZ Pty Ltd, and required to prepare the Balance Sheet and Income Statement for the year ended 30 June 2015. You are given the Balance Sheet and Income Statement for the year ended 30 June 2014 as follows: Additional information: The property, plant and equipment were purchased on 1 July 2013 with the cost of $40,000 The useful life was expected as 5 years. Straight line method was used. The perpetual method is used for inventory. Based on prior experience, XYZ Pty Ltd.'s bad debts expense is normally 2% of net credit sales for the current year. Under taxation legislation, revenue will be taxable when received. The taxation depreciation for PPE is $9,000. Under taxation legislation, no deduction is allowed for entertainment expenditure. Under taxation legislation, no deduction is allowed for bad debts until they have been written off. The company income tax rate is 30%. Ignoring GST impact. During the year 2014-15, the following transactions incurred: 1. The company purchased a land for an office location with the amount of $20,000. The company paid $5,000 in cash and borrowed $15,000 from bank to pay the balance. 2. The company made a payment of $10,000 to its suppliers of computers (linked with "accounts payable" account). 3. The company paid $7,000 for employee salary, $12,000 for rent, $3,000 for accounting fee and $5,000 for entertainment in cash. 4. The company made a loan repayment with the amount of $5,000, of which $4,500 was the interest paid and $500 was the reduction of principal amount. 5. The company purchased 10 computers from its suppliers at $900 each, in cash. The net realisable value is estimated as $950 each. 6. The company sold 90 computers during the year for $1,300 each, on credit. The computers were purchased in last year with the cost of $800 each. 7.5 computers from the sales in Transaction 6 were returned by the customers. 8. The company received $120,000 in cash for the sales invoices previously issued. 9. The company received $3,000 in the bank account as credit interest. 10. The company decided to write off $1,000 from the receivables as it cannot collect the money from the clients after repeated attempts. 11. The company paid last-year income tax during the year. Required: Prepare the Balance Sheet and Income Statement for the year ended 30 June 2015. Show all the working including the journal entries for each transaction. XYZ Pty Ltd Balance sheet For the year ended 30 June 2014 $ $ XYZ Pty Ltd Income statement For the year ended 30 June 2014 $ $ REVENUE Sales 100,000 Total revenue 100,000 Asset CURRENT ASSETS 5.100 20,000 (4,000) COST OF SALES Cash at bank Accounts receivable Less: allowance for doubtful depts Accounts receivable (net) Inventory TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS Cost of sales Total cost of sales 45,000 45,000 16,000 75,000 96,100 GROSS MARGIN 55,000 40,000 5,000 11,000 5,000 (8,000) NON-CURRENT AEESTS Property, plant & equipment - at cost Less: accumulated depreciation - PPE PPE (net) TOTAL NON-CURRENT ASSETS TOTAL ASSETS EXPENSES Accounting fee Rent expense Administrative expense Depreciation expense Salary expense Total expenses 8,000 32.000 32,000 6.000 35.000 128.100 Earning before tax Less: income tax expense Net profit after tax 21.000 6,300 14,700 LIABILITIES CURRENT LIABILITIES Accounts payable Provision for income tax TOTAL CUEENT LIABILITIES TOTAL LIABILITIES 12,000 6,300 18,300 18,300 NET ASSETS 109,800 100 EQUITY Share capital Retained earnings TORAL EQUITY 109,700 109,800
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


